As nouns the difference between pseudoscience and nonscience is that pseudoscience is any body of knowledge purported to be scientific or supported by science but which fails to comply with the scientific method while nonscience is that which is not science, or a specific non-scientific field.
How does pseudo-science differ from true science?
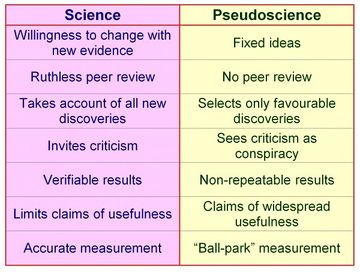
Notable Difference Between Science and Pseudoscience
- Pseudosciences are based on assumptions and deductions without scientific proof, while science produces knowledge through hypothesis testing.
- Experimental results are the basis of science, while anecdotal evidence is the basis of pseudoscience.
- In science, positive and negative results are considered in order to reach the truth. ...
Does pseudoscience follow the scientific method?
Pseudoscience is differentiated from science because – although it usually claims to be science – pseudoscience does not adhere to scientific standards, such as the scientific method, falsifiability of claims, and Mertonian norms. Scientific method
What are the types of pseudoscience?
- Conspiratorias . Those who aspire to reveal to the public a “truth” that has been denied by powerful groups and secrets or consortia of global interests.
- Historicist . Those who try to demonstrate their postulates through reinterpretations of true historical events in light of their doctrine.
- Metaphysical . ...
What is the best definition of pseudoscience?
- Real science is based on scientific methods and mathematical measurements.
- Pseudoscience is something people claim to be scientific, but it is not.
- Astrology is a pseudoscience.

What are three differences between a science and a pseudoscience?
The following table shows some of the differences between science and pseudoscience....SciencePseudoscience2. Based on well-established, repeating patterns and regularities in nature.2. Focuses, without skepticism, on alleged exceptions, errors, anomalies, and strange events.9 more rows•Jan 9, 2008
What is considered non-science?
Non-science encompasses all of the humanities, including: history, including the history of science, the language arts, such as linguistics, specific languages, and literature, philosophy, ethics, and religion, and. art, including music, performing arts, fine arts, and crafts.
What is the simple definition of pseudoscience?
Pseudoscience is a proposition, a finding or a system of explanation that is presented as science but that lacks the rigor essential to the scientific method. Pseudoscience can also be the result of research that is based on faulty premises, a flawed experimental design or bad data.
What is the difference between science and non science?
Thus expanded, scientific knowledge involves any ideas about the world which are based on inductive reasoning and which are open to testing and change. Nonscience is the other sphere of human knowledge. It involves religions, ethical beliefs, moral precepts, and philosophical ideals.
What is the difference between scientific and non-scientific?
The findings of scientific research can be reproduced and demonstrated to be consistent. Nonscientific research is acquiring knowledge and truths about the world using techniques that do not follow the scientific method.
What is a synonym for pseudoscience?
A supernatural practice involving mysterious transmutations. alchemy. chemistry. wizardry. sorcery.
Is Psychology a pseudoscience?
Psychology is a science because it takes the scientific approach to understanding human behaviour. Pseudoscience refers to beliefs and activities that are claimed to be scientific but lack one or more of the three features of science.
Why astrology is a pseudoscience?
Astrology has not demonstrated its effectiveness in controlled studies and has no scientific validity, and is thus regarded as pseudoscience.
What is a pseudoscience quizlet?
Pseudoscience. Means 'false science.' It is a field of study where researchers claim to be scientific in their research and adopt some of the procedures of science, but fail to fulfil the criteria effectively. Not peer reviewed.
What is pseudo research?
Pseudo-research is the type of research that is carried out by a person and involves the argument based on their observations. In this method, the evidence is not considered that is contrary and publish to public consumption. Examples are probability-based research and market research.
What are the characteristics of science?
