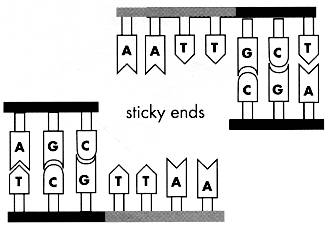
Sticky ends have unpaired bases at the end of the fragments. Blunt ends are created due to a straight cleavage and they have base pairs at the ends. Sticky end ligation
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding.
What are blunt ends and sticky ends in DNA?
Blunt Ends : A straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA. Sticky Ends : Staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs.
Why are sticky ends more advantageous than blunt ends in engineering?
Sticky ends are more advantageous than blunt ends in genetic engineering. When a restriction enzyme cuts the DNA into blunt ends there are no strands on either side of the cut.
What is the difference between blunt ends and cohesive ends?
P. from Chennai Blunt ends may result from the breaking of double-stranded DNA; however, there are no overhangs or unpaired bases. Longer overhangs are called cohesive ends or sticky ends. They are most often created by restriction endonucleases when they cut DNA.
What is a blunt end?
Blunt ends have no overhang. They cannot match up as specifically as DNA with sticky ends; however, they can be useful when sticky ends can't be used. SmaI is a restriction enzyme that makes blunt ends. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.

How are sticky ends different from blunt ends?
In sticky ends, one strand is longer than the other (typically by at least a few nucleotides), such that the longer strand has bases which are left unpaired. In blunt ends, both strands are of equal length – i.e. they end at the same base position, leaving no unpaired bases on either strand.
What is the difference between blunt ends and sticky ends quizlet?
Sticky ends have a jagged cut that expose bases that will bond again with DNA. This allows for inserting DNA into another organism. DNA fingerprinting- Enzymes are used to cut using blunt ends so they don't recombine ans stay in fragments and they can be separated by size using gel electrophoresis.
What's the difference between a sticky end and a blunt end after the restriction enzyme cuts?
Sticky ends are cuts of DNA that have DNA fragments on either side of the cut made by the restriction enzyme. Sticky ends are easier to combine with other DNA. Blunt ends cut DNA symmetrically. When blunt ends are produced there is no overhang on either side of the cut.
How are sticky and blunt ends formed?
Posted November 2, 2020. Sticky ends and blunt ends refer to two types of ends found in DNA strands. Both types of ends are generated when the restriction enzyme cuts the DNA strand. Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences.
What are blunt ends used for?
Ligation refers to the joining or ligating of two nucleic acid fragments through the action of an enzyme. The attaching of blunt-ended DNA fragments by the enzyme DNA ligase is known as blunt end ligation. This is a crucial laboratory procedure used in the molecular cloning of DNA.
What do blunt ends do?
The sticky or blunt ends refer to the properties of the end of DNA molecules, which are commonly generated by restriction enzymes that cut the DNA. A straight cut of restriction enzymes generates blunt ends, where both strands terminate in a base pair.
What is the difference between sticky and and blunt and?
Sticky ends have single strand overhangs, blunt ends do not have single strand overhangs, it terminates in a base pair.
What is the meaning of blunt end?
Definition. (general) The end part (of a body, of a leaf, of a petal, etc.) that has a dull or rounded edge. (molecular biology) The end of a DNA fragment resulting from the breaking of DNA molecule in which there are no unpaired bases, hence, both strands are of the same length.
Why sticky end ligation is more efficient than blunt end?
Sticky end cutters produce sticky or cohesive ends. It does not require matching fragments or complementary bases. It requires complementary bases at the ends to form base pairs. It is more efficient than blunt end ligation.
What does a sticky-end mean?
an unpleasant finish or deathsticky end. noun. informal an unpleasant finish or death (esp in the phrase come to or meet a sticky end)
What are sticky ends definition?
After digestion of a DNA with certain Restriction enzymes, the ends left have one strand overhanging the other to form a short (typically 4 nt) single-stranded segment. This overhang will easily re-attach to other ends like it, and are thus known as "Sticky ends".
Which enzyme causes blunt ends?
Blunt ends are produced when the cut of endonuclease is placed in somewhere centre of the sequence. Sticky ends are produced when the cut by the restriction enzymes is made at the terminal sites providing loose bonds.
What are sticky ends quizlet?
Sticky Ends. the uneven ends of a double-stranded DNA molecule that has been cut with a restriction enzyme. Gene Splicing. DNA from one or more organisms is combined to make Recombinant DNA.
Why are blunt ends better used for DNA fingerprinting?
The blunt ends of DNA and plasmids are less likely to find each other, and thus ligation of blunt ends requires that more DNA is put into the test tube.
Why are they called sticky ends?
These are called sticky ends because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
What is the importance of sticky ends in genetic engineering quizlet?
Why are sticky ends important for making recombinant DNA? Sticky ends are important for making recombinant DNA because it allows the foreign gene to match with the plasmid.
What is the difference between sticky ends and blunt ends?
Sticky ends are cuts of DNA that have DNA fragments on either side of the cut made by the restriction enzyme. Sticky ends are easier to combine wit...
Why are they called sticky ends?
They are called sticky ends because sticky ends are pieces of DNA fragments with short strands on each side that are complementary to each other. S...
What produces blunt ends?
When a restriction enzyme cuts the DNA into blunt ends there are no strands on either side of the cut. The double-stranded DNA is cut right through...
What is an example of a sticky end?
An example of a sticky end is the DNA sequence cut by the restriction enzyme EcoRI. The sequence that EcoRI recognizes is GAATTC on one strand. The...
