
What is the difference between observational learning and Modelling? There are many different ways that we learn new behaviors. A lot of learning also happens indirectly through a process of watching others and then imitating their behavior, in which the imitation is known as modeling.
What are the four processes of observational learning?
There are four mediational processes proposed by Bandura:
- Attention: The individual needs to pay attention to the behavior and its consequences and form a mental representation of the behavior. ...
- Retention: How well the behavior is remembered. ...
- Reproduction: This is the ability to perform the behavior that the model has just demonstrated. ...
- Motivation: The will to perform the behavior. ...
What is an example of observational learning?
Observational Learning Examples
- A child watches their parent folding the laundry. They later pick up some clothing and imitate folding the clothes.
- A young couple goes on a date to an Asian restaurant. ...
- A child watches a classmate get in trouble for hitting another child. ...
- A group of children play hide-and-seek. ...
Which is an example of observational learning?
Examples of Observational Learning
- Understanding Observational Learning. So what is observational learning and what is imitation? ...
- Observational Learning Examples for Children. If you walk into a preschool play kitchen or outdoor tricycle track, you'll see the results of observational learning at work.
- Observational Learning Examples for Adults. ...
- Different Types of Learning. ...
Who highlighted the importance of observational learning?
Observational learning is a major component of Bandura’s social learning theory. He also emphasized that four conditions were necessary in any form of observing and modeling behavior: attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
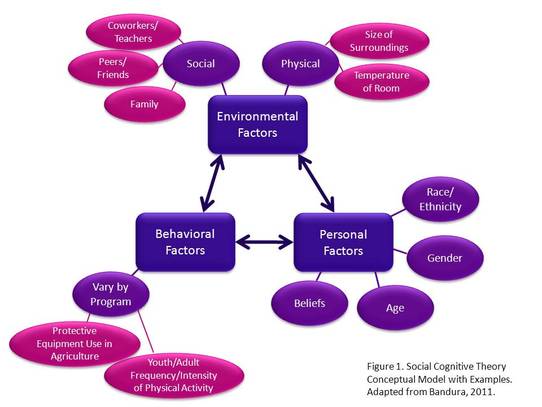
Is modeling the same as observational learning?
Observational learning is the process of learning by watching the behaviors of others. The targeted behavior is watched, memorized, and then mimicked. Also known as shaping and modeling, observational learning is most common in children as they imitate behaviors of adults.
What is Modelling learning?
Modelling is the process of learning by copying others' behaviour. It is also called Observational Learning. Humans model one another naturally – for example, kids use modelling to learn how to tie their shoes or use utensils. Modelling learning involves a particular kind of neuron, known as a mirror neuron.
What is an example of modeling learning?
Modeling means learning by copying the behavior of someone else. Humans naturally model each other – for example, children use modeling to learn how to use utensils or tie their shoes.
What is modeling and observation theory?
Social learning theory, proposed by Albert Bandura, emphasizes the importance of observing, modelling, and imitating the behaviors, attitudes, and emotional reactions of others. Social learning theory considers how both environmental and cognitive factors interact to influence human learning and behavior.
What is modelling in observational learning?
In observational learning, we learn by watching others and then imitating, or modeling, what they do or say. The individuals performing the imitated behavior are called models.
What does modeling mean in psychology?
n. 1. a technique used in cognitive behavior therapy and behavior therapy in which learning occurs through observation and imitation alone, without comment or reinforcement by the therapist.
What is an example of observational learning?
Observational Learning Examples for Children A child learns to chew. After witnessing an older sibling being punished for taking a cookie without asking, the younger child does not take cookies without permission. A child learns to walk. A child learns how to play a game while watching others.
What is Modelling give example?
Modeling involves making a representation of something. Creating a tiny, functioning volcano is an example of modeling. Teachers use modeling when they have a class election that represents a larger one, like a presidential election. Modeling is anything that represents something else, usually on a smaller scale.
What is modeling in a classroom?
What is the "Modeling" instructional strategy? With "Modeling", the teacher engages students by showing them how to perform a skill while describing each step with a rationale. This provides students with both a visual and verbal example of what they will be expected to do.
What is modeling in social learning theory?
Modeling focuses on learning by observing others. It is used to uncover evolved behavior. The attentiveness elaborates on how each individual's cognitive factors and environments influence their own learning.
What is the difference between modeling and modelling?
Whether you're modelling or modeling, you're doing the same thing. The only difference is in the spelling—the one with the single L is preferred in the United States, while the one with two Ls is preferred everywhere else.
What is modeling in social psychology?
Modeling is one way in which behavior is learned. When a person observes the behavior of another and then imitates that behavior, he or she is modeling the behavior. This is sometimes known as observational learning or social learning. Modeling is a kind of vicarious learning in which direct instruction need not occur.
How does observational learning occur?
Observational learning is much more complex. According to Lefrançois (2012) there are several ways that observational learning can occur: You learn a new response. After watching your coworker get chewed out by your boss for coming in late, you start leaving home 10 minutes earlier so that you won’t be late.
How to learn behavior by observing a model?
First, you must be focused on what the model is doing—you have to pay attention. Next, you must be able to retain, or remember, what you observed; this is retention. Then, you must be able to perform the behavior that you observed and committed to memory; this is reproduction. Finally, you must have motivation . You need to want to copy the behavior, and whether or not you are motivated depends on what happened to the model. If you saw that the model was reinforced for her behavior, you will be more motivated to copy her. This is known as vicarious reinforcement. On the other hand, if you observed the model being punished, you would be less motivated to copy her. This is called vicarious punishment. For example, imagine that four-year-old Allison watched her older sister Kaitlyn playing in their mother’s makeup, and then saw Kaitlyn get a time out when their mother came in. After their mother left the room, Allison was tempted to play in the make-up, but she did not want to get a time-out from her mother. What do you think she did? Once you actually demonstrate the new behavior, the reinforcement you receive plays a part in whether or not you will repeat the behavior.
