Impedance and Reactance
- Impedance. Impedance (symbol Z) is a measure of the overall opposition of a circuit to current, in other words: how much the circuit impedes the flow of charge.
- Reactance, X. ...
- Input Impedance Z IN. ...
- Output Impedance Z OUT. ...
- The output impedance of a voltage divider. ...
What is impedance, impedance vs resistance?
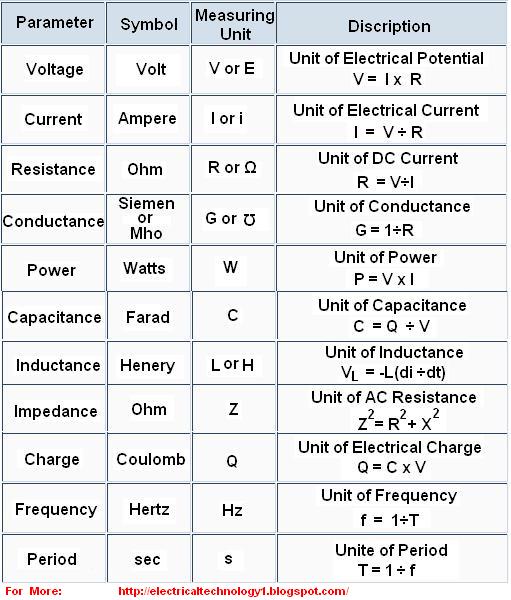
- Impedance – Ω
- Reactance – Ω
- Resistance – Ω
How do you calculate total impedance?
Where:
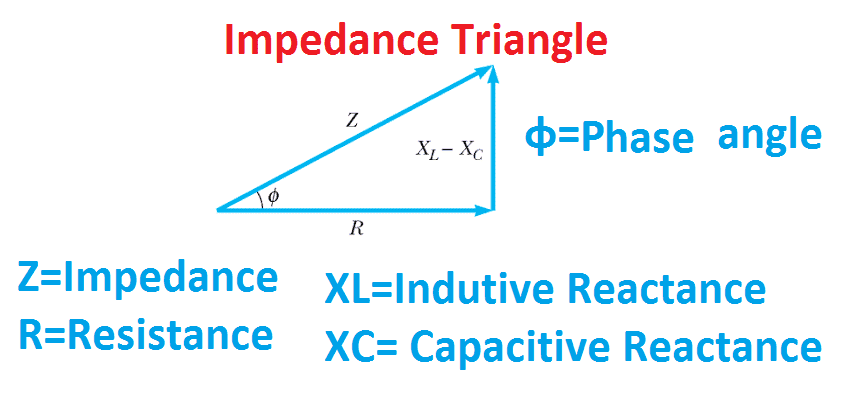
- X L = Inductive reactance (Ω)
- R = Resistance in Ohmnios
- Z = Impedance
What is the formula for impedance?
What is the formula for calculating impedance?
- Impedance Z = R or XLor XC (if only one is present)
- Impedance in series only Z = √ (R2 + X2) (if both R and one type of X are present)
- Impedance in series only Z = √ (R2 + (|XL – XC|)2) (if R, XL, and XC are all present)
- Impedance in any circuit = R + jX (j is the imaginary number √ (-1))
How to calculate the impedance of a circuit?
- Short circuit current, X/R ratio
- Short circuit MVA, X/R ratio
- Actual positive sequence impedance
What is the difference between impedance reactance and resistance?
Very often, reactance and impedance are thought to be the same and are interchangeably used. It is important to understand that reactance is the resistance offered to the AC current by inductors and capacitors only while impedance is the sum of the resistance and reactance.
What is the difference between impedance and resistance?
Impedance- The main difference between Resistance and Impedance is their behavior to AC and DC currents. While resistance controls the flow of AC and DC current, Impedance just determines the alternative current flow. It means that impedance is only used in AC systems and does not have any use in DC diagrams.
What is the relation between impedance and reactance?
Impedance is the combination of resistance and reactance (both inductive and capacitive) and is a complex number, containing both real and imaginary parts. (The real part of impedance is resistance, while the imaginary part is reactance.) Impedance has both magnitude and phase.
What is reactance and impedance in AC?
Reactance: Reactance is resistance offered to the AC currents by inductors and capacitors only. Impedance: It is the sum of the resistance and reactance of inductor.
