Explore
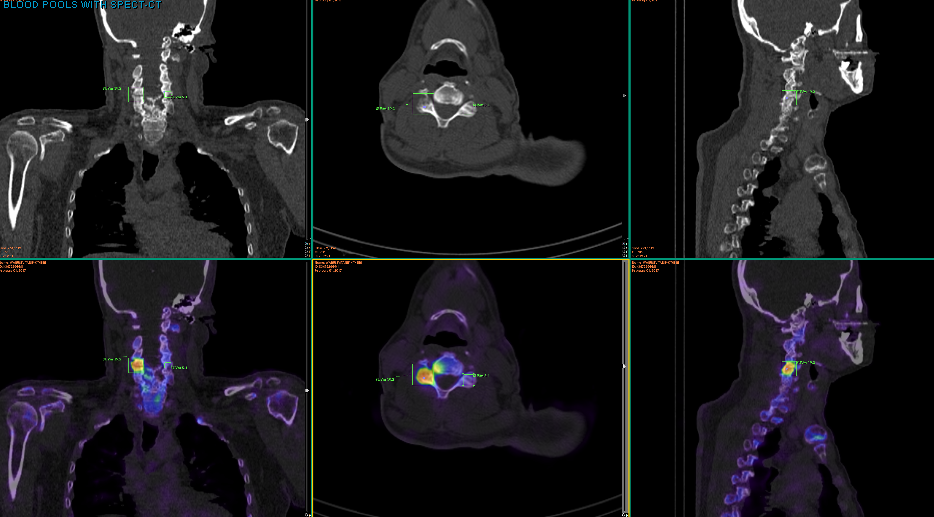
For the SPECT (or single photon emission computed tomography) component, the nuclear medicine gamma camera rotates 360 degrees around the body and creates pictures based on the data it obtains. For the CT (or computed tomography) portion, the CT detector uses a lower dose of radiation to help the SPECT scan create a better image.
What is the difference between a CT and SPECT scan?
The cost of the integrated device parts is heavily weighted toward CT if a high-end CT is used in a SPECT-CT system, and SPECT data acquisition is substantially slower than PET data acquisition.
What is the difference between PET and SPECT-CT?
Combining the information from a nuclear medicine SPECT study and a CT study allows the information about function from the nuclear medicine study to be easily combined with the information about how the body structure “looks” in the CT study.
What is the difference between a nuclear medicine SPECT and CT study?
Your doctor has weighed up the benefits versus risks in having a SPECT-CT scan, and has decided that the benefit of having the information gained from the scan outweighs any risk.
Should I have a SPECT-CT scan?
How does a spectro-CT scan work?
Why do we need a SPECT scan?
What is a single photon emission computed tomography?
Is a SPECT/CT scan safe?
Can a CT scan and a SPECT scan be combined?
See 2 more
About this website

Is SPECT a CT scan?
SPECT is a nuclear imaging scan that integrates computed tomography (CT) and a radioactive tracer. The tracer is what allows doctors to see how blood flows to tissues and organs.
Why is SPECT CT better than SPECT?
SPECT/CT improved anatomic localization of findings in 68 of 144 patient studies (47%) and improved diagnostic cer- tainty of findings in 34/144 studies (24%). SPECT/CT added diagnostic value over SPECT alone in 78 (54%) of the 144 patient studies (Table 2).
What is the difference between PET CT and SPECT CT?
The main difference between SPECT and PET scans is the type of radiotracers used. While SPECT scans measure gamma rays, the decay of the radiotracers used with PET scans produce small particles called positrons. A positron is a particle with roughly the same mass as an electron but oppositely charged.
Why is CT used with SPECT?
CT images are superimposed or fused with the SPECT images, enabling precise anatomical localisation of radiopharmaceutical uptake. The CT also enables correction for potential artefact that results from attenuation of emitted gamma rays by the patient's body tissues before being detected on the rotating gamma camera.
What are the disadvantages of a SPECT scan?
However, SPECT has issues, including long scan times and low-resolution images prone to artifacts and attenuation. Some artifacts can easily be misidentified as perfusion defects. SPECT also does not provide a quantifiable estimate of the blood flow, whereas PET does, experts say.
What is a SPECT scan used to diagnose?
SPECT scanning can detect altered blood flow in the brain and help diagnose or evaluate certain vascular brain disorders, such as moyamoya disease, a condition in which the arteries in the brain become blocked or narrowed.
Which is better a PET scan or a SPECT scan?
PET Scan Images are Clearer PET scan images are generally reported to offer a higher resolution of 5 to 7 mm, compared with a cardiac SPECT scan resolution of 12 to 15 mm. With a higher resolution, radiologists can detect changes to the heart's blood flow at a granular level.
Which one is better SPECT or PET?
For basic research, PET is the more flexible tool, because innovative tracers are more easily synthesised for PET than for SPECT. In addition, the spatial resolution of PET is better than that of SPECT - far better. This is due to the physical nature of nuclear decay of positrons.
How accurate is a SPECT scan?
Sensitivity was 86%; specificity, 73% and the positive predictive value was 92%, with an accuracy of 83%. The authors concluded that SPECT assists in the early and late diagnoses of AD and in the differential-diagnosis of the dementias when there is a complicated or confusing clinical picture.
Does a SPECT scan use radiation?
Importantly, the SPECT scan requires no additional injection of radiopharmaceutical beyond what you would have been given for a standard nuclear medicine scan without SPECT. The CT is usually carried out using a low-dose radiation technique, which is approximately 20–25% the radiation exposure of a normal CT scan.
Is a SPECT CT the same as a bone scan?
A bone scan is performed using a special scanner, called a gamma camera, that detects gamma radiation to create a planar image of the bones and other tissues. If an area needs further study, a SPECT scan is performed using a gamma camera that rotates around the body.
How much radiation is in a SPECT scan?
Conclusion: Total patient exposure from clinical SPECT/CT is 7mSv on average. Individual dose levels vary with the clinical indication and on-site protocol parameters.
Why is PET resolution better than SPECT?
For basic research, PET is the more flexible tool, because innovative tracers are more easily synthesised for PET than for SPECT. In addition, the spatial resolution of PET is better than that of SPECT - far better. This is due to the physical nature of nuclear decay of positrons.
Is a SPECT CT the same as a bone scan?
A bone scan is performed using a special scanner, called a gamma camera, that detects gamma radiation to create a planar image of the bones and other tissues. If an area needs further study, a SPECT scan is performed using a gamma camera that rotates around the body.
Are Spect scans accurate?
In addition, brain SPECT imaging showed the ability to distinguish depression or dementia in people with both with 83% accuracy. Story Source: Materials provided by IOS Press. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
What is the difference between gamma camera and SPECT?
SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) is a diagnostic imaging technique used in nuclear medicine which studies PHYSIOLOGICAL (FUNCTIONAL) processes in the body. Gamma cameras are used to construct an image of the distribution of radiopharmaceuticals spread out in the body of a patient.
SPECT CT Scans - How It Works & What SPECT CT Identifies - Pain Management
For the latest availability please call 020 7060 5109 or fill out the form below. Please note that there may be a 1-2 week appointment lead time.
What is SPECT CT?
SPECT-CT cameras have the advantage that all conventional nuclear medicine imaging can be performed with them, and when required, integrated anatomic and functional imaging can be done without the need for patient repositioning or rescanning elsewhere. No postprocessing is needed for image coregistration with such a system. Additionally or alternatively, when required, the CT data can be used for attenuation correction to improve SPECT image quality ( 3, 4, 5 ).
What is the most relevant application of SPECT?
Clinically, the most relevant application of SPECT is myocardial perfusion imaging. There, SPECT-CT transmission measurements help to eliminate attenuation artifacts in the posterior cardiac wall.
What is quality control in CT?
