
Differences Between Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
| Types | Systolic blood pressure | Diastolic blood pressure |
| Definition | The pressure exerted when the heartbeats | The pressure exerted on the walls of the ... |
| Normal Range | In infants –95mmHg. In adults– 90-120 mm ... | In infants–65 mm Hg. In adults– 60-80 mm ... |
| Ventricles of the Heart | Ventricles contract | Ventricles are relaxed |
| Reading of Blood Pressure | The systolic pressure is high | The diastolic pressure is low |
Can diastolic pressure ever be higher than systolic?
Blood pressure: The diastolic pressure can not be higher than systolic pressure. Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free! Doctors typically provide answers within 24 hours. Educational text answers on HealthTap are not intended for individual diagnosis, treatment or prescription.
What does it mean If diastolic is higher than systolic?
The AHA guidelines also note that a systolic reading of 120 mm Hg and a diastolic reading of 80 mm Hg indicates a high risk of stroke. These guidelines also say that a systolic reading of 140 mm Hg and a diastolic reading of 90 mm Hg is a sign of a heart attack.
Can systolic blood pressure be higher than diastolic?
Systole, cardiac contraction, adds energy bothe kinetic and pressure to the blood stream and therefor systolic pressure is higher than diastolic unless there is another more powerful pump besides your own heart.
What are the different ways to reduce systolic blood pressure?
Some additional diet guidance includes:
- Focus on eating colorful fruits and vegetables, since their high potassium content can help lower blood pressure.
- Choose whole grains whenever possible, and limit white flours such as those found in white bread and pasta.
- Avoid drinking sweetened drinks like juice and soda, and watch for salt in processed foods and canned items.
Which is the most important diastolic or systolic?
Diastolic blood pressurePurpose of review: Diastolic blood pressure has traditionally been considered the most important component of blood pressure and the primary target of antihypertensive therapy.
Why is diastolic pressure important?
The bottom number is your diastolic blood pressure, it's the lowest level your blood pressure reaches between beats. The top number is more important because it gives a better idea of your risk of having a stroke or heart attack.
What is worse high systolic or diastolic?
Over the years, research has found that both numbers are equally important in monitoring heart health. However, most studies show a greater risk of stroke and heart disease related to higher systolic pressures compared with elevated diastolic pressures.
What time of day is blood pressure highest?
Blood pressure has a daily pattern. Usually, blood pressure starts to rise a few hours before a person wakes up. It continues to rise during the day, peaking in midday. Blood pressure typically drops in the late afternoon and evening.
What happens if diastolic pressure is high?
High diastolic pressure is linked to a higher risk of disease involving the large artery called the aorta that carries blood and oxygen from the heart to distant body parts. People with an elevated diastolic reading are more prone to develop an abdominal aortic aneurysm (ballooning in the lining of the aorta).
What is the effect of high diastolic blood pressure?
Diastolic pressure is the bottom number of a blood pressure reading. IDH occurs if someone has elevated diastolic blood pressure, increasing a person's risk of heart disease and stroke. Smoking, consuming alcohol, obesity, and high blood fat may lead to IDH.
What does it mean when diastolic is high?
A: A high diastolic blood pressure (80 mm Hg or higher) that stays high over time means you have high blood pressure, or hypertension, even when systolic blood pressure is normal. Causes of diastolic high blood pressure include both lifestyle factors and genetics, but the disease is multifactorial.
Which blood pressure number is most important?
For years, systolic blood pressure has been seen as the one that really matters. That's based on studies -- including the famous Framingham Heart Study -- showing that high systolic blood pressure is a stronger predictor of heart disease and stroke.
What Is Systolic Blood Pressure?
During a heartbeat, the heart is pushing blood out into the arteries. Doctors call this "systole," and that's why it's called the systolic blood pressure. It's the pressure during a heartbeat and the highest pressure measured.
What causes systolic hypotension?
Systolic hypotension can occur if the blood volume becomes too low (as with severe dehydration or a major bleeding episode), if the heart muscle becomes too weak to eject the blood normally (a condition known as cardiomyopathy ), or if the blood vessels become too dilated (as in vasovagal syncope ).
What is the peak blood pressure during cardiac contraction?
The peak blood pressure reached during active cardiac contraction is called the systolic blood pressure. A “normal” systolic blood pressure when a person is sitting quietly is 120 mmHg or below. 1 .
Why do doctors measure blood pressure?
Doctors measure blood pressure in these numbers so that there is a standard way of describing the force of the pulsing blood. Both the systolic and diastolic pressures are important.
