What is the difference between nucleoside and non nucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase? The nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), have a nucleoside that is structurally similar to the T-cell DNA's nucleoside.... The non-nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors do not get into the cell nucleus or interfere with the DNA.
What is the difference between nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
Both nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors work at the same stage of the viral replication cycle, when the viral RNA converts itself into DNA using reverse transcriptase enzyme. The nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), have a nucleoside that is structurally similar to the T-cell DNA’s nucleoside.
What is the difference between nucleotide and nucleoside?
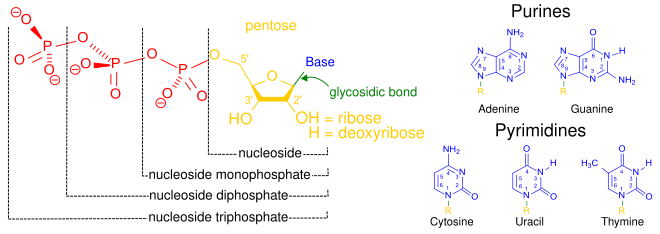
A nucleoside is any nucleotide that does not have a phosphate group but is bound to the 5’ carbon of the pentose sugar. A nucleotide always contains a nucleoside that binds the one to three phosphate groups. A nucleoside is always composed of a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base, which are the same as a nucleotide would have.
What is a nucleoside made of?
A nucleoside is always composed of a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base, which are the same as a nucleotide would have. Examples of nucleosides include cytidine, uridine, guanosine, inosine thymidine, and adenosine. A beta-glycosidic bond binds the 3’ position of the pentose sugar to the nitrogenous base.
What is the difference between a nitrogenous base and nucleotide?
A nitrogenous base is attached to a sugar and somewhere between one to three phosphate groups in case of a nucleotide. A nitrogenous base is covalently attached to sugar which is either ribose or deoxyribose, however, there is no presence of the phosphate group here in case of a nucleoside. Nucleotide = Sugar + Base + Phosphate
What is the difference between NNRTIs and NRTIs?
The NNRTIs differ from the NRTIs in that they do not have a nucleoside structure and do not depend on phosphorylation for activity. They function as noncompetitive substrate analogues and are selective inhibitors of HIV-1, with no activity against HIV-2 strains or even HIV-1 type O.
What does non-nucleoside mean?
/ nɒnˈnu kli əˌsaɪd, -ˈnyu- / PHONETIC RESPELLING. 📙 Middle School Level. noun Pharmacology. any of various antiviral drugs that bind directly to reverse transcriptase and prevent RNA conversion to DNA, used in combination with other drugs to treat HIV infection.
How do NRTIs and NNRTIs work?
NNRTIs work by binding to the HIV enzyme called reverse transcriptase, which is essential to the viral replication process, and therefore blocking HIV from making copies of itself. Dapivirine is an example of an NNRTI. NRTIs work by mimicking nucleotides that are the building blocks of viral DNA.
What do NRTIs do?
NRTIs are one of 6 classes of antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) used to treat HIV as part of antiretroviral therapy (ART). ARVs interfere with the ability of a virus to multiply or reproduce. To treat HIV, NRTIs work by blocking an enzyme HIV needs to make copies of itself.
Where are nucleosides found?
Sources. Nucleosides can be produced from nucleotides de novo, particularly in the liver, but they are more abundantly supplied via ingestion and digestion of nucleic acids in the diet, whereby nucleotidases break down nucleotides (such as the thymidine monophosphate) into nucleosides (such as thymidine) and phosphate.
What does Nnrti and Nrti mean?
To be able to answer your questions about NNRTIs (non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors) and NRTIs (nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors) let me first start by explaining what a nucleoside is and how reverse transcriptase works. A nucleoside is the building block to our DNA and RNA.
What is NNRTIs example?
Following are the FDA-approved individual NNRTIs that are currently part of antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection; common side effects are listed.Delavirdine (Rescriptor) ... Efavirenz (Sustiva) ... Etravirine (Intelence) ... Nevirapine (Viramune, Viramune XR) ... Rilpivirine (Edurant) ... Doravirine (Pifeltro)
What does NNRTIs stand for?
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) bind to and block HIV reverse transcriptase (an HIV enzyme).
How do CCR5 antagonists work?
CCR5 antagonists bind to the CCR5 chemokine coreceptor on host cells, inducing a conformational change that impedes CCR5 interaction with HIV gp120, thereby preventing HIV entry into host cells. Low-molecular-weight inhibitors of HIV binding to the CD4 molecule are a new approach.
What are NRTI drugs?
NRTIs are one of six classes of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV. Antiretroviral drugs interfere with the ability of a virus to multiply or reproduce. To treat HIV, NRTIs work by blocking an enzyme HIV needs to make copies of itself.
What is the difference between nucleotides and nucleosides?
Nucleoside. Nucleotides are built of a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group when it comes to chemical composition. Nucleosides are built of a nitrogenous base and a sugar, however , without the phosphate group when it comes to chemical composition.
What are some examples of nucleosides?
Examples of nucleosides include cytidine, uridine, guanosine, inosine thymidine, and adenosine. A beta-glycosidic bond binds the 3’ position of the pentose sugar to the nitrogenous base. Nucleosides are used as anticancer and antiviral agents.