One of science’s most substantial characteristics is the formation of theories. Scientists mostly use a general theory to explain their observations and experiments rather than simply recording the results. Such fields as psychology, biology, geology and physics stay within the confines of science. However, certain queries tend to be …show more content…
Why is naturalism not a paradigm?
Methodological naturalism is not a suitable paradigm for science, because science is used to explain why things are the way they are. If one excludes a particular possibility of explanation, just for the sake of common ground or because they don 't believe in that possibility, then they 're not keeping an open mind, which is an important part of finding explanations. No one discovers the truth with a closed mind. Long Answer There are five necessary presuppositions of science. Each one is necessary to presume in order to practice science and they can not be established by science itself.…
How did Karl Popper prove that science is true?
Philosopher Karl Popper suggested that it is impossible to prove a scientific theory true using induction, since it is hard to find evidence that will assure us that contrary evidence will not be traced. To argue this, Karl Popper suggested that proper science is accomplished by a method he referred to as deduction. Deduction involves the process of falsification. Falsification is a particular specialized aspect of hypothesis testing. The falsification process generally involves the process of stating some output from a particular theory form and then researching using conflicting or incompatible cases using experiments or observations.…
What is Popper's main objection to the theory of science?
Aside from that, Popper's main objection was that one could not test all proposed predictions of a theory, and even if that was possible, the more confirmations or rejection that arise from empirical experimentation are not definitive and prone to bias. This model allows the scientists more of an opportunity to look for predictions that will be confirmed in an effort to support a desired outcome. Popper's solution is to select predictions that are least likely to be confirmed, and then attempt to falsify a theory. Failure to falsify a theory serves as endorsement of the theory.3 Since law claims can be falsified but not verified, Popper concluded that the way to truth is indirect, by elimination of falsehood. This allows for science to produce errors and mistakes, certainly not a negative thing in the eyes of every true scientist.…
What is pseudoscience in science?
According to this definition, pseudoscience describes claims or statements supported by the science but fails when scrutinized. It can also be a cosmological system, like astrology, that explains astronomical events caused and affected by the universe.
What is the difference between a scientist and a pseudoscientist?
A scientist admits their ignorance, acknowledges their field is complex and rife with loopholes and advances by finding new solutions to existing problems, whereas a pseudoscientist remains undaunted.
Why are false facts used in pseudoscience?
False facts or fabricated facts, on the other hand, are used in pseudoscience to support the agenda of those who promote it.
What is science based on?
The definition of science is that it is knowledge about the world, including facts and generalizations. That means you can learn from what is in the world. It is based on facts. Scientists find these facts, and then they make laws or principles from them. While all sciences are based on valid reasoning and conform to the principles of logic, they are not concerned with the finality of their claims or findings. Essentially, science is anything that is so far proven that provisional consent will be unreasonable to deny.
What are the two main things that are used in formal sciences?
Formal sciences: Mathematics and logical principles are used in formal sciences to study ideas.
What is the Latin word for science?
Science comes from the Latin word scientĭa. Scientĭa means knowledge. Therefore, science is the knowledge that someone has about something and consists of a series of ordered steps to obtain more knowledge. There are many different branches of science.
Why are positive and negative results considered?
In science, positive and negative results are considered in order to reach the truth. However, in pseudoscience, only the positive results are considered and ignore the negative results.
What is pseudo science?
Pseudo-science refers to a theory that belongs to the domain of science, however, it is not scientifically testable. The philosopher Karl Popper thinks that the main differences between science and pseudo-science are whether the theory is scientifically testable. According to Popper, Marxism and Freudian psychology are in the domain ...
What is a non-western perspective of science?