Quality control consists of daily, weekly, and trimonthly tests. On a daily basis, we always reset the gantry parameters and test the pressure-sensitive detector control for patient safety. Daily quality control for the CT simply involves performing a blank scan. A pulse height analysis acquisition, energy peak position, and energy resolution for the gamma camera are obtained by acquiring data from an extrinsic flood source and applying energy, linearity, and sensitivity corrections. The flood uniformity is calculated by using National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standards. A sealed cobalt 57 ( 57 Co) source is preferred to a 99m Tc flood source because it is easier to handle and avoids possible contamination. This quality control test confirms the stability of the system performance characteristics.
Can a stand alone CT scan be used for bone scans?
Instead of using an in-line SPECT-CT, a stand-alone CT system can be used , and images can be fused with dedicated computer software without difficulty, especially in bone scans. Overall, the use of SPECT-CT has significantly reduced the uncertainty of the location of radiotracer uptake in patients.
Is SPECT CT cheaper than PET?
As a result, it may be much less attractive financially to own a SPECT-CT system with a high-end CT, as the expensive CT idles much of the time when the combined system is used for an examination, and billable examination costs for SPECT-CT are typically lower than for PET-CT.
What is a SPECT-CT Scan?
A SPECT-CT scan is a type of nuclear medicine scan where the images or pictures from two different types of scans are combined together. The combined scan can provide precise information about how different parts of the body are working and more clearly identify problems.
Where is a SPECT CT done?
A SPECT-CT scan is done at a nuclear medicine facility with a dedicated SPECT-CT machine. Many large public and private hospitals, as well as some private radiology practices, now have SPECT-CT scanners.
What are the benefits of a SPECT-CT scan?
The similarity between SPECT and CT in the method of processing the images allows the images to be merged and the information to be combined. Combining the information from a nuclear medicine SPECT scan and a CT scan allows information about body ‘function’ from the nuclear medicine scan to be easily combined with the information about where and how the body structure ‘looks’ in the CT scan.
Why would my doctor refer me to have this scan?
Common reasons include joint or bone pain, fracture and arthritis assessment, blood flow to the heart, and blood flow to the lungs.
What happens during a SPECT-CT scan?
After verifying your details and the reason for the scan, the nuclear medicine technologist will insert an intravenous (IV) cannula (a thin tube) into a vein , usually in your hand or arm. The radiopharmaceutical is injected into your blood stream through the IV cannula. You will then be required to lie on a bed while detectors or cameras obtain the scan images.
When can I expect the results of my SPECT-CT scan?
This is usually done in a few days or a week from the time of your scan. The report is then sent to your doctor who referred you for the scan. The time it takes your doctor to receive a written report on the scan will vary depending on:
What is SPECT imaging?
SPECT images are taken after an injection of a nuclear medicine radiopharmaceutical (see InsideRadiology: Nuclear Medicine). The injected medication ‘sticks’ to specific areas in the body, depending on what radiopharmaceutical is used and the type of scan being carried out. For example, it can show bone in a bone scan, and gall bladder and bile ducts in a hepatobiliary scan.
Why is a CT scan used for SPECT?
There are numerous indications where a SPECT CT scan can be useful in providing an accurate diagnosis, as it essentially enables a detailed analysis of internal organs, bone structures and tissue.
What is a SPECT scan?
A SPECT scan (single-photon emission computed tomography) is the technique of using nuclear medicine tomographic imaging techniques with gamma rays to provide detailed 3D images of the body.
What is a sacroiliac joint test?
It is an especially sensitive test of intervertebral disc, facet joint and sacro-iliac joint inflammation, illustrating precisely the areas of spinal inflammation. Invaluable information when deciding on the best possible plan of treatment for the patient.
Is a spinal scan expensive?
As this is an expensive scan, it is not often available in the public environment owing to modern day funding issues; however, these scans are invaluable for precise diagnosis and subsequent treatment of spinal pain.
Is SPECT CT used in the UK?