What's a reactance?
In electrical circuits, reactance is the opposition presented to alternating current by inductance or capacitance. Greater reactance gives smaller current for the same applied voltage.
What is called reactance?
Reactance, denoted X, is a form of opposition that electronic components exhibit to the passage of alternating current (alternating current) because of capacitance or inductance. In some respects, reactance is like an AC counterpart of DC (direct current) resistance.
What is the difference between XC and XL?
In series RLC circuit, the condition XL(Inductive reactance) = XC (Capacitive reactance) is called resonance condition. In this condition the inductive reactance get cancelled by capacitive reactance.
What causes reactance?
Reactance is an unpleasant motivational arousal that emerges when people experience a threat to or loss of their free behaviors. It serves as a motivator to restore one's freedom. The amount of reactance depends on the importance of the threatened freedom and the perceived magnitude of the threat.
What is XL and XC in physics?
XL is called as inductive reactence and Xc is called as capacitive reactence. and the formulae[ XL = 2∏fL, XC = 1/2∏fC ] is given in that website. At resonance the reactence will be same for both cacitence and inductance. That is XL = XC = R.
What is the SI unit of reactance?
Solution : SI unit of reactance and impedance of a.c. circuit is same viz. ohm.
What is reactance in RLC circuit?
The reactance of inductor L = XL = ωL and its impedance Zi = 0 + jωL = 0 + jXL. Thus, the impedance of an inductor is always imaginary, leading the resistor R by 90◦. Curve (a) in Figure 12.7 shows the variation of XL( = ΩL) with the frequency.
What is reactance in AC circuits?
Reactance is the measure of the opposition to the flow of alternating current caused by the inductance and capacitance in a circuit rather than by resistance. Steady electric currents flowing along conductors in one direction undergo opposition called electrical resistance, but no reactance.
What is reactance formula?
Reactance is symbolized by the capital letter “X” and is measured in ohms just like resistance (R). Inductive reactance can be calculated using this formula: XL = 2πfL.
What is called reactance?
Reactance, denoted X, is a form of opposition that electronic components exhibit to the passage of alternating current (alternating current) because of capacitance or inductance. Resistance and reactance combine to form impedance, which is defined in terms of two-dimensional quantities known as complex number.
What is XC and XL?
Now when you type a reactance and frequency, you can calculate L and C at that frequency. XL is called as inductive reactence and Xc is called as capacitive reactence. and the formulae [ XL = 2∏fL, XC = 1/2∏fC ] is given in that website.
What causes reactance?
In electric and electronic systems, reactance is the opposition of a circuit element to the flow of current due to that element's inductance or capacitance. Larger reactance leads to smaller currents for the same voltage applied. As frequency goes up, inductive reactance also goes up and capacitive reactance goes down.
What is the use of impedance?
Applications of Impedance In capacitors, impedance is used to manage the flow of electricity in a circuit board. Without the capacitors controlling and adaptable electrical flow, your electronics that use alternating currents will either fry or go berserk.
What is impedance simple explanation?
The definition of an impedance is any obstruction, or the measure of the opposition of an electric current to the energy flow when voltage is applied. An example of impedance is a line of resistance within an electrical current.
Why is impedance matching needed?
Transmission line matching (Impedance matching) It is very important to transfer radio frequency energy from a generator to a load through transmission lines with zero or minimum power loss. To achieve this, the source and the load impedances have to be matched.
What is the difference between resistance and reactance?
Mathematically, resistance is simply voltage divided by current. Reactance is a property that opposes a change in current and is found in both inductors and capacitors.
Why is reactance specific to AC power?
Because it only affects changing current, reactance is specific to AC power and depends on the frequency of the current. When reactance is present, it creates a 90 degree phase shift between voltage and current, with the direction of the shift depending on whether the component is an inductor or a capacitor. Reactance that occurs in an inductor is ...
What is inductive reactance?
Reactance that occurs in an inductor is known as inductive reactance. When inductive reactance is present, energy is stored in the form of a changing magnetic field, and the current waveform lags the voltage waveform by 90 degrees. Inductive reactance is caused by devices in which wire is wound circularly — such as coils (including line reactors ), ...
What is the reaction of a capacitor?
Reactance that occurs in a capacitor is known as capacitive reactance. Capacitive reactance stores energy in the form of a changing electrical field and causes current to lead voltage by 90 degrees. Capacitance is created when two conducting plates are placed parallel to one another with a small distance between them, filled with a dielectric material (insulator).
What is the difference between AC and DC?
AC circuits, on the other hand, are more complex, since voltage and current alternate direction with a given frequency. Whereas DC circuits have resistance, AC circuits often have resistance and another property, known as reactance. Impedance is the combination of resistance and reactance.
What is reactance in physics?
When it comes to define reactance, it is the measure of opposition of inductance and capacitance to current. Let’s learn more about these two terms in brief.
How to find the impedance of a circuit?
Square both R and X, and sum the two products together. Take the square root of the sum of the squares of R and X to get impedance. Display the answer in ohms.
What are the four electrical quantities that determine the impedance of a circuit?
There are four electrical quantities which determine the impedance (Z) of a circuit: These are: resistance (R), capacitance (C), inductance (L) and frequency (f).
What are the two types of reactance?
Reactance is of two types: 1 Capacitive reactance (Xc), and 2 Inductive reactance (XL).
What is the reactance of a 1mH inductor?
For example, a 1mH inductor has a reactance of only 0.3 for a 50Hz signal, but when frequency is higher at 10 kHz, its reactance is 63.
What is the reactance of a capacitor?
The reactance, which is large at low frequencies and small at high frequencies is known as capaci tive reactance (Xc). Xc is infinite for steady DC, at zero frequency (f=0Hz). This means that the capacitor passes AC but blocks DC.
What is the measurement unit for impedance?
The measurement unit for Impedance is ohms. As impedance considers the effects of inductance and capacitance and varies with the frequency of current passing through the circuit, it is more complex than resistance. As compared to resistance, which is constant regardless of frequency, impedance varies with frequency.
How do impedances in AC and DC circuits work?
Impedances in AC behave analogously to resistances in DC circuits: they add in series, and they diminish in parallel. A revised version of Ohm’s Law, based on impedance rather than resistance, looks like this:
What is the unit of resistance and reactance?
Reactance is mathematically symbolized by the letter “X” and is measured in the unit of ohms (Ω). Impedance is a comprehensive expression of any and all forms of opposition to electron flow, including both resistance and reactance. It is present in all circuits, and in all components.
What is the phase angle of a resistor?
For a perfect resistor, the voltage drop and current are always in phase with each other, and so the impedance angle of a resistor is said to be 0 o . For an perfect inductor, voltage drop always leads current by 90 o, and so an inductor’s impedance phase angle is said to be +90 o. For a perfect capacitor, voltage drop always lags current by 90 o, and so a capacitor’s impedance phase angle is said to be -90 o.
What is the difference between AC and DC?
The only real difference between DC and AC circuit calculations is in regard to power. Because reactance doesn’t dissipate power as resistance does, the concept of power in AC circuits is radically different from that of DC circuits. More on this subject in a later chapter!
What is resistance in electrical conductors?
Impedance. Resistance is essentially friction against the motion of electrons. It is present in all conductors to some extent (except super conductors!), most notably in resistors. When alternating current goes through a resistance, a voltage drop is produced that is in-phase with the current.
Where is alternating current present?
It is present anywhere electric or magnetic fields are developed in proportion to applied voltage or current, respectively; but most notably in capacitors and inductors. When alternating current goes through a pure reactance, a voltage drop is produced that is 90o out of phase with the current.
Do perfect resistors have reactance?
Perfect resistors (Figure below) possess resistance, but not reactance. Perfect inductors and perfect capacitors (Figure below) possess reactance but no resistance. All components possess impedance, and because of this universal quality, it makes sense to translate all component values (resistance, inductance, capacitance) into common terms ...
What is reactance in electronics?
Essentially reactance is the nature of such devices to oppose the temporal change in current (inductor) or voltage (capacitor) as opposed to resistance which reduces current uniformly over time. Eileen Wong. , lives in Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
What is the most important thing to remember about impedance?
The most important thing to remember about impedance is that it applies more to current which frequentl. Continue Reading. No difference; the two are directly related. Circuit impedance is measured in Ohms and is the aggregate of three phenomena: Resistance, capacitive reactance, and inductive reactance.