What is a compound composed of a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group that is attached to?
Nucleotide. Compounds consisting of a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group which is attached to a pentose sugar, which can be either deoxyribose or ribose, is called a nucleotide. The pentose sugar with 5’ carbon can have anywhere between one to three phosphate groups.
How to find a nitrogenous base?
A nitrogenous base is covalently attached to sugar which is either ribose or deoxyribose, however, there is no presence of the phosphate group here in case of a nucleoside. Nucleotide = Sugar + Base + Phosphate.
What is a nucleotide?
A nucleoside is any nucleotide that does not have a phosphate group but is bound to the 5’ carbon of the pentose sugar. A nucleotide always contains a nucleoside that binds the one to three phosphate groups. A nucleoside is always composed of a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base, which are the same as a nucleotide would have.
What are the functions of nucleotides?
Nucleotides have various functions in the field of biology: 1 The DNA and RNA acts as a place for data storage 2 ATP in nucleotides provides energy 3 Helps in co-enzyme catalysis 4 The cAMP or ATP act as allosteric regulators, thereby helping chemical communication among cells and also helps in regulating metabolism 5 These are the building blocks of life
Is nucleic acid a base or a nucleotide?
Additionally, a nucleotide occurs before the formation of DNA and RNA, but a nucleoside occurs before the formation of a nucleotide.
What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside?
A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate group, whereas a nucleoside lacks the phosphate group. Let’s understand these three components involved in nucleotide & nucleoside formation.
What is the nucleotide of a nucleoside?
The nucleoside (base + sugar) combines with a phosphate group to form the nucleotide. A phosphate group is attached to the 5`-OH of the nucleoside with the help of a phosphodiester linkage. Therefore, a nucleotide is formed from a nucleoside.
What gives rise to a nucleotide?
The addition of a phosphate group to a nucleoside gives rise to a nucleotide .
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of three components, namely a nitrogenous base, phosphate group, and sugar. A nucleoside is composed of two components, namely a nitrogenous base and sugar. This is the basic difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Before understanding the various differences between nucleotide and nucleoside, let’s have a basic introduction about the same.
What is added to the 5-OH nucleoside?
The phosphate group is added to the 5`-OH of the nucleoside with the help of a phosphodiester linkage.
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases?
Nitrogenous bases are classified into two categories - Purines and Pyrimidines.
What are nucleosides used for?
Nucleosides are used for the synthesis of medicinal agents. They are mostly used for the synthesis of antiviral and anti-cancer drugs.
What is the building block of DNA?
A nucleoside is the building block to our DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic code which makes us what we are. It is what determines if we have blue eyes or a wonky nose, what we look like and to some people, if we are susceptible to any genetic medical conditions. Our body is constantly renewing itself and making new cells.
How do NNRTIs and NRTIs interact?
Both the NRTIs and the NNRTIs interact with the reverse transcriptase to stop it working. This stops HIV replicating so the amount of virus in the body will go down.
How does HIV change its DNA?
To do this it has to first change its RNA to DNA. HIV uses a compound called reverse transcriptase to convert its RNA to DNA.
Can HIV replicate itself?
The single-stranded RNA then goes on to become the proteins that make up our skin, organs, hair, nails etc. HIV alone is not able to replicate. It has to put its own genetic material into our genetic material so that we can replicate the parts of the virus ourselves.
What is a nucleoside transcriptase inhibitor?
The nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), have a nucleoside that is structurally similar to the T-cell DNA’s nucleoside. Mimicking the T-cell enables the NRTIs to integrate with the T-cell DNA and stop the production of viral DNA proteins. The non-nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors do not get into the cell nucleus or interfere with the DNA.
What is NNRTI in HIV?
Non-nu cleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are one of the classes of drugs that form part of the antiretroviral therapy (ART) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. An NNRTI drug may be part of a cocktail of ART drugs that each target HIV at different points in its replication cycle to help lower the level of virus in the body and prevent HIV from causing AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). AIDS may lead to death from secondary infections after immune system collapse.
Do non-nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors interfere with DNA?
The non-nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors do not get into the cell nu cleus or interfere with the DNA. NNRTIs bind directly to the HIV’s reverse transcriptase enzyme and inhibit its activity.
What is the first class of RNA reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
The first class of these drugs is the Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs). To understand how these work, consider the mechanism of RT action. The enzyme ‘grips’ the RNA template strand hydrogen bonded to the 3’ end of the growing DNA reverse transcript and allows 2’-deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dATP, dGTP, dCTP, or dTTP) to diffuse into the active site.
How do NRTIs and NNRTIs work?
Since NRTIs and NNRTIs work through different mechanisms on the same target, combination therapies, where one or more drugs of each class are administered simultaneously, should be expected to—and do—provide a synergistic effect, not only through combined reduction in net RT activity, but also by making mutational escape from inhibition dramatically less likely. It’s possible that a single mutation in RT can confer some level of resistance to either a specific NRTI or NNRTI, but for an RT to be resistant to a multidrug cocktail containing both, that RT must simultaneously gain both mutations.