As nouns the difference between prometaphase and prophase is that prometaphase is (biology) the stage between prophase and metaphase in mitosis while prophase is the first stage of mitosis, during which chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes.
What does prometaphase look like?
prometaphase-nuclear membrane and nucleoli disappear-chromosomes look like dark bodies scattered in the cytoplasm-mitotic spindle forms
What is the simple definition of prophase?
prophase. 1. (Biology) the first stage of mitosis, during which the nuclear membrane disappears and the nuclear material resolves itself into chromosomes. See also metaphase, anaphase, telophase. 2. (Biology) the first stage of meiosis, divided into leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis phases.
What happens in prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase?
What happens during prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase? 1) Prophase: chromatin into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope break down, chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres 2) Metaphase: chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (centre of the cell) 3) Anaphase: sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the ...
What is prophase 1 and prophase 2?
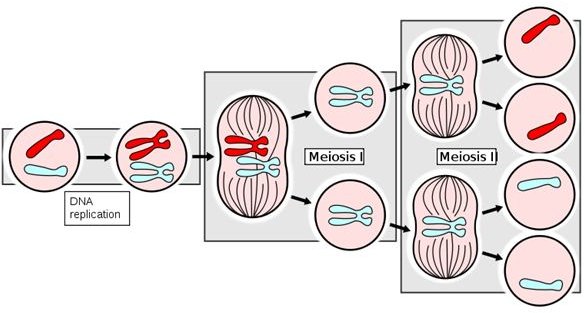
Prophase I is the beginning phase of Meiosis I while Prophase II is the beginning phase of Meiosis II. There is a long interphase before Prophase I, whereas Prophase II occurs without an interphase. The pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in Prophase I, whereas such process cannot be seen in Prophase II.

Is prometaphase and prophase the same?
In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. The chromosomes become even more condensed, so they are very compact. The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes.
What is prometaphase and prophase?
Prometaphase is the stage of eukaryotic cell division that falls between prophase and metaphase. During prophase, the cell's chromosomes have condensed and the cell's centrosome, or microtubule organizing center, has divided and moved to opposite sides of the cell.
What is the difference between late prophase and prometaphase?
Late prophase displays thick and condensed chromosomes. Chromatids are visible. The centrosomes have moved to the poles of the cell. Prometaphase involves the formation of and connection between microtubules, the formation of the spindle.
What happens in the prometaphase?
At prometaphase (late prophase) the chromosomes condense inside the nuclear envelope and asters of fibers appear on the outside of the chromosomes. When the nuclear envelope has disappeared, a spindle forms in prometaphase.
What is prometaphase in simple words?
Prometaphase is the second phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. During prometaphase, the physical barrier that encloses the nucleus, called the nuclear envelope, breaks down.
What is prophase in simple words?
1. the first stage of mitosis, during which the nuclear membrane disappears and the nuclear material resolves itself into chromosomes.
What happens during prophase?
During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses. The chromatin coils and becomes increasingly compact, resulting in the formation of visible chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of a single piece of DNA that is highly organized.
What is the opposite of prometaphase?
Telophase is the fifth and final phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells.
What does prometaphase of mitosis look like?
0:391:45Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase & TelophaseYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn prometaphase the nuclear envelope breaks down and microtubules emanating from the centrosomesMoreIn prometaphase the nuclear envelope breaks down and microtubules emanating from the centrosomes attach to the chromosomes.
How do I memorize prometaphase?
1:274:58Cell cycle phases of Mitosis and meiosis | easy tricks to rememberYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then P stand for prophase M of milk stands for metaphase a stands for anaphase. And T stands forMoreAnd then P stand for prophase M of milk stands for metaphase a stands for anaphase. And T stands for telophase.
What are the 5 events in prophase?
Meiotic prophase I is subdivided into five stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
What is after prometaphase?
After prometaphase ends, metaphase—the second official phase of mitosis—begins.
What happens in a prophase?
During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses. The chromatin coils and becomes increasingly compact, resulting in the formation of visible chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of a single piece of DNA that is highly organized.
What are the 3 stages of prophase?
Stages of ProphaseLeptotene – The chromosomes begin to condense and are attached to the nuclear membrane via their telomeres.Zygotene – Synapsis begins with a synaptonemal complex forming between homologous chromosomes.Pachytene – Crossing over of genetic material occurs between non-sister chromatids.More items...
What happened in prophase in mitosis?
The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
What are the 4 stages of prophase?
The main events of prophase are: the condensation of chromosomes, the movement of the centrosomes, the formation of the mitotic spindle, and the beginning of nucleoli break down.
What is the major event marking a cell's entry to prometaphase?
The major event marking a cell's entry to prometaphase is the breakdown of the nuclear envelope into small vesicles. Kinetochores also become fully matured on the centromeres of the chromosomes. The disruption of the nuclear envelope allows for the mitotic spindles to gain access to the mature kinetochores. As the microtubles of the mitotic spindle enter the nuclear region, some attach to the kinetochores making them kinetochore microtubules. The remaining microtubules are called non-kinetochore microtubules. Sister chromatids are captured by microtubules stemming from centrosomes on opposite ends of the cell. Once they have captured chromosomes, the kinetochore mictrotubles begin to exert force on the chromosomes, moving them.