What determines the current in an AC circuit?
Impedance determines overall current in AC circuits. Impedance is a broader parameter which combines both resistance and reactance vectorially.
What is the measure of resistance of a device?
The reactance of a device is a measure of its opposition to current flow due to electric or magnetic fields being set up inside or around the device. Continue Reading. The resistance of a device is a measure of its opposition to current flow due to the fact that it is not an ideal electrical conductor.
Which two circuit devices exhibit reactance?
The two main circuit devices exhibiting reactance are the capacitor and the inductor. The capacitor is effectively two parallel conductor plates with an insulating material between them. This exhibits infinitely high reactance at DC because electric current cannot flow through an insulator.
What is resistance in electrical engineering?
Resistance means that the component is ‘resisting’ the flow of current through it. Such components are called resistors. Their abilities to resist current flow is called resistance, and this is measured in Ohms.
What is R resistance?
R-- resistance is that property of a material which opposes the flow of current.
Why is impedance more complex than resistance?
Impedance is more complex than resistance because the effects of capacitance and inductance vary with the frequency of the current passing through the circuit and this means impedance varies with frequency . The effect of resistance is constant regardless of frequency. Impedance, Z =. V.
What is reactance in electrical?
Reactance (symbol X) is a measure of the opposition of capacitance and inductance to current. Reactance varies with the frequency of the electrical signal. Reactance is measured in ohms ( ). There are two types of reactance: capacitive reactance (Xc) and inductive reactance (X L ).
What are the four electrical quantities that determine the impedance of a circuit?
Four electrical quantities determine the impedance (Z) of a circuit: resistance (R), capacitance (C), inductance (L) and frequency (f).
What is reactance X?
Reactance X (the part which varies with frequency due to capacitance and inductance) The capacitance and inductance cause a phase shift (see note) between the current and voltage which means that the resistance and reactance cannot be simply added up to give impedance.
What is the output of a circuit?
The output of any circuit or device is equivalent to an output impedance (Z OUT ) in series with a perfect voltage source (V SOURCE ). This is called the equivalent circuit and it represents the combined effect of all the voltage sources, resistance, capacitance and inductance connected to the output inside the circuit or device. Note that V SOURCE is usually not the same as the supply voltage Vs.
What is the reactance of a 1 f capacitor?
For example: a 1µF capacitor has a reactance of 3.2k for a 50Hz signal, but when the frequency is higher at 10kHz its reactance is only 16.
What is the measure of the overall opposition of a circuit to current?
Impedance. Impedance (symbol Z) is a measure of the overall opposition of a circuit to current, in other words: how much the circuit impedes the flow of charge. It is like resistance, but it also takes into account the effects of capacitance and inductance. Impedance is measured in ohms ( ). Impedance is more complex than resistance because ...
What is the difference between resistance and reactance?
The crucial difference between resistance and reactance is that resistance is the hindrance to the flow of electric current by only resistor. As against reactance is the opposition to the change in current by either inductor or capacitor.
What is the reaction of an electric circuit?
Definition of Reactance. The obstruction to the flow of alternating or changing current in electric circuits is known as reactance. The reactance to the circuit is the opposition in the flow of varying current. The reason behind the reactance of the circuit is such that its value is the factor of the presence of either capacitor or inductor as load.
What is the difference between a capacitive and a resistive circuit?
Whereas in a capacitive or inductive circuit, the device does not fully consume the total supplied power.
Which two components are responsible for the opposition to the flow of current?
So, from this discussion, it can be concluded that both resistance and reactance are responsible for the opposition to the flow of current and thus acts as impedance for any electrical circuit when present combinedly in it.
What is the property of opposing the current?
This property of opposing the flowing current is known as resistance. Resistance is the property possessed by resistors in electrical circuits.
Is resistor a DC or AC circuit?
Resistance is the property associated with both ac and dc circuit. However, reactance to the property is only associated with ac circuits. Pure resistors generate resistance. As against ideal inductors or capacitors give rise to reactance in the circuit. Resistance is associated with the real part of the impedance.
Is offered resistance the same as constant current?
Thus offered resistance is specified as: It is to be noted here that resistance offered by the conductors is the same for constant or varying current. In resistive circuits, the power consumed is given as: As both the terms in the product are real values thus the consumed power will also be a real term.