SPECT CT scanning is rarely used in practice in the UK, in the investigation of spinal pain . It is however, used in many other countries, and perhaps the helpfulness of these scans will become recognised here in the near future. Due to the highly detailed information provided, these scans help eliminate the guesswork out of diagnosing inflammatory causes of spinal pain.
What is hybrid spect/CT?
Hybrid SPECT/CT combines the 3-dimensional functional information of SPECT with the anatomic information of CT, thereby improving preoperative localization. Early SPECT/CT in combination with any delayed imaging method (SPECT/CT, SPECT, or planar imaging) was statistically superior to dual-phase planar imaging or dual-phase SPECT. For all 3 methodologies (planar imaging, SPECT, and SPECT/CT), dual-phase imaging was superior to single-phase imaging. These findings strongly suggest that dual-phase imaging, with early SPECT/CT whenever possible, should be part of the routine preoperative evaluation of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism in this new age of minimally invasive parathyroidectomy.
What is the advantage of spectroscopic tracheoesophageal tracheo answer?
A major advantage of SPECT/CT seems to be its ability to differentiate inferior from inferior-posterior glands (superior glands in the tracheoesophageal groove). The statistical advantage of SPECT/CT was not evident when analysis was done with the inferior and inferior-posterior locations combined.
Is early SPECT/CT better than dual phase planar imaging?
In our investigation, early SPECT/CT alone was not significantly better than dual-phase planar imaging for parathyroid adenoma localization. However, dual-phase SPECT/CT was statistically significantly superior to single-phase SPECT/CT and superior to dual-phase planar imaging and dual-phase SPECT. Early SPECT/CT in combination with delayed SPECT or delayed planar imaging was also statistically superior to dual-phase planar imaging or SPECT.
Is SPECT a single time interval?
SPECT is often acquired at a single time interval, either early or delayed. With early SPECT, one investigational group has reported a high sensitivity (96%) ( 22, 24 ). Using delayed SPECT, one large study reported good sensitivity (87%) ( 25 ). However, another report found poorer results (78%) ( 19 ). Only one prior investigation directly compared early and delayed SPECT ( 26 ); these authors found that early SPECT had higher sensitivity (91%) than delayed SPECT (74%), although no statistically significant difference was reported. Our data showed a trend toward superior sensitivity and AUC for parathyroid adenoma localization for early SPECT than for delayed SPECT; however, this trend did not reach statistical significance. Dual-phase SPECT was statistically significantly superior to single-phase SPECT.
Does SPECT help detect parathyroids?
Several investigations have reported improved sensitivity for the detection and localization of hyperfunctioning parathyroids with SPECT, compared with planar imaging ( 21 – 24 ), although 2 studies did not find SPECT superior to planar imaging ( 19, 20 ). Most studies have acquired only a single set of SPECT images, either early or delayed ( 19, 22, 24, 25 ); 2 studies performed dual-phase SPECT ( 26, 27 ). The addition of anatomic imaging with CT software fusion ( 28) or hybrid SPECT/CT ( 29, 30) has the potential to improve preoperative localization. Investigations using hybrid imaging have been few, with limited numbers of patients studied and mixed results.
Is parathyroid scintigraphy better than planar?
For various radiopharmaceuticals and different types of scintigraphic studies, the superior contrast resolution of SPECT, compared with that of planar imaging, has often translated into increased lesion detectability. For parathyroid scintigraphy, several studies have reported higher sensitivity for SPECT than for planar imaging—from 11% to 18% higher—although no study has reported a statistically significant difference ( 21 – 24 ). Two studies reported no advantage for SPECT over planar imaging ( 19, 20 ). Although our data showed a trend toward higher sensitivity, AUC, and PPV for SPECT than for planar imaging, the difference was not statistically significant.
What is bone scan?
A bone scan involves injecting a small amount of a radioactive substance that attaches to the bones. Images are then taken in what is called a "planar" format. For a bone scan with SPECT/CT imaging, a "SPECT" scan is combined with a "CT" scan to help localize an area of abnormal activity that may be present on the planar bone scan image.
Can you breathe during CT scan?
