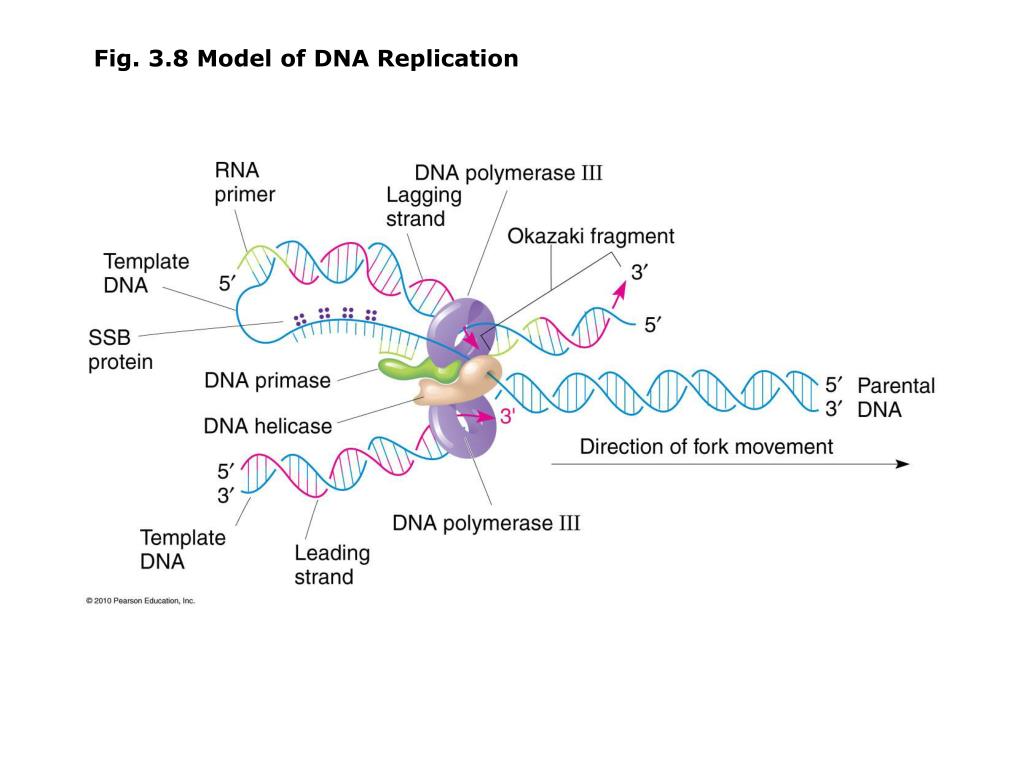
What is the difference between leading and lagging strand?
What You Need To know About Lagging Strand
- Lagging strand is a replicated strand of DNA which is formed in short segment called Okazaki fragments. ...
- Lagging strand requires DNA ligase to ligate Okazaki fragments together.
- Formation of lagging strand behind a bit later than that of the leading strand.
What is a leading strand and a lagging strand?
The leading strand is the strand of nascent DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The synthesis of leading strand is continuous. The lagging strand, on the other hand, is the strand of new DNA whose direction is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork.
Why does lagging strand occur?
Why lagging strand is formed? This strand is made in fragments because, as the fork moves forward, the DNA polymerase (which is moving away from the fork) must come off and reattach on the newly exposed DNA. This tricky strand, which is made in fragments, is called the lagging strand. 36 Related Question Answers Found
Is the leading strand the template strand?
The 3' to 5' direction of replication is called the "leading" strand, while the original template strand is called the "lagging" strand. The term "replication fork" describes the growing chain on each of the strands as it moves away from the origin of replication.

What is the Difference Between Lagging and Leading Strand?
In definition, lagging strand is one of the two strands produced in fragments during the DNA replication. In contrast, leading strand is the strand produced continuously during the DNA replication . Thus, this is the key difference between lagging and leading strand. Furthermore, lagging strand template is facing the 3’ to 5’ direction while leading strand template is facing the 5’ to 3’ direction. So, this is a significant difference between lagging and leading strand. Moreover, a further difference between lagging and leading strand is the synthesis process. The synthesis of lagging strand occurs discontinuously in fragments while the synthesis of leading strand occurs continuously during the replication process.
