- Meiosis. Prophase 1: Meiosis 1 begins with prophase 1. ...
- Interphase. Prophase 1: Prophase 1 follows a long interphase. ...
- Centrosome Duplication. Prophase 1: Centrosome is duplicated during the interphase, which is a process prior to prophase 1. ...
- Involvement of chromosomes. ...
- Diploid vs Haploid. ...
- Plane. ...
- Occurrence of Crossovers. ...
- Recombination. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is the difference between prophase 1 and 2?
- Prophase I is the beginning phase of Meiosis I while Prophase II is the beginning phase of Meiosis II.
- There is a long interphase before Prophase I, whereas Prophase II occurs without an interphase. ...
- The pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in Prophase I, whereas such process cannot be seen in Prophase II.
What are the majors phases of meiosis 1 and 2?
Summary of Difference between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2:
- The main Difference between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 is that the former is reduction division while the latter is equational division.
- Crossing over takes place during meiosis 1 while there is no crossing over in the subsequent decision.
- 2 daughter cells are formed at the end and the cell becomes haploid during meiosis 1.
What are the main differences between meiosis 1 and 2?
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 quizlet?
- Meiosis II. Accordingly, what is the major difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2? ...
- Meiosis
- are. Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not.
- meiosis II. What is the purpose of meiosis 2? ...
What are facts about meiosis 1 and 2?
- Diploid cells are countless cells in all living organisms.
- Human are diploid organisms with somatic cells having 46 chromosomes which comes in 2 complete set (23 each set).
- Through the process of meiosis, haploid cells are produced.
- During fertilization gametes (egg and sperm) fused and a diploid zygote is produced.

What is the difference between prophase 1 and prophase 2 quizlet?
Prophase 1 is the beginning phase of meiosis while prophase 2 is the beginning phase of prophase 2. There is a long interphase before prophase 1, whereas prophase 2 occurs without an interphase. It directly goes from telophase 1 to prophase 2.
What happens in prophase 1 and 2 of meiosis?
Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not. This occurs in meiosis I in a long and complicated prophase I, split into five sub-phases. The equatorial plane in meiosis II is rotated 90° from the alignment of the equatorial plane in meiosis I.
What is the difference between metaphase 1 and 2 in meiosis?
Metaphase 1 is associated with meiosis 1 whereas the metaphase 2 is associated with meiosis 2. The main difference between metaphase 1 and 2 is that chromosomes are attached as homologous pairs at the equator during the metaphase 1 and during metaphase 2, single chromosomes are attached at the equator.
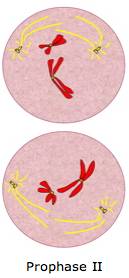
What happens in prophase 2 of meiosis?
During prophase II, the chromosomes condense, and a new set of spindle fibers forms. The chromosomes begin moving toward the equator of the cell. During metaphase II, the centromeres of the paired chromatids align along the equatorial plate in both cells.
What characteristic is seen in prophase 1 but not in prophase 2?
In prophase I, the first stage is known as leptotene. This stage involves the unwinding of the DNA structure to enable an exchange of alleles between homologous chromosome pairs. No crossing over occurs in prophase II. Therefore, prophase II does not feature leptotene.
What exactly happens during prophase I?
During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. The paired chromosomes are called bivalents, and the formation of chiasmata caused by genetic recombination becomes apparent. Chromosomal condensation allows these to be viewed in the microscope.
What is the major difference between metaphase 1 and metaphase?
In metaphase 1 the pairs of chromosomes referred to as bivalents are totally condensed. Moreover the in metaphase 1 of meiosis there is no centromere division whereas in metaphase of mitosis it does. They align on the metaphase plate in between the poles.
Which of the following best explains a distinction between metaphase I and metaphase II?
Which of the following best explains a distinction between metaphase I and metaphase II? Homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned during metaphase II, but individual chromosomes are aligned during metaphase IIII. You just studied 24 terms!
What is the difference between prophase I and prophase II?
The key difference between prophase I and prophase II is that the prophase I is the beginning phase of meiosis I, and there is a long interphase before it while the prophase II is the first phase of meiosis II without an interphase prior to it.
What happens during prophase I and II?
Prophase I occurs after interphase while prophase II occurs after telophase I. This is another difference between prophase I and prophase II. Furthermore, during the prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads and exchange genetic materials between each other. But this is not happening in prophase II.
What happens in prophase I?
In prophase, I, crossing over between homologous chromosomes occurs, and the mixing of genetic material occurs while both are not possible in prophase II. The below infographic tabulates the difference between prophase I and prophase II in more detail.
What is the first phase of meiosis?
Prophase I is the first phase of Meiosis I. There is a long interphase before prophase I. During the prophase I , chromosomes become visible, and they synapse to form tetrads. Resulting tetrads contain two pairs of chromosomes, hence the name bivalents. Crossing over is another important process that takes place in prophase I and allows ...
What are the other events that occur in prophase I?
Disappearing of the nuclear envelope, moving spindle fibres into the centre, and connecting the tetrads to the spindle fibres by kinetochores are the other events that occur in prophase I.
Why is meiosis important?
Among them, meiosis is a vital process for sexual reproduction. For a successful sexual reproduction process, it is necessary to produce gametes that contain half of the chromosome number of a normal cell. All eukaryotes have a unique chromosome number for each species.
How many stages are there in meiosis?
Each meiosis has four stages. Prophase I is the beginning phase of meiosis I while prophase II is the initial phase of meiosis II. This is the key difference between prophase I and prophase II. Another difference between prophase I and prophase II is the possibility of crossing over and mixing genetic material.
What is the difference between Prophase I and Prophase II?
Prophase I is the beginning phase of Meiosis I while Pro phase II is the beginning phase of Meiosis II. There is a long interphase before Prophase I, whereas Prophase II occurs without an interphase. The pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in Prophase I, whereas such process cannot be seen in Prophase II. Click to see full answer.
How many haploid cells are there in meiosis 2?
During meiosis 2, the two diploid cells each split into two haploid cells (have half the amount of chromosomes to survive). Meiosis ends with four haploid cells. Moreover, what is the difference between prophase 1 in meiosis and mitosis?
Does meiosis 2 occur before or after replication?
While chromosome duplication took place prior to meiosis I, no new chromosome replication occurs before meiosis II.
Which phase of meiosis is preceded by interphase?
Meiosis can only occur in eukaryotic organisms. It is preceded by interphase, specifically the G phase of interphase. Both Meiosis I and II have the same number and arrangement of phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Both produce two daughter cells from each parent cell.
What is the longest phase of meiosis?
Prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis, with three main events occurring. The first is the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes that can be seen through the microscope; the second is the synapsis or physical contact between homologous chromosomes; and the crossing over of genetic material between these synapsed chromosomes. These events occur in five sub-phases:
What is the first prophase event?
Leptonema – The first prophase event occurs: chromatin condenses to form visible chromosomes. Condensation and coiling of chromosomes occur. Zygonema – Chromosomes line up to form homologous pairs, in a process known as the homology search. These pairs are also known as bivalents.
How many haploid cells are in meiosis?
However, Meiosis I begins with one diploid parent cell and ends with two haploid daughter cells, halving the number of chromosomes in each cell. Meiosis II starts with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell. Homologous pairs of cells are present in meiosis I ...
How does meiosis end?
Meiosis I ends when the chromosomes of each homologous pair arrive at opposing poles of the cell. The microtubules disintegrate, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each haploid set of chromosomes. The chromosomes uncoil, forming chromatin again, and cytokinesis occurs, forming two non-identical daughter cells.
What is the process of eukaryotic cells reproducing sexually?
Meiosis is how eukaryotic cells (plants, animals, and fungi) reproduce sexually. It is a process of chromosomal reduction, which means that a diploid cell (this means a cell with two complete and identical chromosome sets) is reduced to form haploid cells (these are cells with only one chromosome set). The haploid cells produced by meiosis are germ ...
What happens during the G phase of meiosis?
During the G phase proteins and enzymes necessary for growth are synthesized, while during the S phase chromosomal material is doubled. Meiosis is then split into two phases: meiosis I and meiosis II. In each of these phases, there is a prophase, a metaphase, and anaphase and a telophase. In meiosis I these are known as prophase I, metaphase I, ...
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2?
The main difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 is that genetic recombination occurs in meiosis 1 and no recombination of DNA can be observed in meiosis 2. 1.
What happens during prophase 1?
During prophase 1, homologous chromosomes are paired by an event known as synapsis. During synapsis, genetic variation is allowed by two ways. First is the independent orientation of the pairs of the homologous chromosomes in the cell equator.
How are separated chromosomes pulled to the opposite poles?
The separated chromosomes are pulled to the opposite poles by the kinetochore microtubule contraction at the telophase 1. After the completion of telophase 1, new nuclear envelopes are formed surrounding the chromosomes in the opposite poles.
How does meiosis occur?
Meiosis is the mechanism of producing gametes during the organisms’ sexual reproduction. Meiosis occurs through two stages, meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. Each stage is composed of four phases, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and the telophase. During meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes pair follow the law of independent assortment. Chromosomal cross-over takes place between non-sister chromatids at chiasmata, leading to produce new combinations of alleles through genetic recombination. Homologous chromosomes of a diploid parent cell are separated into two haploid daughter cells at meiosis 1. Meiosis 2 is similar to the mitotic cell division, equalizing the number of chromosomes in a parent cell produced at meiosis 1 and daughter cell, produced by meiosis 2. The main difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 is that genetic recombination occurs in meiosis 1 and no recombination of DNA can be observed in meiosis 2.
