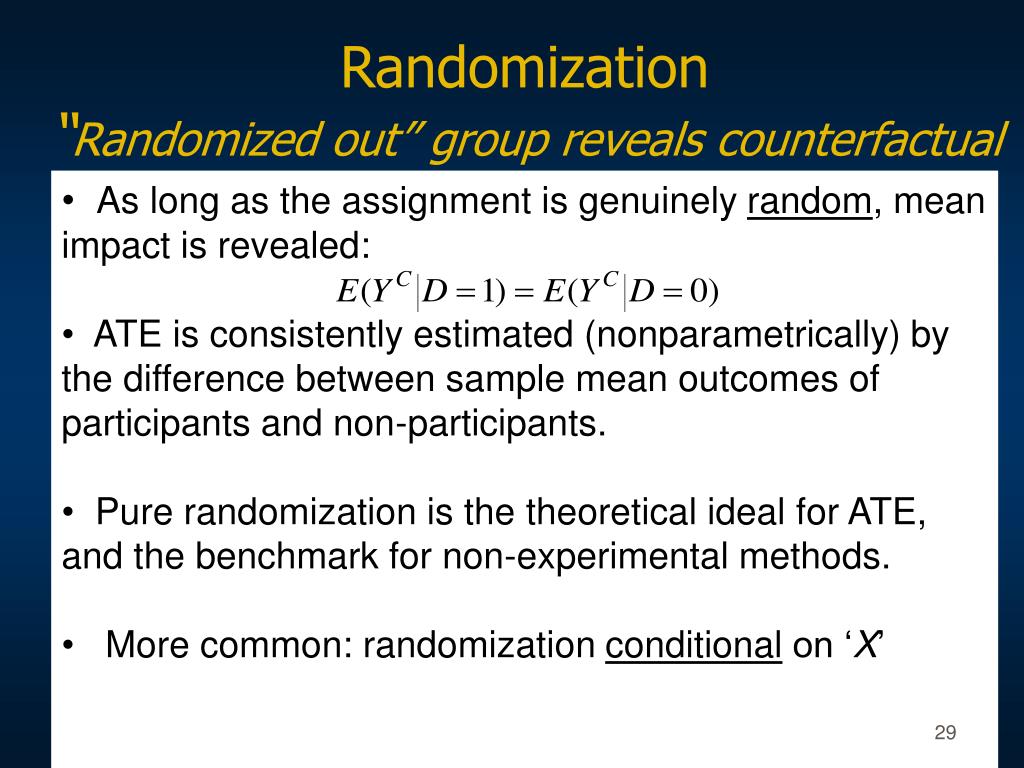
Random selection refers to how the sample is drawn from the population as a whole, while random assignment refers to how the participants are then assigned to either the experimental or control groups. It is possible to have both random selection and random assignment in an experiment.
What is the difference between random randint and randRange?
You can see that both the examples have the same syntax and return a random number between -100 and -1. But the difference is randint()will include -1 in its random numbers but randrange()won’t. How to generate a positive and negative integer number in Python?
What is the goal of random assignment?
The purpose of random assignment is to allow the experimenter to prevent the participants from knowing which condition they were assigned to. What does random assignment mean in research? Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to ...
How to do random assignments in an experiment?
The Definition of Random Assignment According to Psychology
- Overview. Random assignment might involve tactics such as flipping a coin, drawing names out of a hat, rolling dice, or assigning random numbers to participants.
- Random Assignment In Research. To determine if changes in one variable lead to changes in another variable, psychologists must perform an experiment.
- Random Selection. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random sampling?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods?
- Reduce Cost. It is cheaper to collect data from a part of the whole population and is economically in advance.
- Greater Speed.
- Detailed Information.
- Practical Method.
- Much Easier.

What is the difference between random sampling and random assignment?
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups.
What is the difference between random selection and random assignment quizlet?
random selection is used to obtain a sample that resembles the population (i.e., to obtain a representative sample). random assignment is used to create groups that are similar to one another.
How does random selection differ from random assignment to group?
How does random selection differ from random assignment? Random selection refers to how the sample is drawn from the population as a whole, while random assignment refers to how the participants are then assigned to either the experimental or control groups.
Which is more important random selection or random assignment?
Random selection is thus essential to external validity, or the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population. Random assignment is central to internal validity, which allows the researcher to make causal claims about the effect of the treatment.
What is random assignment in statistics?
Random assignment refers to the method you use to place participants into groups in an experimental study. For example, say you are conducting a study comparing the blood pressure of patients after taking aspirin or a placebo.
What is random assignment in research?
Random assignment. Random assignment is a procedure used in experiments to create multiple study groups that include participants with similar characteristics so that the groups are equivalent at the beginning of the study.
What is an example of a random assignment?
Example of Random Assignment Imagine that a researcher is interested in learning whether or not drinking caffeinated beverages prior to an exam will improve test performance. After randomly selecting a pool of participants, each person is randomly assigned to either the control group or the experimental group.
What is another word for random selection?
chance, desultory, haphazard, hit-or-miss, indiscriminate, spot, unplanned.
What is random selection in biology?
Random selection, also called random sampling, is a way of choosing who participates in a study in which each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
How do you do random selection?
There are 4 key steps to select a simple random sample.Step 1: Define the population. Start by deciding on the population that you want to study. ... Step 2: Decide on the sample size. Next, you need to decide how large your sample size will be. ... Step 3: Randomly select your sample. ... Step 4: Collect data from your sample.
Why is random assignment important in statistics?
Random assignment helps reduce the chances of systematic differences between the groups at the start of an experiment and, thereby, mitigates the threats of confounding variables and alternative explanations.
Why do we use random sampling in research?
Random sampling ensures that results obtained from your sample should approximate what would have been obtained if the entire population had been measured (Shadish et al., 2002). The simplest random sample allows all the units in the population to have an equal chance of being selected.
What is a random assignment in psychology quizlet?
Random Assignment. -A method of assigning participants to conditions such that each participant has an equal chance of being placed into experimental groups. -Assignment is the process by which participants are put into either an experimental or control group.
What is random selection in psychology quizlet?
Random selection. Selection of participants using a random sampling method. Random assignment. Placement of participants into experimental conditions on the basis of a chance process.
What is random assignment psychology?
Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group. Study participants are randomly assigned to different groups, such as the experimental group or treatment group.
How do randomization and random sampling differ quizlet?
How do randomization and random sampling differ? The purpose of random sampling is to increase generalizability and the purpose of randomization is to decrease spuriousness. The key feature of an experimental design that distinguishes it from a quasi-experimental design is the ?
What’s the difference between method and methodology?
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and...
What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative methods?
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Quantitative methods allow yo...
What is sampling?
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in...
What’s the difference between reliability and validity?
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something: Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the r...
What is the difference between internal and external validity?
I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables . Ext...
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you ne...
What are independent and dependent variables?
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the ca...
What is the difference between quantitative and categorical variables?
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age). Categorical variables are any variables...
What is the difference between discrete and continuous variables?
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables : Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a...
What is the difference between random assignment and random sampling?
In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups. Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
What is an example of random sampling?
The American Community Survey is an example of simple random sampling. In order to collect detailed data on the population of the US, the Census Bureau officials randomly select 3.5 million households per year and use a variety of methods to convince them to fill out the survey.
Why is random sampling important?
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. If the population is in a random order, this can imitate the benefits of simple random sampling.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
What is a method in science?
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys, and statistical tests ). In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section.
What is random selection?
Random selection requires the use of some form of random sampling (such as stratified random sampling, in which the population is sorted into groups from which sample members are chosen randomly).
What is random assignment in psychology?
In a true experiment, all study participants are randomly assigned either to receive the treatment (also known as the stimulus or intervention) or to act as a control in the study (meaning they do not receive the treatment).
Why is random selection important?
Random selection is thus essential to external validity, or the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population. Random assignment is central to internal validity, which allows the researcher to make causal claims about the effect of the treatment. Nonrandom assignment often leads to non-equivalent groups, meaning that any effect of the treatment might be a result of the groups being different at the outset rather than different at the end as a result of the treatment. The consequences of random selection and random assignment are clearly very different, and a strong research design will employ both whenever possible to ensure both internal and external validity.
How do researchers use random number generators?
Using a random number generator, the researcher selects 100 students from the school to participate in the study (the random sample). All students’ names are placed in a hat and 50 are chosen to receive the intervention (the treatment group), while the remaining 50 students serve as the control group. This design uses both random selection and random assignment.
How do researchers get a list of all students enrolled at a particular school?
A researcher gets a list of all students enrolled at a particular school (the population). Using a random number generator, the researcher selects 100 students from the school to participate in the study (the random sample).
Can random selection be used to determine the effect of a study?
A study using only random selection could randomly select students from the overall population of the school, but then assign students in one grade to the intervention and students in another grade to the control group. While any data collected from this sample could be used to make inference to the population of the school, the lack of random assignment to be in the treatment or control group would make it impossible to conclude whether the intervention had any effect.
Can random assignment be done outside of controlled laboratory conditions?
Although random assignment is a simple procedure (it can be accomplished by the flip of a coin), it can be challenging to implement outside of controlled laboratory conditions. A study can use both, only one, or neither.
What is random assignment?
Random assignment refers to the method you use to place participants into groups in an experimental study. For example, say you are conducting a study comparing the blood pressure of patients after taking aspirin or a placebo. You have two groups of patients to compare: patients who will take aspirin ...
Why is random assignment important?
Random assignment is a fundamental part of a “true” experiment because it helps ensure that any differences found between the groups are attributable to the treatment, rather than a confounding variable. So, to summarize, random sampling refers to how you select individuals from the population to participate in your study.
What is random sampling?
Random sampling refers to the method you use to select individuals from the population to participate in your study. In other words, random sampling means that you are randomly selecting individuals from the population to participate in your study. This type of sampling is typically done to help ensure the representativeness of the sample (i.e., ...
What is random selection?
Basically, random selection is the way a researcher chooses the participants in a study. This requires the researcher to identify the population and the sample. A population is all members of a specified group. Once you know the population, you can use random selection to determine the sample.
What is random selection in Aubree's study?
Basically, random selection is the way Aubree will choose who will be a part of her study. Most studies use some sort of random sampling to select participants. There are different ways you can select participants for a study. First, Aubree will need to decide on her population.
Why would Aubree use random selection?
If Aubree did not want to find the cause and effect of orange consumption but simply wanted to see if there is a correlation between people that consume oranges, those that don't consume oranges, and the person's overall health, then she could use random selection for her participants. This would be an observational study because she would only be collecting data from the participant's natural eating patterns, not experimenting with the effects of orange consumption. Observational studies only use random selection; they do not use random allocation.
What is the purpose of random allocation?
Random allocation is the method used to select members of a sample to receive the treatment in an experiment. This is how a researcher will determine the control and the experimental group.
How to get a sample from a population?
These include random sampling, simple random sampling, cluster sampling, stratified sampling, and systematic sampling. Now that we have covered random selection, let's move on to random allocation.
Can Aubree conduct a random study?
For example, Aubree can conduct her study with a random selection of students in certain classes at the college, or she can select every other student that is willing to be a part of the study. There are many different ways you can get a sample from your population.
Can a study have random allocation?
A study can have any combination of random allocation and random selection or have neither. Remember, random allocation is only used for experimental studies with a control and a treatment, and observational studies only use random selection. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.