
How does quiet breathing differ from forced breathing? Quiet expiration is a passive process occurring at rest, whereas forced expiration is an active process that occurs during exercise.
What is normal quiet breathing?
Quiet breathing, also known as eupnea, is a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions.
What is the phobia for fear of breathing in breath?
Halitophobia (delusion halitosis) Halitosis is commonly known as bad breath and is caused by bacteria in the mouth that put off odorous sulfur compounds. The causes of bad breath are numerous, but typical reasons include naturally-occurring bacteria on the tongue, periodontal gum disease, and dietary habits.
What are the steps in the breathing process?
What Are the Steps of Breathing?
- The Urge to Breathe. The urge to breathe comes from the respiratory center, located at the base of your brain. ...
- Inhalation. When you breathe, the diaphragm -- the large muscle that divides your chest and abdomen -- contracts and moves downward.
- Gas Exchange. ...
- Exhalation. ...
What is quiet breathing in anatomy?
Quiet breathing, also known as eupnea, is a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract.
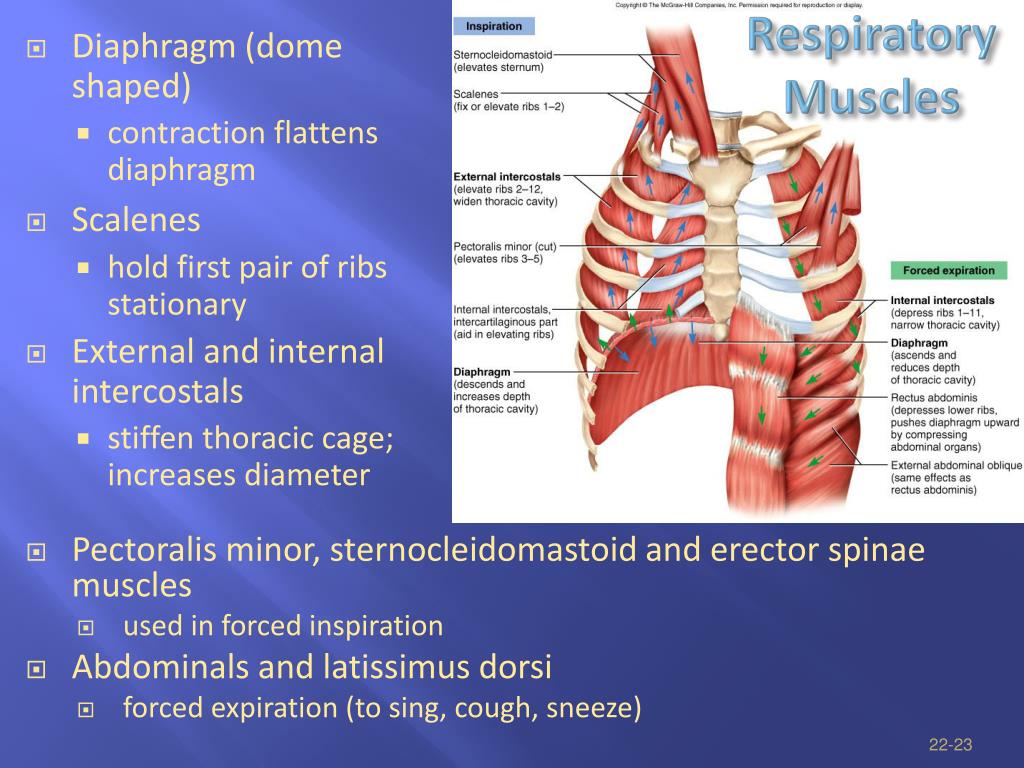
What is forced breathing?
Forced breathing is, to breath deeply and slowly for certain duration of time voluntarily, overcoming the autonomic or involuntary breathing drive.
What happens quiet breathing?
During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract. As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. A shallow breath, called costal breathing, requires contraction of the intercostal muscles.
How does quiet breathing differ from forced breathing quizlet?
During normal quiet breathing, the expiratory area is inactive; during forceful breathing, the inspiratory area activates the expiratory area.
What is the term for quiet breathing?
1) Eupnea: a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. During eupnea, also referred to as quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract.
Is quiet breathing passive?
Expiration during quiet breathing is predominantly a passive phenomenon, as the respiratory muscles are relaxed and the elastic lung and chest wall return passively to their resting volume, the functional residual capacity. However, during exercise, many other muscles become important to respiration.
What is forced inspiration?
9:4412:24How Do We Accomplish Forced (Active) Breathing? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then forcibly exhale. You'll actually feel your abdominal muscles contract. The way this worksMoreAnd then forcibly exhale. You'll actually feel your abdominal muscles contract. The way this works is actually by contracting the abdominal muscles you actually increase the pressure inside the
What muscles are used during quiet inhalation?
Respiratory movements during quiet breathing are described first. The muscles that contribute to quiet breathing are the external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. (The external and internal intercostals are the muscles that fill the gaps between the ribs.)
What are the muscles used during quiet inspiration?
Normal and quiet inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. Simultaneously, muscles of inspiration elevate the rib cage. These muscles are mainly the external intercostals.
Why is alveolar ventilation more important than minute ventilation?
Alveolar ventilation is the most important type of ventilation for measuring how much oxygen actually gets into the body, which can initiate negative feedback mechanisms to try and increase alveolar ventilation despite the increase in dead space.
What is the difference between quiet and forced expiration?