What happens when the heart beats?
When the heart beats, blood pulses through the arteries to travel throughout the body. It is not the steady stream you might see from a garden hose or water faucet.
What happens if your blood pressure is low?
If this low blood pressure is serious enough, it can cause lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting. If it lasts long enough and it isn't treated, it may cause organs like your kidneys to start shutting down.
What is the term for the time when the heart relaxes?
This period of ventricular relaxation is called “diastole, ” and the blood pressure during diastole is called the diastolic blood pressure.
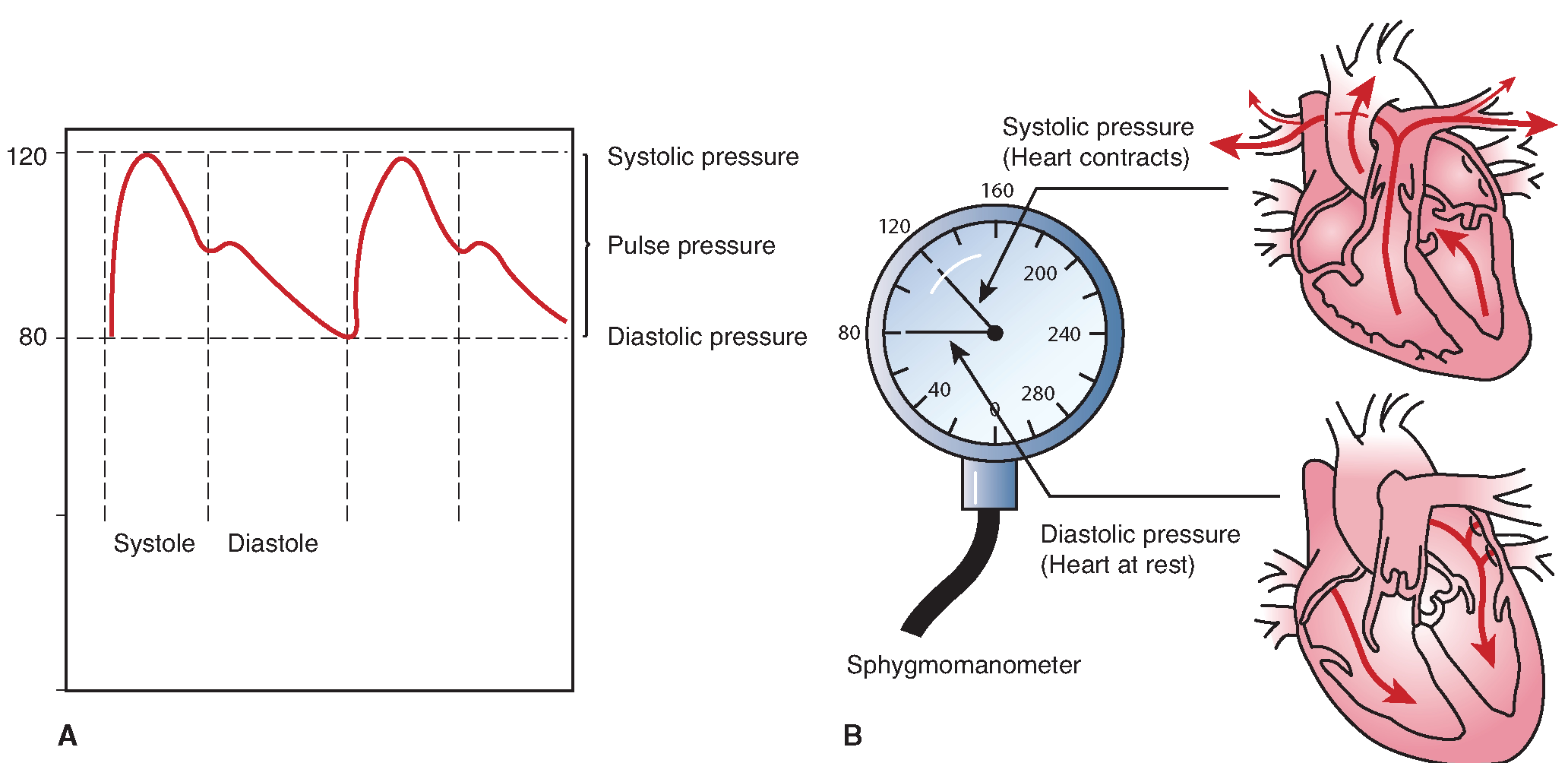
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
Your systolic blood pressure is the top number on your reading. It measures the force of blood against your artery walls while your ventricles — the lower two chambers of your heart — squeeze, pushing blood out to the rest of your body. Your diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number on your reading .