During imaging, please hold as still as you can. You may breathe normally, but other movements can blur the images and make them more difficult to interpret. Please let your technologist know if you are not comfortably positioned on the bed. Any necessary SPECT/CT imaging will be performed towards the end of this appointment.
What are the two types of cardiac imaging?
Cardiac imaging modalities can be divided into 2 broad groups, though some overlap does exist (Figure 1). Modalities such as CTA and CMR angiography provide primarily anatomical data, allowing for the assessment of coronary stenosis. Alternatively, functional imaging modalities such as SPECT, PET, CMR, and stress ECHO provide measures of ischemia. The distinction between anatomical and functional imaging modalities is important because anatomical stenosis does not reliably predict ischemia or hemodynamic significance. Thus, the choice between anatomical and functional modalities potentially depends on the clinical question at hand.
Why is it important to distinguish between functional and anatomical imaging?
The distinction between anatomical and functional imaging modalities is important because anatomical stenosis does not reliably predict ischemia or hemodynamic significance. Thus, the choice between anatomical and functional modalities potentially depends on the clinical question at hand.
Is stress echo a symptomatic test?
Stress ECHO is appropriate for symptomatic patients with an intermediate pretest probability of CAD and contraindication to regular treadmill stress testing. 36 Using stress ECHO, myocardial ischemia is characterized as a worsening or new wall motion abnormality. Specific diagnostic criteria for severe CAD can be identified by stress ECHO (Table 2).
Can MPI be used with SPECT?
MPI with SPECT is a commonly available test. Though exercise is the stressor of choice, vasodilator stress is indicated in patients with left bundle branch block (LBBB), for those who cannot exercise, and those who cannot achieve their target heart rate. 9,10 Vasodilators, such as adenosine and dipyridamole, can exacerbate bronchospasm; therefore, ...
Is CTA a secondary role in functional imaging?
In patients with a high pretest probability of, or already-documented, CAD, noninvasive anatomical imaging with CTA, or CMR angiography (MRA ) may play a secondary role to functional imaging. More important to patient care is the understanding of a patient’s prognosis, which will provide pertinent information needed to guide therapy and determine the need for invasive angiography and revascularization. Patients deemed to be at high pretest probability of having CAD may be risk stratified by SPECT, PET, stress ECHO or CMR.
What doctor will analyze a SPECT scan?
A radiologist or doctor with advanced training in nuclear medicine will analyze the results of your SPECT scan and send them to your doctor. Pictures from your scan may show colors that tell your doctor what areas of your body absorbed more of the radioactive tracer and which areas absorbed less.
How long does it take for radioactive tracer to leave your body?
Most of the radioactive tracer leaves your body through your urine within a few hours after your SPECT scan. Your doctor may instruct you to drink more fluids, such as juice or water, after your SPECT scan to help flush the tracer from your body. Your body breaks down the remaining tracer over the next few days.
What is a SPECT scan?
A SPECT scan is a type of nuclear imaging test, which means it uses a radioactive substance and a special camera to create 3-D pictures.
What is a spectrometer?
The SPECT machine is a large circular device containing a camera that detects the radioactive tracer your body absorbs. During your scan, you lie on a table while the SPECT machine rotates around you. The SPECT machine takes pictures of your internal organs and other structures. The pictures are sent to a computer that uses the information to create 3-D images of your body.
How long do you have to lie in a room before a radioactive tracer scan?
The tracer dose is very small. You may feel a cold sensation as it enters your body. You may be asked to lie quietly in a room for 20 minutes or more before your scan while your body absorbs the radioactive tracer.
What happens to the body when you have a seizure?
For instance, during a seizure, the area of your brain causing the seizure may retain more of the radioactive tracer, which allows doctors to pinpoint the area of your brain causing your seizures.
What happens if the arteries that feed the heart muscle become narrowed or clogged?
If the arteries that feed the heart muscle become narrowed or clogged, the portions of the heart muscle served by these arteries can become damaged or even die. Reduced pumping efficiency. SPECT can show how completely your heart chambers empty during contractions.