What is the first phase of meiosis?
What is Meiosis 1. Meiosis 1 is the initial period of the cell cycle and is followed by meiosis 2. During meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells, reducing the chromosome number by half, relative to the parent cells’ chromosome number. Meiosis 1 is composed of four phases: prophase 1, metaphase 1, ...
How many phases does meiosis 2 take?
Meiosis 2 proceeds through four sequential phases: prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2 and telophase 2. During prophase 2, nuclear envelop and nucleolus disappear, thickening the chromatids to form chromosomes. A new pair of centrosomes appears in the opposite poles of the second cell equator, which is in a rotated position by 90 degrees relative ...
What is the second division of meiosis?
The second division of meiosis is meiosis 2 which is involved in the equal segregation and separation of bivalent chromosomes. Meiosis 2 is only physically similar to the mitosis (vegetative cell division), not genetically since it produces haploid cells, which are used as gametes later, starting from diploid cells.
What is the metaphase of meiosis 2?
The metaphase found in meiosis 2 is known as metaphase 2. The events happening in metaphase 2 are similar to the metaphase of the mitosis. During the metaphase 2, single chromosomes arrange in the metaphase plate. Hence it is different from the metaphase 1 since pairs of homologous chromosomes arrange in the metaphase plate.
What is the difference between metaphase 1 and 2?
The key difference between metaphase 1 and 2 is that in metaphase 1, homologous chromosomes pair up at the metaphase plate while in metaphase 2, single chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate. Meiosis is the process that converts a diploid cell into four haploid cells during the gamete formation.
What is the stage of cell division in which the chromosomes arrange along the metaphase plate?
Hence, metaphase is the stage of cell division in which the chromosomes arrange along the Metaphase plate. Metaphase 1 can be found in meiosis I while metaphase 2 can be found in meiosis II. Metaphase 1 and 2 are different from each other.
How many cycles does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs through two cycles, which are meiosis 1 and 2. Each meiotic cycle has four subphases. Metaphase of the meiosis 1 is known as metaphase 1 while metaphase of the meiosis 2 is known as meiosis 2. In metaphase 1, pairs of homologous chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell while single chromosomes line up at ...
How many phases are there in meiosis?
In each meiotic cycle, there are four main phases. They are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Metaphase 1 belongs to meiosis 1, and metaphase 2 belongs to meiosis 2.
Why is meiosis important in sexual reproduction?
Meiosis is vital in sexual reproduction due to its importance in haploid cell formation. Meiosis occurs via two successive nuclear divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II. Each nuclear division can be subdivided again into Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
Which stage of the cell contains half of the chromosomes that of the parent cell?
Then to each centromere of the chromosome, spindle fibres from each pole attach. At this stage, the cell contains half of the chromosomes that of in the parent cell. Metaphase 2 occurs after prophase 2. Anaphase 2 is the next phase after metaphase 2.

Recap: What Is meiosis?
What Happens Before meiosis?
- Before meiosis, the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell replicate to produce double the amount of chromosomal material. After chromosomal replication, chromosomes separate into sister chromatids. This is known as interphase, and can be further broken down into two phases in the meiotic cycle: Growth (G), and Synthesis (S). During the G phase proteins and enzymes ne…
The Phases of Meiosis I
- After Interphase I meiosis I occurs after Interphase I, where proteins are grown in G phase and chromosomes are replicated in S phase. Following this, four phases occur. Meiosis I is known as reductive division, as the cells are reduced from being diploid cells to being haploid cells.
The Phases of Meiosis II
- Meiosis II may begin with interkinesis or interphase II. This differs from interphase I in that no S phase occurs, as the DNAhas already been replicated. Thus only a G phase occurs. Meiosis II is known as equational division, as the cells begin as haploid cells and end as haploid cells. There are again four phases in meiosis II: these differ slight...
How Is Meiosis I Different from Meiosis II?
- Meiosis is the production of four genetically diverse haploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell. Meiosis can only occur in eukaryotic organisms. It is preceded by interphase, specifically the G phase of interphase. Both Meiosis I and II have the same number and arrangement of phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Both produce two dau…
Why Is Meiosis Important?
- Meiosis is essential for the sexual reproduction of eukaryotic organisms, the enabling of genetic diversity through recombination, and the repair of genetic defects. The crossing over or recombination of genes occurring in prophase I of meiosis I is vital to the genetic diversity of a species. This provides a buffer against genetic defects, susceptibility to disease and survival of …
Meiosis I and Meiosis II Biology Review
- We now know that meiosis is the process of the production of haploid daughter cells from diploid parent cells, using chromosomal reduction. These daughter cells are genetically distinct from their parent cells due to the genetic recombination which occurs in meiosis I. This recombination is essential for genetic diversity within the population and the correction of genetic defects. Mei…