What is Lagging Strand?
Lagging strand is one of the two newly synthesized DNA strands in DNA replication. It occurs in 3’-5’ direction, which is the direction opposite to the growing replication fork. The synthesis of a new strand of replication DNA in lagging strand is by the creation “Okazaki fragments”, which are short segments of various length.
What is the direction of synthesis of a lagging strand?
The direction of synthesis of lagging strand is 3’→5’. However, the direction of synthesis of leading strand is 5’→3’. Apart from that, lagging strand synthesis requires new primers, often to accommodate repetitive initiation events. However, DNA replication of the leading strand needs to be primed only once.
How often does DNA replication need to be primed?
However, DNA replication of the leading strand needs to be primed only once. Below infographic summarizes the difference between lagging and leading strand in tabular form.
What are the two new strands produced during DNA replication?
The two new strands produced during the DNA replication are lagging strand and leading strand. In summarizing the difference between lagging and leading strand, the lagging strand is the strand produced discontinuously in Okazaki fragments in the 3’ – 5’ direction while leading strand is the strand produced continuously in the 5’- 3’ direction. ...
What is the process of DNA replication?
DNA replication is an important biological process that occurs in all living organisms. At the beginning of the replication process, double strands of the double helix unwind from each other and open up for the process. Then each strand acts as a template for the daughter strand.
What enzyme is responsible for DNA replication?
DNA replication takes place at the “replication fork” created by helicase enzyme, which is responsible for the breakdown of hydrogen bonds, connecting the two DNA strands together. The resulting single DNA strands serve as templates for the newly synthesized DNA strands called “lagging and leading strands”.
What is the difference between a leading strand and a lagging strand?
1.A leading strand is the strand which is synthesized in the 5’-3’direction while a lagging strand is the strand which is synthesized in the 3’-5’ direction. 2.The leading strand is synthesized continuously while a lagging strand is synthesized in fragments which are called Okazaki fragments.
Why is the synthesis of the lagging strand more complicated than the leading strand?
The continual synthesis of the lagging strands is prevented by the original DNA orientation; this is the reason why the synthesis of the lagging strand is more complicated than the leading strand.
What is the name of the strand that is synthesized in the 5’-3’ direction?
The DNA splits forming a “fork.”. A new DNA strand is always synthesized in a 5’ to 3’ manner, thus the replication of both the strands goes two different ways. Leading strand. A leading strand is the strand which is synthesized in the 5’-3’direction or the direction the same as the replication fork movement.
Why is DNA discontinuous?
It grows or is synthesized away from the fork. Its movement in the opposite direction is the cause why it is discontinuous; it is synthesized in fragments. The primase, which is responsible for adding an RNA primer, has to wait for the fork to open before putting in the primer. The lagging strands have fragments of DNA which are called Okazaki ...
What is the role of DNA in the transmission of hereditary traits?
DNA is responsible for the transmission of all hereditary characteristics to the next generation by means of replicating and making two exact copies of its original self. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is a chromosome’s main constituent. DNA is responsible for all the hereditary characteristics of a person and the transmission ...
How many polynucleotides are in DNA?
The DNA molecule has two polynucleotide chains; they are in the form of a helix and contain sugar deoxyribose and phosphates which are linked by hydrogen bonds. These hydrogen bonds are between complementary thymine and bases of adenine, guanine, and cytosine. DNA is self-replicating. DNA replication.
Is DNA self-replicating?
DNA is self-replicating. DNA replication. DNA replication is a biological process which is necessary for the inheritance of characteristics. It is the process by which the DNA is copied; the double-stranded molecule replicates to produce two identical copies of the molecule.
Which strand begins a bit later than that of leading strand?
7. Formation of lagging strand begins a bit later than that of leading strand.
What is the direction of growth of the leading strand?
3. The direction of growth of the leading strand is 5′ —> 3
When does the leading strand form?
7. Formation of leading strand begins immediately at the beginning of replication.