Quiet expiration is a passive process occurring at rest, whereas forced expiration is an active process that occurs during exercise. Quiet respiration depends on elastic recoil of the lungs after inspiratory stretching, elastic recoil of the costal cartilages, and the relaxation of the inspiratory muscles.
What are the two types of breathing?
The process of breathing consists of two types:Inspiration or Inhalation: Taking atmospheric air into the lungs. This process is inhalation. ... Expiration or exhalation: This is the process that involves discharging the air from lungs.
What is the difference between active and passive breathing?
As the muscles use energy for contraction, inspiration is called active process. During expiration, muscles of the diaphragm relax. The pressure inside the lungs becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure without the use of energy and the air gushes out of the lungs. Thus, expiration is a passive process.
Is breathing supposed to be silent?
What should breathing feel like? If you're breathing effectively, your breath will be smooth, steady, and controlled. You should feel relaxed and as though you're able to get enough air without straining. It should feel easy to breathe, and your breath should be silent or quiet.
What is quiet inspiration?
Quiet inspiration is a function of two muscles: Diaphragm: A musculotendinous domed structure that divides the thoracic and abdominal cavity. It is the main muscle of respiration. As it contracts it moves down increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity, this results in air being drawn in down its pressure gradient.
What muscles are used during quiet inspiration?
The muscles that contribute to quiet breathing are the external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. (The external and internal intercostals are the muscles that fill the gaps between the ribs.) When drawing breath (i.e., during inspiration), the external intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract simultaneously.
What is the process of breathing?
Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing, which is driven by pressure differences between the lungs and the atmosphere. Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by gases present in the atmosphere. The force exerted by gases within the alveoli is called intra-alveolar (intrapulmonary) pressure, whereas the force exerted by gases in the pleural cavity is called intrapleural pressure. Typically, intrapleural pressure is lower, or negative to, intra-alveolar pressure. The difference in pressure between intrapleural and intra-alveolar pressures is called transpulmonary pressure. In addition, intra-alveolar pressure will equalize with the atmospheric pressure. Pressure is determined by the volume of the space occupied by a gas and is influenced by resistance. Air flows when a pressure gradient is created, from a space of higher pressure to a space of lower pressure. Boyle’s law describes the relationship between volume and pressure. A gas is at lower pressure in a larger volume because the gas molecules have more space to in which to move. The same quantity of gas in a smaller volume results in gas molecules crowding together, producing increased pressure.
What causes the lungs to be pulled outward during inspiration?
This is because of the adhesive nature of the pleural fluid, which allows the lungs to be pulled outward when the thoracic wall moves during inspiration. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostals muscles (found between the ribs) cause most of the pressure changes that result in inspiration and expiration. These muscle movements and subsequent pressure changes cause air to either rush in or be forced out of the lungs.
What is intrapleural pressure?
Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing.
Why does air flow down a pressure gradient?
The difference in pressures drives pulmonary ventilation because air flows down a pressure gradient, that is, air flows from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure. Air flows into the lungs largely due to a difference in pressure; atmospheric pressure is greater than intra-alveolar pressure, and intra-alveolar pressure is greater than intrapleural pressure. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure.
What is the respiratory system disorder?
Disorders of the Respiratory System: Sleep Apnea. Sleep apnea is a chronic disorder that can occur in children or adults, and is characterized by the cessation of breathing during sleep. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced.
What is the ability to breathe?
However, the ability to breathe—to have air enter the lungs during inspiration and air leave the lungs during expiration —is dependent on the air pressure of the atmosphere and the air pressure within the lungs.
What is the name of the breathing that occurs at rest?
Quiet breathing, also known as eupnea, is a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract.
What is the difference between "quiet inspiration" and "quiet expiration"?
What Is "quiet Inspiration" and What Is "quiet Expiration"? "Quiet inspiration" is the intake of air into the lungs via the contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles only, while "quiet expiration" is output of air from the lungs by relaxing these same muscles. They stand in contrast to forced inspiration and expiration.
What is quiet expiration?
Quiet expiration, by contrast, is purely passive, a simple relaxation of the muscles that causes the chest cavity to expand, returning it to its original volume and forcing the inhaled air out.
What muscles are used to breathe?
In forced inspiration, extra accessory muscles are used to take in air faster, while in forced expiration abdominal and other muscles force air out faster. Quiet inspiration and expiration are the normal methods humans use to breathe when relaxed and unstressed.
Is inspiration passive or active?
This causes the air under normal atmospheric pressure outside to rush in, carrying the oxygen needed for survival. Quiet expiration, by contrast, is purely passive, ...
Does quiet inspiration fill the lungs?
Normal quiet breathing exchanges less than half the air in the lungs, and quiet inspiration does not fill the lungs to their full capacity, according to McGraw Hill Education. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is quiet breathing?
Quiet breathing is the relaxed, normal breathing state that requires no control of any type. It pairs with fast breathing and deep breathing to form one of the types of pranayama breathing exercises employed in yoga.
Why does a yogi breathe when there is no movement?
When the body moves, respiration is affected because of the body's need for oxygenated blood. The breath becomes faster and sometimes deeper, but when there's no body movement, breathing is smooth and in its relaxed state. This is what is known as quiet breathing. Typically, after the yogi settles into and holds the final position of any pose, quiet breathing takes over. To ensure quiet breathing, the yogi should relax the body in the stabilized position of the pose. At this point, the yogi observes the breath, noticing the gentle inhale and exhale without influencing it.