What is the normal systolic level?
Normal: less than 120 systolic and 80 diastolic. Elevated: 120–129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic. Stage 1 hypertension: 130–139 systolic or 80–89 diastolic. Stage 2 hypertension: at least 140 systolic or at least 90 diastolic. Hypertensive crisis: higher than 180 systolic and/or higher than 120 diastolic.
What causes low blood pressure when sitting?
If you’re older than 65, you may be at risk of orthostatic hypotension, a condition in which your blood pressure drops when you move from sitting to standing. Endocrine problems, neurological diseases, heart problems, heart failure, and anemia may also cause the condition.
How to prevent low blood pressure?
Preventing low blood pressure. To help prevent low blood pressure, drink plenty of fluids, preferably water, to prevent dehydration . Stand up slowly from a sitting position to help prevent orthostatic hypotension. Also, notify your doctor right away if you feel a medication is causing your blood pressure to drop.
How does gender affect blood pressure?
Your gender affects your risk of high blood pressure. The American Heart Association states that men are at a higher risk of high blood pressure than women are until age 64. But at 65 years and older, women are at higher risk than men. Your risk is also higher if:
Why is it important to check your blood pressure?
This is an important step because your blood pressure is a measure of how hard your heart’s working.
What is the time when your heart relaxes between beats?
It measures the force of blood against your artery walls as your heart relaxes and the ventricles are allowed to refill with blood. Diastole — this period of time when your heart relaxes between beats — is also the time that your coronary artery is able to supply blood to your heart.
What is the Difference Between Systolic and Diastolic Pressure?
Systolic and diastolic pressure are two measurements that imply the blood pressure of an individual. Systolic pressure is the pressure the blood extends on the arterial walls when the heart muscles contracts and the heart pumps blood into arteries. In contrast, diastolic pressure is the pressure the blood extends on the arterial walls when the heart is relaxing in between heartbeats. So, this is the key difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
What is Systolic Pressure?
Systolic pressure is one of the two values described in blood pressure. It is the pressure blood exerts against the artery walls when the heart beats. Heart muscles contract and the heart pumps blood to the aorta with a force. Then the blood exerts a pressure on the artery wall.
Why is systolic pressure important?
When comparing these two values, systolic pressure is more important since it increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. A healthy individual has 120 mm Hg systolic pressure and 80 mm Hg diastolic pressure. Therefore, we can consider this also as a difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
What is the second value of blood pressure?
Diastolic pressure is the second value indicated in the blood pressure. It is the pressure the blood exerts against the artery walls when the heart is resting or relaxing. Diastolic pressure occurs between heartbeats. At this point, the heart does not actively pump blood into arteries. It is the ventricular relaxation period and the preparation period for the next heart muscle contraction.
What is the meaning of pressure in the heart?
The heart is the organ that acts as a pump to carry out the blood circulation throughout the body. When the heart pumps, the blood will enter the aorta with a force. When the pressurized blood enters the aorta it exerts pressure on its wall, and aorta has an elastic capacity to extend and distend a bit. After that, the heart will be relaxed again and the blood supply to the aorta stops and the valves at the beginning of aorta closes. At this time, the aorta comes back to the normal position from the distended position. Again, this recoiling will exert pressure on the blood.
What is the diastolic pressure of a healthy individual?
Moreover, diastolic pressure of a healthy individual is 80 mm Hg or below.
Do pressures vary depending on activity?
Both pressures vary depending on the individual’s activity.
What is the normal range of systolic blood pressure?
The normal range of systolic blood pressure should be 90 – 120 mm Hg.
What is the blood pressure of an individual?
Blood pressure is the force of blood against the arteries. An individual should maintain a normal blood pressure from 90 – 120 / 60 – 80 mm Hg.
What percentage of the population has blood pressure?
Blood Pressure. Blood pressure is a serious health problem which affects nearly 40 to 50 per cent of the total population. Blood is a fluid connective tissue which is carried to all parts of our body with the help of arteries.
What is the difference between systole and diastole?
Diastole is when the heart muscle relaxes and systole is when the heart muscle contracts. Diastole is defined by the following characteristics: Diastol e is when the heart muscle relaxes. When the heart relaxes, the chambers of the heart fill with blood, and a person’s blood pressure decreases. Systole is defined by the following characteristics: ...