What are the kinetochores in prophase?
Late in prophase, kinetochores assemble on the centromeres. Specialized microtubules, called kinetochore microtubules later attach to these sites. Duplicated centrosomes, which are the organizing centers of microtubules, begin to separate towards opposite poles of the cell.
What is the physical characteristic of cells beginning mitosis?
Another physical characteristic of cells beginning mitosis is the sprouting of microtubules from replicated centrosomes.
What are the requirements for entering the M phase?
As we discussed in cell cycle, before cells are allowed to enter M phase they must meet certain cellular requirements. Among these requirements are appropriate cell size and cellular environment. Following DNA replication in S phase, cells contain twice their normal number of chromosomes. Because cells that undergo mitosis are diploid, their number of chromosomes can be represented as 2 N, where N equals the number of distinct chromosomes in the cell. Cells about to enter M phase, which have passed through S phase and replicated their DNA, have 4 N chromosomes. Entry into M phase is allowed by the formation of the mitotic cyclin-Cdk complex known as M phase-promoting factor that occurs as a cell cycle regulatory mechanism in the G2 phase.
What is the first phase of mitosis?
The first phase of mitosis within M phase is called prophase. It follows G2, the final phase of interphase. A cell entering M phase manifests a number of physicsl signs. Among these are condensation, or thickening, of chromosomes. Chromosome condensation is visible through a microscope and is required for subsequent chromosome separation ...
How many chromosomes are in a cell during mitosis?
Because cells that undergo mitosis are diploid, their number of chromosomes can be represented as 2 N, where N equals the number of distinct chromosomes in the cell. Cells about to enter M phase, which have passed through S phase and replicated their DNA, have 4 N chromosomes.
What is the stage of eukaryotic cell division that occurs between prophase and metaphase?
Prometaphase Definition. Prometaphase is the stage of eukaryotic cell division that falls between prophase and metaphase. During prophase, the cell ’s chromosomes have condensed and the cell’s centrosome, or microtubule organizing center, has divided and moved to opposite sides of the cell. During prometaphase, several key steps take place, ...
What are the colors of the cells during prometaphase?
The following is a picture of a cell during late prometaphase. The bright colors in the photograph have been created by fluorescent molecules that attach to various structures. The green lines are the spindle fibers, or microtubules. The red dots represent individual kinetochores. The blue is created by fluorescent molecules attached to the DNA. The bright green lines are kinetochore microtubules, and prometaphase will continue until all of the red kinetochores are attached to microtubules.
What is the spindle checkpoint in meiosis?
In the first division of meiosis, however, the meiotic spindle is created, which aligns homologous chromosomes on the metaphase plate. Prometaphase has a checkpoint, the spindle checkpoint, which will not allow the cell to move to the next stage of cell division. This checkpoint relies on all chromosomes being attached to the spindle.
What is the function of the centrosome in mitosis?
Also, the microtubule organizing center, or centrosome, can add or remove monomers of the microtubule, increasing or decreasing its overall length. This can push and pull the chromosomes towards the metaphase plate for the next stage in eukaryotic cell division. During prometaphase of mitosis, the mitotic spindle is formed, ...
Why are sister chromatids divided during anaphase?
These sister chromatids will be divided during anaphase, because the proteins that hold them together at the centromere will be released. In meiosis, the stage of prometaphase is usually broken into the late parts of prophase or the early parts of metaphase, but the processes of prometaphase must still happen.
When do chromosomes reassemble?
They will be reassembled during telophase before the cell is fully divided into two new cells. The breakdown of the nuclear membrane allows the attachment of microtubules to the chromosomes. Chromosomes have special regions associated with proteins that allow sister chromatids to attach to each other.
When does the nuclear membrane break apart?
Although the breakdown of the nuclear membrane is not clearly understood, it is known that the membrane breaks apart during prometaphase. The nuclear membrane is made of two lipid bilayers, with many pores that allow ribosomes to pass through membrane. At the onset of prometaphase, proteins are released that remove specific molecules from the nuclear membranes. Without the molecule, the membranes fall apart. They will be reassembled during telophase before the cell is fully divided into two new cells.
What is the Difference Between Prophase and Metaphase?
Metaphase is the second phase of the M phase in which chromosomes line up in the centre of the cell attaching to spindle fibres.
What is followed by prophase?
Followed By, Prophase is followed by metaphase. Metaphase is followed by anaphase. Main Occurrences. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindles form at opposite “poles” of the cell..
What is Metaphase?
Metaphase is the second phase of the M phase. Metaphase starts at prophase, and it is followed by anaphase. During the metaphase, homologous chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate or the centre of the cell. Nuclear membrane disappears completely. Two pair of centrioles aligns at two poles. Spindle fibres extend from poles towards the chromosomes and attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
What are the phases of cell division?
