What is the difference between electricity and magnetism?
Electricity is due to the presence and movement of charge carriers. While magnetism is the result of the interaction between moving charges. Electricity is known to be an invisible force, while magnetism is regarded as an outcome of current electricity. Electricity is known to be the result of the movement of charge carriers in conductors.
What is the difference between a static and magnetic field?
The term static refers to a situation where the fields do not vary with time. Static electric and magnetic fields are two distinct phenomena, both characterized by steady direction, flow rate and strength (thus a frequency of 0 Hz). A static electric field (also referred to as electrostatic field) is created by charges that are fixed in space;
What is the meaning of magnetism?
Magnetism is an interaction between moving charges. And materials that can be magnetized to a certain extent by a magnetic field are called magnetic. It is a byproduct of electricity which occurs when electric charges begin to move or change.
What is a static electric field?
The term static refers to a situation where the fields do not vary with time. Static electric and magnetic fields are two distinct phenomena, both characterized by steady direction, flow rate and strength (thus a frequency of 0 Hz).
Is static the same as magnetic?
Static and low-frequency electric fields emanate from electric charges. They exert forces on other electric charges. Magnetic fields are caused by moving electric charges. They occur e.g. around current-carrying electric conductors.
What is static electricity and how does it relate to magnetism?
A static electric field (also referred to as electrostatic field) is created by charges that are fixed in space; A static magnetic field is created by a magnet or charges that move as a steady flow (as in appliances using direct current).
Are electricity and magnetism the same thing?
3) Electricity and magnetism are essentially two aspects of the same thing, because a changing electric field creates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field creates an electric field. (This is why physicists usually refer to "electromagnetism" or "electromagnetic" forces together, rather than separately.)
Is static electricity a magnetic force?
Static magnetic fields are created by magnets or charges that move at a steady flow (current), such as in direct current (DC) electricity. They exert an attracting force on metallic objects, and so magnets are commonly used for this purpose.
What are the 4 types of static electricity?
If one object loses electrons, another object must pick them up. There are four methods by which charges can redistribute themselves to build up static electricity: by friction, by conduction, by induction, and by polarization.
How do you explain static electricity?
Static electricity is the result of an imbalance between negative and positive charges in an object. These charges can build up on the surface of an object until they find a way to be released or discharged. One way to discharge them is through a circuit.
Can you turn magnetism into electricity?
Magnetic fields can be used to make electricity Moving a magnet around a coil of wire, or moving a coil of wire around a magnet, pushes the electrons in the wire and creates an electrical current. Electricity generators essentially convert kinetic energy (the energy of motion) into electrical energy.
What is electricity and magnetism in simple words?
Electricity and magnetism are two related phenomena produced by the electromagnetic force. Together, they form electromagnetism. A moving electric charge generates a magnetic field. A magnetic field induces electric charge movement, producing an electric current.
Does magnetism come from electricity?
Magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric charges. Every substance is made up of tiny units called atoms. Each atom has electrons, particles that carry electric charges.
Is static magnetic field?
Static magnetic fields are constant fields, which do not change in intensity or direction over time, in contrast to low and high frequency alternating fields. Hence, they have a frequency of 0 Hz.
What type of force is static electricity?
non-contact forcesElectrostatic forces are non-contact forces; they pull or push on objects without touching them. Rubbing some materials together can result in something called 'charge' being moved from one surface to the other.
What objects can produce static electricity?
Materials that tend to gain or lose electrons include wool, human hair, dry skin, silk, nylon, tissue paper, plastic wrap and polyester—and when testing these materials you should have found that they moved the aluminum ball similarly to how the Styrofoam plate did.
How are electricity and magnetism related?
Electricity and magnetism are closely related. Flowing electrons produce a magnetic field, and spinning magnets cause an electric current to flow. Electromagnetism is the interaction of these two important forces.
Does static electricity affect magnetic field?
A charge which is moving is created a field of magnetic, but a static charge could not originate a field which is magnetic the reason behind of it, the stationary charges is not able to affect the magnet. The magnetic field and electric field both are characterized by steady direction, flow rate and strength.
What is static electricity explain with example?
Static electricity is a familiar electric phenomenon in which charged particles are transferred from one body to another. For example, if two objects are rubbed together, especially if the objects are insulators and the surrounding air is dry, the objects acquire equal and opposite charges…
How do magnets and electricity work together?