What is the balance between diastole and systole?
The balance between diastole and systole determines a person’s blood pressure. The heart is a pump that supplies all tissues and organs of the body with oxygen-rich blood. The heartbeat is caused by the heart muscles relaxing and contracting. During this cycle, the period of relaxation is called diastole and the period of contraction is called ...
What is the first number in blood pressure?
These measurements are given as millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The first number is the systolic pressure and the second is the diastolic pressure.
How does systolic pressure affect blood pressure?
Diastole and systole affect a person’s blood pressure differently, as follows: When the heart pushes blood around the body during systole, the pressure placed on the vessels increases. This is called systolic pressure. When the heart relaxes between beats and refills with blood, the blood pressure drops.
What is the name of the blood pressure drop?
When the heart relaxes between beats and refills with blood, the blood pressure drops. This is called diastolic pressure.
Why is high blood pressure more likely to occur in obese people?
This is because a higher volume of blood circulates through blood vessels to supply the cells with oxygen and nutrients. Because there is more blood circulating , there is a higher pressure on the vessel walls. Lifestyle habits.
What is the systole of the heart?
Systole is defined by the following characteristics: Systole is when the heart muscle contracts. When the heart contracts, it pushes the blood out of the heart and into the large blood vessels of the circulatory system. From here, the blood goes to all of the organs and tissues of the body.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures?
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressures is known as the pulse pressure. (If this doesn't make sense, please see another answer of mine where I explained the meanings of the different components of blood pressure.)
Why does the aorta have to relax during diastole?
If the aorta has access to the ventricle as it relaxes during diastole, the ventricle acts as a pressure sink, resulting in lower systemic pressures during that phase, increasing pulse pressure.
Why does the diameter of the systolic vessels increase with age?
Physiologically, this is because the large vessels tend to "stiffen" with age to calcification. As such, when the heart pumps blood into them (systole), they aren't especially elastic, so the diameter doesn't increase much. The result is higher systolic pressure. Similarly, in the period of diastole when flow is lower, the arteries don't rebound to a smaller diameter as robustly as young vessels, so the pressure falls. It is common in 80+ year-olds to see blood pressures like 180/60. I've never seen such a pressure in a young person.
What valve doesn't let blood through during systole?
The converse of this is aortic stenosis, which is a valve that doesn't let adequate blood through during systole. Because the flow is less, the pumping ventricle does not change the pressure in the systemic circulation as much as it normally would.
Is pulse pressure a predictor of cardiovascular disease?
Pulse pressure as a predictor of cardiovascular disease. There is extensive literature addressing the question of whether pulse pressure is a (semi-) independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, beyond that provided by systolic or diastolic pressure alone. I provide a few references below.
Is pulse pressure a risk factor?
There is extensive literature addressing the question of whether pulse pressure is a (semi-) independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, beyond that provided by systolic or diastolic pressure alone. I provide a few references below. The upshot is that the relationship between pulse pressure and risk is complicated and highly age-dependent. A high pulse pressure may be a better predictor of cardiovascular events than systolic pressure itself among the elderly.

Causes
Mechanism
- Because the heart beats, the blood flow through the arteries is not steady (as with a fire hose), but pulsatile, and the flow of blood, and the pressure it exerts, fluctuate from moment to moment.
Signs and symptoms
- If the systolic blood pressure is lower than normal, systolic hypotension is said to be present. If systolic hypotension is severe enough, it can cause lightheadedness, dizziness, syncope, or (if it lasts long enough), organ failure. Systolic hypotension can occur if the blood volume becomes too low (as with severe dehydration or a major bleeding episode), if the heart muscle becomes too …
Function
- The diastolic blood pressure is the pressure the blood exerts within the arteries in between heartbeats, that is, when the heart is not actively ejecting blood into the arteries. After the heart is finished contracting, the cardiac ventricles relax momentarily so that they can be refilled with blood, in preparation for the next contraction. This period of ventricular relaxation is called diast…
Diagnosis
- What this means is that, in order to diagnose hypertension accurately, it is important to control for as many external factors as possible. The standard recommended by experts requires the blood pressure to be taken in a calm, warm environment after you have been resting quietly for at least five minutes. Measuring blood pressure this way is a challenge in todays typical, harried doctor…
Significance
- Systolic and diastolic blood pressures represent the pressures within the blood vessels during different parts of the cardiac cycle. Accurately measuring both of these values is important in diagnosing and managing hypertension.