...TOWARDS A NON-WESTERN PERSPECTIVE ON SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE I The available studies on the phenomenon and institution of science suffer from a curious limitation. It is as if all those who analyse the subject were overawed by the grandeur of modern science, and their studies were in the nature of tributes laid at the feet of this great saviour. All analysis starts from the assumption that modern science is a set of value-free theories that uniquely explain reality. After the scientists in the early 20th century started overhauling their theories in a big way, it was granted that the value-free theories of science that explain reality may do so only partially at a given time, but as science progresses, its theories explain more and more of reality and the process converges towards the ‘ultimate’, ‘unique’ law that explains everything. Committed to this idealist picture of a unique value free science, the philosophy of science is reduced to a set of attempts at finding the epistemological criterion, internal to science, that allows the scientist, unencumbered by any extraneous considerations, to choose the true theory out of a competing set; the sociology of science is reduced to writing down the set of social norms, self-imposed by the scientific community, which ensure that the technical criterion that guarantees the selection of the ‘true’ theory is strictly adhered to and the historiography of science is reduced to writing a catalogue of the achievements of modern science,......
What is the study of the mind?
Almost a hundred years ago, John Watson decided that psychology should be a science: not just a vague and introspective reflection on our own thoughts and feelings. Watson urged that psychology be defined as the scientific study of behavior. Since about 1920, most university psychologists have accepted Watson's definition. So, think of psychologists as scientists who study behavior. Introspection was the first technique for studying the mind There are some terms related to psychology that are frequently confused with it. Psychiatry is a branch of medicine specializing with mental disorders. Psychiatrists are medical doctors, and have been through medical school, an internship, residency training, and board certification as specialized physicians. The letters M.D. usually appear at the end of the name. The letters at the end of the name of a psychologist may be 1 fPh.D., Ed.D., or Psy.D., and so it may be appropriate to address a psychologist as "Dr." but he or she is not a physician. There is one important difference between what psychologists and psychiatrists can do. Under the current laws of most states and countries, the ability to write prescriptions for psychiatric medication is limited to physicians. So, if you needed a prescription for an anti-depressant like......
What is the difference between pseudoscience and science?
Another difference between science and pseudoscience is that science uses arguments based on logical or mathematical reasoning whereas pseudoscience often attempts to appeal to emotions, faith, and distrust of science. In addition, science does not accept personal experiences or testimonials as evidence whereas pseudoscience may accept personal experiences or testimonials as evidence.
What is Pseudoscience?
Pseudoscience is a collection of beliefs or practices that claim to be scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method . The Oxford English dictionary defines it as “a pretended or spurious science; a collection of related beliefs about the world mistakenly regarded as being based on scientific method or as having the status that scientific truths now have”. Pseudoscience is only a pretense or a masquerade of real science. It does not involve proper scientific evidence to explain a phenomenon. That means; there may be superficial beliefs or unexplained evidences used to explain a process or a set of processes.
What is Science?
Science is the mechanism by which phenomena are explained with facts. Some definitions state that it is a set of principles used to explain facts and phenomena. Scientific explanations are based on evidence; opinions, theories, tools and methods, results or indicators, and thorough discussions provide stable explanations for phenomena.
What is the purpose of scientific experimentation?
In science, scientists use careful observation and experimentation to reject or confirm a hypothesis about a certain phenomenon. They search for evidence for and against theories and laws and study them closely. If the hypothesis cannot be proven, then it is discarded. However, in pseudoscience, creator of a hypothesis only looks for evidence to support his/her hypothesis; he/she performs no scientific experimentation and ignores or hides conflicting evidence.
Why is the scientific method important?
One of the most important features of scientific method is that it is rigorous and meticulous, and those properties result in accurate validations from several sources of information . Those sources of information are authentic, and the truthfulness is always checked through validating techniques. Science does not use irrational criteria to come up with a conclusion; it always uses the rational and unbiased methodology. A scientist always follows the scientific method to explain a certain phenomenon or a set of processes.
What are the most important features of science?
One of the most important features of science is that most of the new findings are related to the past discoveries. Some of those are extensions while there are some explanations that invalidate the former ones. Charles Darwin’s explanation of evolution is a scientific theory that changed the world. The explanation of the DNA structure by Watson and Crick is another scientific discovery that has been able to describe many biological phenomena inside organisms.
What is science based on?
Some definitions state that it is a set of principles used to explain facts and phenomena. Scientific explanations are based on evidence; opinions, theories, tools and methods, results or indicators, and thorough discussions provide stable explanations for phenomena. ...