Why does pure behaviorism not explain why learning can take place in the absence of external reinforcement?
He felt that internal mental states must also have a role in learning and that observational learning involves much more than imitation. In imitation, a person simply copies what the model does.
How to be able to perform the behavior that you observed and committed to memory?
Then, you must be able to perform the behavior that you observed and committed to memory; this is reproduction . Finally, you must have motivation.
What is symbolic model?
A symbolic model can be fictional characters or real people who demonstrate behaviors in books, movies, television shows, video games, or Internet sources. (a) Yoga students learn by observation as their yoga instructor demonstrates the correct stance and movement for her students (live model).
How can we learn from watching others?
Summary. According to Bandura, learning can occur by watching others and then modeling what they do or say. This is known as observational learning. There are specific steps in the process of modeling that must be followed if learning is to be successful.
What is the second step in observational learning?
Next, observers must be able to remember what they have observed. This second step is known as retention.
What is model learning?
Modeling is not quite as simple as ''monkey see, monkey do.''. It's actually a complex process that involves observing a behavior performed by another person ( for example a ''model''), retaining what you've observed, and then reproducing the behavior on your own. Observational learning is particularly common during childhood.
Why was Joanna less motivated to imitate her co-worker's behavior?
Joanna was less motivated to imitate her co-worker's behavior because she saw him being punished for it. Observational learning is a type of learning that happens indirectly through a process of watching others and then imitating, or modeling, their behavior, with the imitating being called modeling.
What are the four conditions that must be followed for observational learning to occur?
Bandura's research identifies four conditions, or steps, in the modeling process that must be followed for successful observational learning to occur. First, observers must pay attention to what's happening around them. They must be focused on what the model is doing.
How do children learn new behaviors?
Children often learn new behaviors by modeling the behaviors of authority figures and their peers. However, adults often learn through modeling too. Think of the first time you visited your favorite coffee shop.
What is the term for learning through direct experiences?
We often learn through direct experiences, such as when a child is rewarded with stickers during potty training. This type of learning is called associative learning. A lot of learning also happens indirectly through a process of watching others and then imitating their behavior, in which the imitation is known as modeling. ...
How does Bradley retain what he observed?
Bradley retains what he's observed by creating a mental image of the game board and rehearsing his parents' moves in his mind. Once observers retain a behavior in their memory, they must be physically and intellectually capable of performing the behavior themselves. This is known as reproduction.
Modeling Behavior Definition
Students become quiet when the teacher is quiet, or the child experiences fear whenever seeing a spider because they observed that action in another person and then imitated that behavior. The definition of modeling behavior is learning through observation and imitation alone. As a result, the behavior manifests in the observer.
Bandura's Psychological Findings
In addition to Bandura's four steps of observational behavior, his famous Bobo doll experiment consisted of four significant psychological findings:
Bandura's Neurological Findings
Neurology is the study of the nervous system, and Bandura's findings were so moving that they even affected this community. As a result of the Bobo doll experiment, neurologists were inspired to examine the nervous system, which was surprising.
What is observational learning?
Observational learning is also called shaping or modeling because it involves modeling the behaviors of other people. This style of learning can take place at any point in a person's life, but much of it happens during childhood when children are learning how to socialize by observing the behavior of adults around them.
Benefits of observational learning
Observational learning happens indirectly, meaning that there is no formal process for teaching or learning with this method. People simply learn by watching others and mimicking what they see. Here are some of the key benefits of observational learning:
4 Stages of observational learning
Albert Bandura claimed that there were four stages that needed to occur for observational learning to happen:
Observational learning examples
A married couple decides to go out and eat sushi for dinner. They've never used chopsticks before, so they observe some of the other people in the restaurant who are using chopsticks. They practice a few times and can then successfully use their chopsticks to eat the sushi.
What is observational learning?
For other uses, see Social learning (disambiguation). Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. It is a form of social learning which takes various forms, based on various processes.
How does observational learning differ from imitative learning?
Observational learning differs from imitative learning in that it does not require a duplication of the behavior exhibited by the model. For example, the learner may observe an unwanted behavior and the subsequent consequences, and thus learn to refrain from that behavior.
What is Albert Bandura's theory of observational learning?
Observational learning suggests that an individual's environment, cognition, and behavior all incorporate and ultimately determine how the individual functions and models.
Why is observational learning important?
The importance of observational learning lies in helping individuals, especially children, acquire new responses by observing others' behavior. Albert Bandura states that people's behavior could be determined by their environment. Observational learning occurs through observing negative and positive behaviors.
How do mirror neurons help with observational motor learning?
In observational motor learning, the process begins with a visual presentation of another individual performing a motor task, this acts as a model. The learner then needs to transform the observed visual information into internal motor commands that will allow them to perform the motor task, this is known as visuomotor transformation. Mirror neuron networks provide a mechanism for visuo-motor and motor-visual transformation and interaction. Similar networks of mirror neurons have also been implicated in social learning, motor cognition and social cognition.
What is the role of culture in learning?
Culture plays a role in whether observational learning is the dominant learning style in a person or community. Some cultures expect children to actively participate in their communities and are therefore exposed to different trades and roles on a daily basis.
How does observational learning spread across cultures?
Through observational learning, individual behaviors can spread across a culture through a process called diffusion chain. This basically occurs when an individual first learns a behavior by observing another individual and that individual serves as a model through whom other individuals learn the behavior, and so on.