Magnetic fields can be used to make electricity Moving magnetic fields pull and push electrons. Metals such as copper and aluminum have electrons that are loosely held. Moving a magnet around a coil of wire, or moving a coil of wire around a magnet, pushes the electrons in the wire and creates an electrical current.
What is the force of nature that is responsible for magnetic forces and magnetic fields?
Magnetism is the force of the nature that is responsible for magnetic forces and magnetic fields. In this article, we are going to discuss what electricity and magnetism are, the definitions of electricity and magnetism , the relationship between electricity and magnetism , and finally the difference between electricity and magnetism .
What are the forces that create magnetic fields?
Magnetism, along with electricity created electromagnetism which is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Magnetic dipoles create magnetic fields. Similar magnetic poles oppose each other whereas dissimilar magnetic poles attract each other.
What are the two topics discussed in physics?
Electricity and magnetism are two very important topics discussed under physics. The concepts of electricity and magnetism are vital in many fields apart from physics, as well. Electricity is the force of the nature that is responsible for electric currents and electric fields. Magnetism is the force of the nature that is responsible for magnetic forces and magnetic fields. In this article, we are going to discuss what electricity and magnetism are, the definitions of electricity and magnetism, the relationship between electricity and magnetism, and finally the difference between electricity and magnetism.
How is an electric field produced?
An electric field is said to be produced by all electric charges whether they are moving or stationary. An electric field can also be produced using any time varying magnetic fields. There are several important factors of electric fields.
What is the force that occurs due to electric charges?
Electricity. Electricity is a fundamental force in the nature when it is combined with magnetism. Electricity can be defined as the phenomenon that occurs due to electric charges. This is rather an intuitive idea and cannot be defined properly. Electric forces are the forces that occur due to electric charges.
Is an electric charge positive or negative?
They are positive and negative. An electric charge is described by the electric field associated with it. The electric field and the electric charge are like the “chicken and egg” problem. One is required to describe the other.
Is magnetism a duality?
The magnetism also has a duality. The magnetic poles created by moving electric charges are termed as north poles and south poles. Magnetic poles always occur in pairs. There are no magnetic monopoles. Magnetism, along with electricity created electromagnetism which is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
What is the relationship between magnetism and electricity?
The fact is magnetism and electricity, and the relationship between the two is fundamental to how the modern world works and how are we totally dependent on them for almost everything. These invisible force fields are almost impossible to describe adequately in verbal terms. Physics describes these two terms in two related ways.
What is Magnetism?
Magnetism is a physical phenomenon, a byproduct of electricity which is produced when electric charges begin to move which results in attraction and repulsion between objects. Consider a magnet that attaches to a refrigerator door due to the magnetic properties of the door and the magnetism of the magnet. The magnet’s ability to attract ferrous objects from a distance has captivated countless curious minds over two millennia. It is magnetism that makes magnets stick to other magnets or metals, such as iron. Materials that stick to magnets are called magnetic. However, the force of magnetism doesn’t work on all metals. For example, magnets do not work with copper and aluminum because they are not magnetic.
Why are magnets and electricity like two sides of the same coin?
Magnetism and electricity are like two sides of the same coin, because a changing magnetic field creates electric field and vice-versa. Take a magnet, for example, and move it around you and all of a sudden you surround yourself with an electric field. Both are invisible forces that coexist and we use these forces almost every day.
How are electric and magnetic forces related?
Both can be either attractive or repulsive, but both the forces are intimately related to the property of matter called charge. However, this seeming symmetry is broken by the existence of electric monopoles and the absence of magnetic monopoles. Electric monopoles do exist in the form of particles with positive or negative electric charge, such as protons or electrons. On the contrary, magnetic monopoles do not exist because magnetic charges are produced in opposite pairs making magnetism relatively different than electricity.
What makes a magnet stick to a metal?
It is magnetism that makes magnets stick to other magnets or metals, such as iron. Materials that stick to magnets are called magnetic. However, the force of magnetism doesn’t work on all metals. For example, magnets do not work with copper and aluminum because they are not magnetic.
What is the movement of electrons called?
Electricity . The movement of electrons or electric charge is called electricity. It is more like a phenomenon that occurs due to electric charges. It’s an invisible force that occurs due to the change in electric charges. Electricity is what keeps the lights on or the television running or makes the machines working.
Why do we use electricity?
We use electricity every day to power almost everything we need on a daily basis. But what you don’t realize is when you flip a switch, electricity and magnetism both are involved. And the interaction between them is electromagnetism. This is why physics refers to both the forces together, rather than separately.
What is static electric and magnetic field?