What is the difference between PET and SPECT?
Injected activity: The short half-life of some PET radiotracers allows injection of higher activity leading to increased detection sensitivity on a scan while in SPECT, particles tend to release less energy than PET so radiation dose exposure (dosimetry) tends to be more acceptable.
Which is better, PET or SPECT?
PET affords higher image quality, contrast and spatial resolution compared to SPECT and has higher sensitivity (100-1000 times higher than SPECT) in addition to being a more quantitative imaging method than SPECT. However, SPECT scanners are more widely available that PET scanners and the technology is more affordable that PET.
Why is PET shorter than SPECT?
Imaging timeframe: Because of the differences in isotope half-life, PET is associated with a shorter scanning time than SPECT allowing imaging multiple areas of the body and rapid monitoring of biological processes over short periods of time (for example uptake of metabolites into tissues).
What is the technique used to detect radioactive substances?
These techniques use radioactive substances called radioisotopes (in very small amounts) attached to biological molecules which are injected into the patient and the signal produced from the isotope once it is on the body is tracked (visualized) when a patient is scanned. The information can be analyzed in a visual and in a quantitative manner to determine where the tracer goes and how much of it accumulates in different areas of the body before clearing away from the circulation. The imaging of molecules with this approach is also referred to as molecular imaging.
Which organs give high signals on a FDG PET scan?
The brain is an organ that uses high amounts of glucose and will also give high signal on an FDG-PET scan. 99mTc-tetrofosmin (MyoviewTM) SPECT: This uses small amounts of a drug that is attached to a radioactive technetium tracer ( 99m Tc) which is rapidly taken up by the heart and patients are scanned under conditions of stress (exercise) and rest.
Can SPECT imaging be performed with different tracers?
Energy levels and multi-isotope imaging: While in PET all radioisotopes have the same energy level so it is difficult to carry out simultaneous imaging of different tracers (though methods are being developed), SPECT isotopes have different energy levels so could permit simultaneous imaging of different processes.
How effective is a CT scan?
With a CT scan, we can create an image of almost the entire body, from the neck to the thighs , in a few seconds. CTs are incredibly useful for diagnosing and staging cancer, checking whether it has come back, and monitoring whether a treatment is working. It’s very effective for surveying the entire body to look for places where the cancer has spread , such as the lungs, liver, or bone. These are called metastases. Most of the time, CT is the first choice to stage cancer.
What is the difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed pictures of organs , bones, and other tissues. The person lies on a table that moves through a scanning ring, which looks like a large doughnut. The data collected can be assembled to form three-dimensional images. The images reveal abnormalities in both bone and soft tissues, such as pneumonia in the lungs, tumors in different organs, or bone fractures.
How do doctors decide which imaging a person should receive?
We usually use CT first for most people, unless a tumor is much better seen on MRI. But we go back and forth as needed. If we see something on a CT scan we’re unsure about, we may recommend an MRI for further evaluation. If someone has several MRIs and is unable to lie still or hold their breath so we can get a good image, we may suggest a CT as an alternative. We’re guided by the principle of whether the benefits of a test outweigh its risks. That’s what medical imaging is about.
What are some disadvantages of each imaging method?
Because CTs use ionizing radiation, they could damage DNA and may very slightly raise the risk of developing cancer. The Food & Drug Administration estimates that the extra risk of any one person developing a fatal cancer from a typical CT procedure is about 1 in 2,000. MRIs do not use ionizing radiation, so there is no issue of raising cancer risk. But they take much longer to complete than CTs. MRIs require the person to lie still within a closed space for about 20 to 40 minutes. This can affect some people with claustrophobia, and the procedure is noisy, which is why we provide ear protection.
What imaging method is used to detect cancer?
Radiologists use both CT and MRI to detect and monitor cancer. Each imaging method has strengths that make it appropriate for a particular reason. Learn how doctors choose which technique to use.
Why do we need contrast dye for MRI?