Why is demarcation between science and non-science important?
In brief, the philosophical problem of demarcation between science and non-science is of great practical importance for a contemporary civilized society and its solution is a task of utmost urgency.
What are the Characteristics of a Scientific Theory?
Traditionally, the problem of demarcation has dealt mainly with determining whether certain theories are scientific or not. That is, in order to answer the more general question of distinguishing science and non-science, philosophers have focused on answering the more specific question of identifying features that distinguish scientific theories from unscientific theories. Thus, they have been concerned with the question:
How to tell if an empirical theory is scientific?
So, to recap, how do we tell if an empirical theory is a scientific theory or not? We do so by consulting the demarcation criteria of that particular community, at that particular time in history. If a theory satisfies the demarcation criteria employed by the community, it is considered scientific; if it doesn’t satisfy the demarcation criteria, it is considered unscientific. What about pseudoscience? A theory is considered pseudoscientific if it is assessed to be unscientific by the scientific community’s employed demarcation criteria but is nevertheless presented as though it were scientific. Just as with any other method, all of these demarcation criteria are changeable; they change in accord with the third law of scientific change.
What are the three components of the scientific method?
You may recall that we mentioned demarcation criteria back in chapter 4 as one of the three components of a scientific method, along with acceptance criteria and compatibility criteria . A scientific method consists of all criteria actually employed in theory assessment Demarcation criteria are a specific subset of those criteria which are employed to assess whether a theory is scientific or not.
Is empirical science testable?
Indeed, it seems customary in contemporary empirical science to expect a theory to be testable. Thus, it seems that in addition to explaining, by and large, the known facts of their domains, scientific empirical theories are also expected to be testable, at least in principle.
Should we teach pseudoscience?
A solid educational system is one of the hallmarks of a contemporary civilized society. It is commonly understood that we shouldn’t teach our children any pseudoscience but should build our curricula around knowledge accepted by our scientific community. For that reason, we don’t think astrology, divination, or creation science have any place in school or university curricula. Of course, sometimes we discuss these subjects in history and philosophy of science courses, where they are studied as examples of non-science or as examples of what was once considered scientific but is currently deemed unscientific. Importantly, however, we don’t present them as accepted science. Therefore, as teachers, we must be able to tell pseudoscience from science proper.
Is intelligent design a pseudoscience?
Not only is the theory of intelligent design unscientific, but it is pseudoscientific, as it camouflages and presents itself as a legitimate science. In short, while not all non-science is pseudoscience, all pseudoscience is definitely non-science. While pseudoscience is the most dangerous subspecies of non-science, ...
Why is scientific method not always accurate?
Not always, because we do not always have all information. Sometimes new evidence comes along and changes our conclusions. However, for the information available, scientific method gives us the most accurate conclusions.
What is Aristotle's study of reality?
Aristotle is metaphysics - study of reality. He described what he saw in categories. Kant epistemology - study of knowledge. He grouped the categories logically and using rational thought of characteristics rather than observations, and created subcategories.
What is normal inference?
For example, normal inference is simply probability likelyhood, when causal inference is more precise and fluctuates with the new data added.
Can science be empirically tested?
Science - can be empirically tested with a goal to disprove.
Is science a theory?
Science is by one theory anything that can be empirically tested. Math is a science. You can test and retest its theories with the numbers etc. Biology is a science you can test theories with eyes and measuring equipment. Psychology is a science, because you can observe theories you test. Science also hits advanced level where you can no longer test due to the lack of means to test with. The means have not been created. This is where advanced science become philosophy.
Is deductive reasoning more accurate than inductive reasoning?
Deductive reasoning is more accurate, because inductive reasoning only estimates. However, deductive reasoning is often impossible in science. For example, children we observed all like chocolate milk. We conclude that all children like chocolate milk. However, we haven't examined all children in the world, so we use inductive reasoning. It is impossible to examine all children in the world.