What are static electric and magnetic fields? Electric and magnetic fields are invisible lines of force generated by natural phenomena such as the Earth’s magnetic field or lightning, but also by human activities, mainly through the use of electricity. An electric field is the force field created by the attraction ...
How is a static magnetic field created?
A static electric field (also referred to as electrostatic field) is created by charges that are fixed in space; A static magnetic field is created by a magnet or charges that move as a steady flow (as in appliances using direct current ).
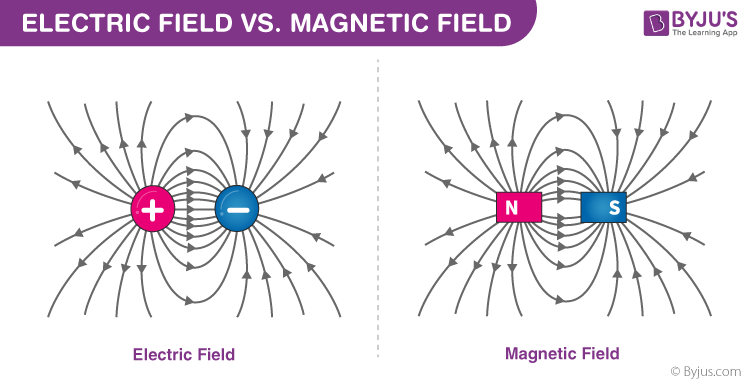
What is the difference between magnetic and electric fields?
An electric field is the force field created by the attraction and repulsion of electric charges (the cause of electric flow), and is measured in volts per meter (V/m). A magnetic field is a force field created by a magnet or as a consequence of the movement of the charges (flow of electricity).
What is static field?
The term static refers to a situation where the fields do not vary with time. Static electric and magnetic fields are two distinct phenomena, both characterized by steady direction, flow rate and strength (thus a frequency of 0 Hz). A static electric field (also referred to as electrostatic field) is created by charges that are fixed in space;
Do magnetic fields weaken with distance?
Both electric and magnetic fields weaken with distance from the source. More...
Do microwaves have electromagnetic fields?
In contrast, time-varying electromagnetic fields, which reverse their direction at a regular frequency, are produced by appliances using alternating current ( AC) as well as by cellular telephone antennas, microwaves, etc. In this case, the electric and magnetic fields are interrelated and are both associated with a specific frequency.
What is the difference between electricity and magnetism?
The difference between electricity and magnetism is electricity is that magnetism is generated when there is an interaction between the two moving charges, Where the like poles repel each other but the, unlike poles, attract each other. Phenomena between electricity and magnetism led to the discovery of electromagnetism.
How is static electricity formed?
There are two kinds of charges static electricity and current electricity.Static electricity is formed by rubbing two objects simultaneously at a very high pace to generate a small amount of electricity. Static electricity can even be produced with insulators. For example, rubber, current electricity is electricity that is mainly used in every aspect. It is defined as the charged particles’ free flow movement, which can only be passed through conductors. There are two types of currents, AC and DC.
What is Magnetism?
Magnetism is defined as a phenomenon that is the interaction between two different moving charges in which the poles either attract or repel each other. The, unlike poles, always attract each other, which is North and South, and the like poles always repel each other that is north and North or South and South.
What is the relationship between two moving charges that attract or repel each other?
Magnetism is defined as a phenomenon that is the interaction between two different moving charges in which the poles either attract or repel each other. The, unlike poles, always attract each other, which is North and South, and the like poles always repel each other that is north and North or South and South.
How is a magnetic field formed?
The magnetic field is formed when electricity is passed through an object, which creates a magnetic field around it, and items can be magnetized in the area. The magnetic field is not an invisible force; unlike electricity, it can be check using a compass or a magnetic needle that shows deflection when placed in a magnetic field.
What is the purpose of a magnet?
A magnet is a dipolar system because of two poles; the magnet is used in many objects, from computer parts to store data to the electromagnet. An electromagnet is a magnet category in which the magnetic field around the object is created using electricity. It consists of a copper coil. When current is passed through, it acts as a magnet that starts to attract magnetic pieces towards it; its intensity can be controlled using the current more the magnetic attraction; if the current is reduced, the magnetic field will reduce. An electromagnet is used in much modern industry to pick and drop heavy external objects. William Gilbert was the first person to coin the term magnetism.
Can electricity exist without magnetic field?
Electricity can also exist independently without any magnetic charge. In contrast, the flow of current electricity is required to form the magnetic field for creating a continuous path of charges.