This helps the radiologist see organs and other tissues within the body more clearly .
What imaging tests do doctors use?
Our doctors use advanced imaging tests, such as CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans, to help detect and diagnose disease, make appropriate treatment recommendations, and monitor your response to therapy.
How does a spectro-CT scan work?
How a SPECT/CT Scan Works. A SPECT/CT scan typically involves 3 main components: A radioactive tracer is injected into the body’s bloodstream. This tracer can be seen by a gamma scanner, which shows metabolic functions of tissues and organs, such as blood flow and potential abnormalities in the tissues.
Why do we need a SPECT scan?
A SPECT/CT scan may be particularly useful when trying to get a look at a metabolic abnormality, as well as its location in relation to the bone. For example, SPECT/CT may show that an abnormality suspected of causing back pain is actually located in the facet joint rather than the vertebral body or another part of the spine.
What is a single photon emission computed tomography?
Single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) combines two different diagnostic scans into one for a more complete view of the body region being studied. The SPECT scan uses nuclear medicine to give good images of metabolic abnormalities, whereas the CT scan may be able to help narrow down specifically where the problem is occurring, such as in the bone or nearby tissue.
Is a SPECT/CT scan safe?
While SPECT/CT is considered relatively safe, this combined scan tends to use more radiation than other scans. Women who are pregnant are not recommended to have a SPECT/CT scan due to the risks associated with radiation exposure.
Can a CT scan and a SPECT scan be combined?
Since the SPECT and CT scans both form cross-section images of the same areas, the computer is able to combine these images. The resulting cross-section images show the x-ray images of the bones overlaid with the nuclear imaging.

Significance
- SPECT-CT is where two different types of scans are taken and the images or pictures from each are fused or merged together. The fused scan can provide more precise information about how different parts of the body function and more clearly identify problems such as tumours (lumps) or Alzheimers disease, etc.
Analysis
- Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT): SPECT images are obtained following an injection of a radiopharmaceutical that is used for nuclear medicine scans. The injected medication sticks to specific areas in the body, depending on what radiopharmaceutical is used and the type of scan being performed, for example. it will show bone for a bone scan, and gall bl…
Applications
- The similarity between SPECT and CT in the method of image processing allows the images to be combined. Combining the information from a nuclear medicine SPECT study and a CT study allows the information about function from the nuclear medicine study to be easily combined with the information about how the body structure looks in the CT study.
Preparation
- No extra preparation is required for being imaged on a SPECT-CT machine, as this is usually done at the same time you are having other types of scans that use a nuclear medicine gamma camera. Women who are breastfeeding and people who are the primary or sole carer for small children may need to make special preparations for after the test, to stop breastfeeding for a short time, …
Diagnosis
- It is important that you let staff at the hospital or radiology practice where you are having the scan done know if you are (or think you could be) pregnant or are breast feeding.
Contraindications
- This study may not be suitable for pregnant women because of the radiation dose to the growing foetus. Please discuss this with your doctor.
Results
- It takes 30-40 minutes to obtain the SPECT and CT images, then you are allowed to leave. After you have left the hospital department or radiology practice a nuclear medicine technologist will process the images and accurately fuse (merge) the SPECT and CT images. It is important that you discuss the results with your doctor, either in person or on the telephone, so that they can ex…
Risks
- There are no risks involved in the nuclear medicine SPECT scan or the CT scan procedures. The test involves a small dose of ionising radiation from the radiopharmaceutical injected into your vein, and also from the CT scan. (See radiation risk of medical imaging for adults and children) Your doctor has weighed up the benefit versus risk for having a SPECT-CT scan and has decide…
Benefits
- SPECT-CT provides the ability to merge or combine the images often allowing the nuclear medicine specialist to more accurately pinpoint the site of any abnormality on your nuclear medicine scan. This may be of particular importance in certain clinical situations, when the interpretation of an area of interest may change depending on its location. For example, in smal…
Participants
- Please feel free to ask the private practice, clinic, or hospital when the written report will be provided to your doctor.