Cell division occurs via three major phases namely interphase, M phase and cytokinesis. During the interphase, cell prepares for the cell division by accumulating nutrients, synthesizing proteins and replicating the DNA. During the M phase, nuclear division occurs, and cytoplasm divides into two cells by creating two daughter cells. M phase proceeds via four phases namely prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Prophase is the first phase of M phase, and during the prophase, nuclear membrane starts to break, chromatin condenses into visible chromatids, spindle fibres form and chromosomes start to pair. Prophase is followed by metaphase, and during the metaphase, nuclear membrane completely breaks down, chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, and spindle fibres attach with centromeres of the chromosomes. Both phases are important phases of cell division. This is the difference between prophase and metaphase.
What happens when a spindle fibre is in metaphase?
If the homologous chromosomes line up wrongly, daughter cells will receive an abnormal amount of chromosomes that can cause genetic disorders.
What are the phases of meiosis and mitosis?
Both phases can be seen in meiosis and mitosis. Both phases are vitally important for cell division. In both phases, the cell does not grow. There are two prophases and two metaphases in meiosis. There are one prophase and one metaphase in mitosis. In both phases, the nuclear membrane breaks.
How many prophases are there in mitosis?
The invisible genetic material becomes visible under the microscope during the prophase of the cell cycle. There is one prophase in mitosis while there are two prophases in meiosis.
What happens during prometaphase?
The short version of what happens during prometaphase is that the nuclear membrane breaks down .
How many copies of each chromosome are there in a cell during prophase?
Since each of the parent cell’s chromosomes were replicated during interphase, there are two copies of each chromosome in the cell during prophase. Once the chromatin has condensed into individual chromosomes, the genetically-identical chromosomes come together to form an “X” shape, called sister chromatids.
What Is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a process that occurs during the cell cycle. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis. Mitosis results in two new nuclei—which contain DNA—that eventually become two identical cells during cytokinesis .
What is the line that divides the sister chromatids down the middle of the cell called?
This imaginary line dividing the cell down the middle is called the metaphase plate or equatorial plane .
How many phases does mitosis occur in?
In order to accomplish this goal, mitosis occurs in four discrete, consistently consecutive phases: 1) prophase, 2) metaphase, 3) anaphase, and 4) telophase . We have an overview of mitosis here, which is more of an intro to what mitosis is and how it works. If you're a little shaky on mitosis still, that's definitely where you should start.
What is interphase in biology?
We can think of interphase as a transitional phase. Interphase is when the parent cell prepares itself for mitosis. This phase isn’t considered part of mitosis, but understanding what happens during interphase can help the steps of mitosis make a little more sense.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The main purpose of mitosis is to accomplish cell regeneration, cell replacement, and growth in living organisms. Mitosis is important because it ensures that all new cells that are generated in a given organism will have the same number of chromosomes and genetic information. In order to accomplish this goal, mitosis occurs in four discrete, consistently consecutive phases: 1) prophase, 2) metaphase, 3) anaphase, and 4) telophase .
What is the Difference Between Prophase I and Prophase II?
Each meiosis has four stages. Prophase I is the beginning phase of meiosis I while prophase II is the initial phase of meiosis II. This is the key difference between prophase I and prophase II. Another difference between prophase I and prophase II is the possibility of crossing over and mixing genetic material. In prophase, I, crossing over between homologous chromosomes occurs, and the mixing of genetic material occurs while both are not possible in prophase II.
What is Prophase I?
Prophase I is the first phase of Meiosis I. There is a long interphase before prophase I. During the prophase I, chromosomes become visible, and they synapse to form tetrads. Resulting tetrads contain two pairs of chromosomes, hence the name bivalents. Crossing over is another important process that takes place in prophase I and allows the chromosomes to exchange genetic materials and to produce genetically different recombinants or genetically distinct gametes.
What happens during prophase I and II?
Prophase I occurs after interphase while prophase II occurs after telophase I. This is another difference between prophase I and prophase II. Furthermore, during the prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads and exchange genetic materials between each other. But this is not happening in prophase II.
What happens in prophase I?
In prophase, I, crossing over between homologous chromosomes occurs, and the mixing of genetic material occurs while both are not possible in prophase II. The below infographic tabulates the difference between prophase I and prophase II in more detail.
What are the physical links between homologous chromosomes?
These crossing over physical links in homologous chromosomes are the Chiasmata, and they are extremely important in producing genetically variable offspring population. Disappearing of the nuclear envelope, moving spindle fibres into the centre, and connecting the tetrads to the spindle fibres by kinetochores are the other events that occur in prophase I.
Why is meiosis important?
Among them, meiosis is a vital process for sexual reproduction. For a successful sexual reproduction process, it is necessary to produce gametes that contain half of the chromosome number of a normal cell. All eukaryotes have a unique chromosome number for each species.
Where is Prophase II?
Prophase II can be found in Meiosis II. It is the beginning phase of another subsequent cell division after meiosis I. unlike before prophase I, there is no interphase before prophase II. Hence, prophase ii directly starts after telophase I. This process is identical to the prophase found in Mitosis, in many aspects.