Why are there sticky ends?
Sticky ends get their name because they have overlaps that allow the two ends to base-pair and join together with another DNA strand. Blunt ends have no overlap. {"error":true,"iframe":true}.
Why do scientists use sticky ends?
Using sticky ends helps scientists ensure the DNA sequences they are working with can be joined together easily. They fit together perfectly, like pieces of a puzzle. The restriction enzyme EcoRI makes sticky ends when it cuts DNA. If both sequences are cut with EcoRI, they can be joined together.
What enzymes make sticky ends?
EcoRI is a restriction enzyme that makes sticky ends. Restriction enzymes can also make blunt ends. Blunt ends have no overhang. They cannot match up as specifically as DNA with sticky ends; however, they can be useful when sticky ends can't be used. SmaI is a restriction enzyme that makes blunt ends.
Why do two pieces of DNA have sticky ends?
These sticky ends are helpful for research scientists. If two pieces of DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme, they would both have the same sticky ends with the same overlaps. When these two pieces of DNA are combined, they have complementary sticky ends, meaning they could base-pair together.
Which sequence cuts the G and A?
EcoRI cuts this sequence on both strands between the G and the A. So, each of the two strands of DNA is cut, and looks like this:
Can you line up DNA with sticky ends?
They cannot line up specifically the same way DNA with sticky ends can. However, because there is no base-pairing required, blunt ends are useful when sticky ends can't be lined up perfectly between two pieces of DNA. Lesson Summary. Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences.
Does restriction enzyme overhang DNA?
Instead the restriction enzyme cuts both strands of DNA evenly, so there's no overhang. You can see that both strands are even. These are the blunt ends. Blunt ends aren't as helpful as sticky ends for scientists, because there is no guarantee the strands will line up as desired.
How are sticky ends generated?
Such ends may be generated by restriction enzymes that cut the DNA – a staggered cut generates two sticky ends, while a straight cut generates blunt ends.
Why are blunt ends not always desired in biotechnology?
Blunt ends are not always desired in biotechnology since when using a DNA ligase to join two molecules into one, the yield is significantly lower with blunt ends. When performing subcloning, it also has the disadvantage of potentially inserting the insert DNA in the opposite orientation desired.
What is a long overhang in DNA?
Longer overhangs are called cohesive ends or sticky ends. They are most often created by restriction endonucleases when they cut DNA. Very often they cut the two DNA strands four base pairs from each other, creating a four-base 5' overhang in one molecule and a complementary 5' overhang in the other.
What is the overhang of adenine and thymine?
The product is joined with a linear DNA molecule with a 3' thymine overhang. Since adenine and thymine form a base pair, this facilitates the joining of the two molecules by a ligase, yielding a circular molecule. Here is an example of an A-overhang: Longer overhangs are called cohesive ends or sticky ends.
What is a nonblunt end?
Non-blunt ends are created by various overhangs. An overhang is a stretch of unpaired nucleotides in the end of a DNA molecule. These unpaired nucleotides can be in either strand, creating either 3' or 5' overhangs. These overhangs are in most cases palindromic.
What are the two non-identical ends of DNA?
A single-stranded non-circular DNA molecule has two non-identical ends, the 3' end and the 5' end (usually pronounced "three prime end" and "five prime end"). The numbers refer to the numbering of carbon atoms in the deoxyribose, which is a sugar forming an important part of the backbone of the DNA molecule. In the backbone of DNA the 5' carbon of one deoxyribose is linked to the 3' carbon of another by a phosphodiester bond linkage. The 5' carbon of this deoxyribose is again linked to the 3' carbon of the next, and so forth.
What is the end of DNA?
DNA ends refer to the properties of the end of DNA molecules, which may be sticky or blunt based on the enzyme which cuts the DNA. The restriction enzyme belong to a larger class of enzymes called exonucleases and endonucleases. Exonucleases remove nucleotide from ends whereas endonuclease cuts at specific position within the DNA.
What are sticky ends?
Blunt and sticky ends areresult of restriction endonuclease action on double stranded DNA.Sticky Ends – are staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs. Blunt Ends are a straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA.
What is a blunt end?
Blunt Ends : A straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA.
What is the end of a DNA molecule called?
Sticky Ends : Staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs. The simplest DNA end of a double stranded molecule is called a blunt end. In a blunt-ended molecule both strands terminate in a base pair.
What are some examples of blunt ends?
Here is an example of a small piece of blunt-ended DNA: verhangs and sticky ends . Non-blunt ends are created by various overhangs. An overhang is a stretch of unpaired nucleotides in the end of a DNA molecule. These unpaired nucleotides can be in either strand, creating either 3' or 5' overhangs.
What is a straight cut down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the?
Blunt Ends : A straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA. Sticky Ends : Staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs.
What is the simplest end of DNA?
The simplest DNA end of a double stranded molecule is called a blunt end. In a blunt-ende d molecule both strands terminate in a base pair. Blunt end s are not always desired in biotechnology since when using aDNA ligase to join two molecules into one, the yield is significantly lower with blunt ends. When performing subcloning, it also has the disadvantage of potentially inserting the insert DNA in the opposite orientation desired. On the other hand, blunt end s are always compatible with each other. Here is an example of a small piece of blunt-ende d DNA:
What are the ends of DNA called?
These ends are called cohesive since they are easily joined back together by a ligase. Blunt Ends : A straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA. Sticky Ends : Staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs.