
Cauda equina Definition. It is a bundle of spinal nerve roots that begins at the level of first lumbar vertebra and surrounds the filum terminale. In Latin, it means “horse’s tail” due to the appearance as described by the French anatomist Andreas Lazarius. It is usually pronounced as cauda e·qui·na.
What is the cauda equina?
A group of nerve roots that travel down from the spinal cord and the conus medullaris is called the cauda equina.
What are filum terminale and cauda equina AVFs?
On angiography, filum terminale AVFs were invariably supplied by the extension of the anterior spinal artery accompanied by a closely paralleling filum terminale vein. Cauda equina AVFs were fed by either a radicular or a spinal artery or both arteries, often with a characteristic wavy radicular-perimedullary draining vein.
What is the filum terminale of the spinal cord?
Also extending distally from the apex of the conus medullaris is the filum terminale, a vestigial remnant of the distal part of the spinal cord . This thin, approximately 20 cm long filament of connective tissue is actually an extension of the pia mater that runs distally surrounded by the spinal nerve roots of the cauda equina.
Is there AVF below the conus medullaris in the filum terminale?
Intradural AVF below the conus medullaris may develop either on the filum terminale or the cauda equina (lumbosacral and coccygeal radicular nerves). Although not a few filum terminale AVFs are found in the literature, only 3 detailed cauda equina AVFs have been reported. Here, we analyze the angiog …
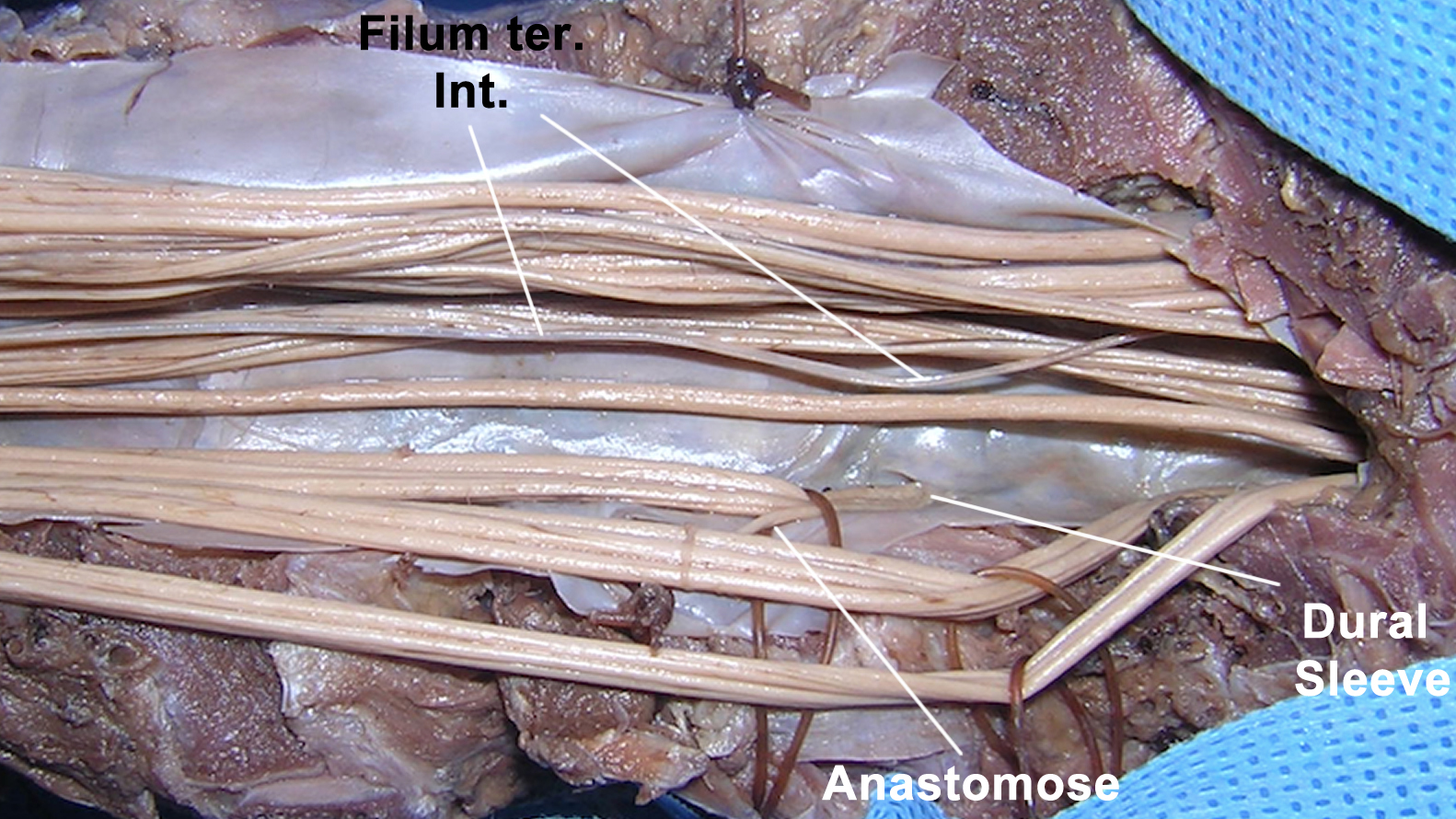
Is the filum terminale part of the cauda equina?
The cauda equina comprises the lumbosacral, the coccygeal nerve roots, and the filum terminale.
What forms the cauda equina and filum terminale?
The space inside the arachnoid mater is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Below the conus medullaris, this space is enlarged. This enlargement is called the lumbar cistern and contains CSF, the filum terminale, and the cauda equina.
What is a filum terminale?
The filum terminale (FT) is a fibrous band that extends from the conus medullaris to the periosteum of the coccyx, and its functions are to fixate, stabilize, and buffer the distal spinal cord from normal and abnormal cephalic and caudal traction.
How can you distinguish between cauda equina and conus medullaris?
The symptoms and signs of cauda equina syndrome tend to be mostly lower motor neuron (LMN) in nature, while those of conus medullaris syndrome are a combination of LMN and upper motor neuron (UMN) effects (see Table 1, below).
What is the cauda equina?
The collection of nerves at the end of the spinal cord is known as the cauda equina, due to its resemblance to a horse's tail. The spinal cord ends at the upper portion of the lumbar (lower back) spine.
What are the two parts of the filum terminale?
filum terminale internum: upper three quarters of the filum; covered by the spinal dura and arachnoid meninges. filum terminale externum: lower quarter of the filum; fuses with the investing dura mater and continues inferiorly to attach to the dorsal coccyx.
What forms the cauda equina?
The cauda equina (from Latin horse's tail) is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord.
What is filum terminale made of?
The filum terminale is the nonfunctional continuation of the end of the spinal cord. It usually consists of fibrous tissue without functional nervous tissue.
What level is filum terminale?
second sacral vertebraThe ligament is made up of an upper and a lower part: The upper part, or filum terminale internum, measures some 15 cm in length and reaches the level of the lower edge of the second sacral vertebra.
How do you find the filum terminale?
The filum is differentiated from nerve roots by presence of characteristic squiggly vessel on surface of filum. Also, under the microscope, the filum has a distinctively whiter appearance than the nerve roots, and ligamentous-like strands can be seen running through it.
What is the filum terminale What does it attach to?
an extension of the pia mater that extends from the terminal end of the spinal cord to the tailbone. The filum terminale helps to anchor the spinal cord in place.
At which spinal level does the cauda equina begin?
levels L1-L5The cauda equina is a group of nerves and nerve roots stemming from the distal end of the spinal cord, typically levels L1-L5 and contains axons of nerves that give both motor and sensory innervation to the legs, bladder, anus, and perineum.
What is the most common cause of cauda equina syndrome?
Cauda equina syndrome is most commonly caused by a massive disc herniation in the lumbar spine (low back). A disc herniation occurs when the jelly-like core of a disc herniates, or shifts out of position, putting pressure on nearby nerves in the spine.
Where is cauda equina located?
Overview. The spinal cord ends in the lumbar area and continues through the vertebral canal as spinal nerves. Because of its resemblance to a horse's tail, the collection of these nerves at the end of the spinal cord is called the cauda equina.
What is another name for cauda equina?
The most distal bulbous part of the spinal cord is called the conus medullaris, and its tapering end continues as the filum terminale. Distal to this end of the spinal cord is a collection of nerve roots, which are horsetail-like in appearance and hence called the cauda equina (Latin for horse's tail).
What happens if you have cauda equina?
If patients with cauda equina syndrome do not seek immediate treatment to relieve the pressure, it can result in permanent paralysis, impaired bladder and/or bowel control, loss of sexual sensation, and other problems. Even with immediate treatment, some patients may not recover complete function.
Can you walk with cauda equina?
Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency that calls for urgent surgical intervention. If patients with cauda equina syndrome do not receive treatment quickly, adverse results can include paralysis, impaired bladder, and/or bowel control, difficulty walking, and/or other neurological and physical problems.
Which accurately describes the filum terminale?
Which accurately describes the filum terminale? It is a membrane that protects the spinal cord.
Is filum terminale dura mater?
In addition, it is surrounded by the nerves forming the cauda equina, from which it can be easily recognized by its bluish-white color. The lower part, or filum terminale externum, closely adheres to the dura mater....Filum terminaleTA98A14.1.01.401TA25384, 5414FMA83977Anatomical terminology3 more rows
What is the filum terminale quizlet?
filum terminale. a strand of fibrous tissue, originating at the conus medullaris and extending through the vertebral canal to the second sacral vertebra, ultimately becoming part of the coccygeal ligament.
Why does the cauda equina develop?
Causes. Cauda equina syndrome may be caused by a herniated disk, tumor, infection, fracture, or narrowing of the spinal canal.
What is the cauda equina quizlet?
Cauda Equina. "horse tail" = spinal nerves within the vertebral canal. After the spinal cord tapers out, the spinal nerves continue as dangling nerve roots called cauda equina. Cerebrospinal Fluid.
Where does the spinal cord end and the cauda equina begin?
The fibrous extension of the cord, the filum terminale, is a nonneural element that extends down to the coccyx. The cauda equina (CE) is a bundle of intradural nerve roots at the end of the spinal cord, in the subarachnoid space distal to the conus medullaris.
What is the most common cause of cauda equina syndrome?
Cauda equina syndrome is most commonly caused by a massive disc herniation in the lumbar spine (low back). A disc herniation occurs when the jelly-like core of a disc herniates, or shifts out of position, putting pressure on nearby nerves in the spine.
What causes Cauda Equina syndrome?
Causes. There are many causes. The most common is through severe. trauma to the lower back caused by auto accidents, gunshot wounds, falls, or. hard blows. There are many causes. One of the most common is a central. herniated disc.
Is conus medullaris similar to cauda equina?
Conus Medullaris Syndrome and Cauda Equina Syndrome have similar symptoms and can cause it to be difficult to distinguish between the two. Despite similarities, the two spinal cord injuries often manifest themselves in different ways. The chart below compares and contrasts Conus Medullaris Syndrome and Cauda Equina Syndrome to showcase some of the key differences:
What is the filum terminale?
Also extending distally from the apex of the conus medullaris is the filum terminale, a vestigial remnant of the distal part of the spinal cord . This thin, approximately 20 cm long filament of connective tissue is actually an extension of the pia mater that runs distally surrounded by the spinal nerve roots of the cauda equina. At the level of S2 vertebra, it becomes covered by the dura and arachnoid layers and attaches to the coccyx, anchoring the distal end of the spinal cord and spinal meninges .
What is the spinal cord that is distal to the conus medullaris?
Distal to the conus medullaris is a collection of spinal nerve roots called the cauda equina, that emerges from the lumbosacral part of the spinal cord below the L1 vertebra and descends toward the coccyx. The cauda equina is translated from Latin into ‘horse’s tail’, and was so named due to its resemblance to the tail of a horse.
What is the conus medullaris?
The conus medullaris (medullary cone) is the cone-shaped terminal portion of the spinal cord . The tip of the conus medullaris is found between the L1 and L2 vertebra in the average adult. The conus medullaris is tethered to the coccyx by a fibrous cord called the filum terminale, which stabilizes the distal end of the spinal cord.
