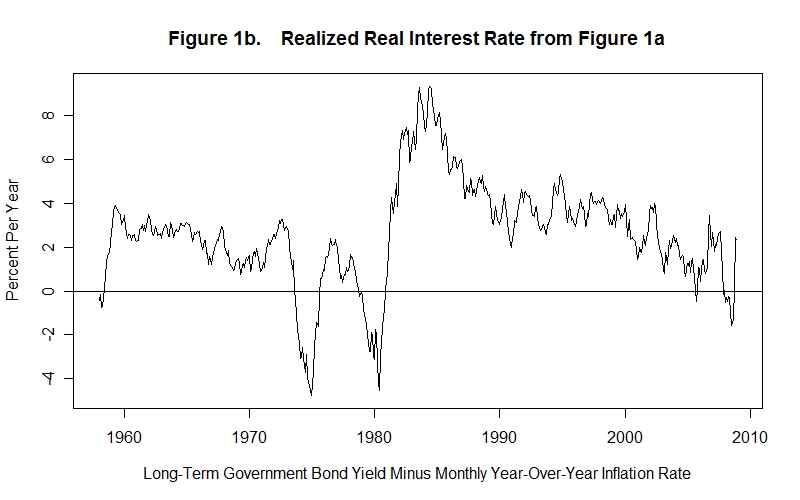
The key difference between the nominal and real interest rate is that while the nominal interest rate is the rate which is adjusted for inflation, the real interest rate is the rate that is not adjusted for inflation.
What does real interest rate tell you?
The real interest rate reflects the rate of time-preference for current goods over future goods. The real interest rate of an investment is calculated as the difference between the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate:
How do you calculate nominal rate?
You can calculate the nominal interest rate using the following formula: NIR = RIR + IR where: NIR refers to the nominal interest rate. RIR refers to the real interest rate. IR refers to the inflation rate You can also use the same equation but move the values around if you want to compute for the real interest rate that you’re receiving or paying:
How do you calculate nominal annual interest rate?
- Enter the effective rate and press SHIFT, then EFF%.
- Enter the number of compounding periods and press SHIFT, then P/YR.
- Calculate the nominal rate by pressing SHIFT, then NOM %.
How do you convert nominal to real?
Converting Nominal to Real GDP
- Look at (Figure), to see that, in 1960, nominal GDP was ?543.3 billion and the price index (GDP deflator) was 19.0.
- To calculate the real GDP in 1960, use the formula: Real GDP = Nominal GDP Price Index / 100 = ?543.3 billion 19 / 100 = ?2,859.5 billion ...
- Use the same formula to calculate the real GDP in 1965. ...
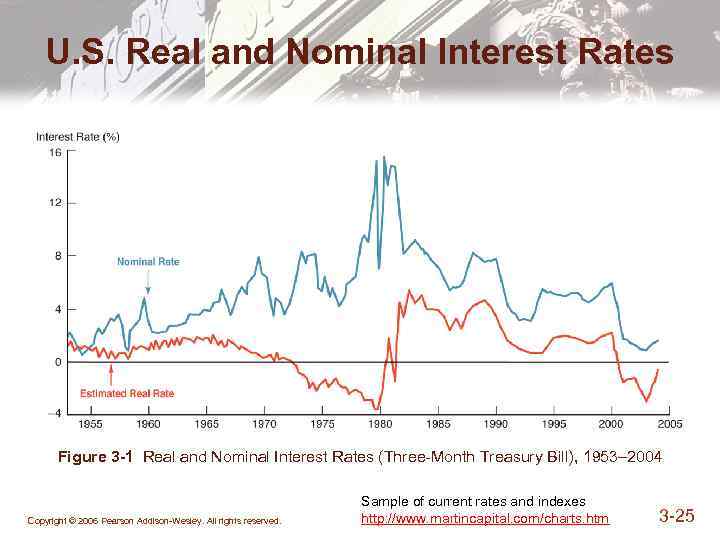
What is the difference between nominal and real interest rate quizlet?
The nominal interest rate is the rate you pay on a loan. The real interest rate is the nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation. a higher real interest rate reduces a borrowing firm's profit and hence its willingness to borrow.
What causes difference between real and nominal interest rate?
A real interest rate is one that has been adjusted for inflation, to show the real cost and purchasing power of money that is lent or invested. The nominal interest rate shows the price of money and reflects current market conditions.
What is the difference between real and nominal?
Definition: The nominal value of a good is its value in terms of money. The real value is its value in terms of some other good, service, or bundle of goods.
What is the difference between the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate What is the insight behind the Fisher equation?
In the Fisher Effect, the nominal interest rate is the provided actual interest rate that reflects the monetary growth padded over time to a particular amount of money or currency owed to a financial lender. Real interest rate is the amount that mirrors the purchasing power of the borrowed money as it grows over time.
What is an example of nominal interest rate?
The nominal interest rate is often used in banks to describe interest on different loans and in the investment field. For example, if the nominal rate on a loan is 5%, you can expect to pay $50 of interest for $1,000 borrowed. At the year's end, you'll pay $1,050.
What does real interest rate tell you?
The real interest rate measures the percentage increase in purchasing power the lender receives when the borrower repays the loan with interest..
How do you find the real interest rate?
To calculate a real interest rate, you subtract the inflation rate from the nominal interest rate. In mathematical terms we would phrase it this way: The real interest rate equals the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
Why is real better than nominal?
Nominal values are the current monetary values. Real values are adjusted for inflation and show prices/wages at constant prices. Real values give a better guide to what you can actually buy and the opportunity costs you face.
How do you calculate nominal and real?
Real GDP Calculation In general, calculating real GDP is done by dividing nominal GDP by the GDP deflator (R). For example, if an economy's prices have increased by 1% since the base year, the deflating number is 1.01.
What is the difference between real and nominal return?
Real return is what is earned on an investment after accounting for taxes and inflation. Real returns are lower than nominal returns, which do not subtract taxes and inflation.
Why should investors know the difference between nominal and real interest rates quizlet?
Why should investors know the difference between nominal and real interest rates? To recognize the effects of inflation.
Which of the following best describes the difference between nominal interest rates and real interest rates?
The real interest rate is the nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation and is equal to the nominal interest rate minus the expected inflation rate.
What causes real interest rates to change?
Interest rate levels are a factor of the supply and demand of credit: an increase in the demand for money or credit will raise interest rates, while a decrease in the demand for credit will decrease them.
What affects nominal interest rate?
Nominal interest rates can be impacted by different factors, including the demand and supply of money, the action of the federal government, the monetary policy of the central bank, and many others. Central banks implement the short-term nominal interest rate as a tool of monetary policy.
Why is it essential to differentiate between real and nominal growth rates?
Nominal GDP growth rate does not take into account the inflation that occurred in a year and thus an increase in GDP might have been an increase in prices during that particular year. So, it cannot indicate the living standards of a country while real growth rate could indicate it.
What determines real interest rates?
Fundamentally, real interest rates are determined by the levels of saving and fixed investment in the economy. All else equal, a decrease in the real interest rate occurs if saving increases or fixed investment decreases; an increase in the real interest rate occurs if saving decreases or fixed investment increases.
What is the relationship between nominal interest rate and real interest rate?
The relationship that captures this is called the Fisher equation, which states: Nominal interest rate = real interest rate + rate of inflation.
What is nominal rate?
The nominal rate is the one people are most familiar with. When you go to bank, mortgage dealer or another source of loans, the rate they quote is the nominal rate. However, the nominal interest rate isn't what people should care about when evaluating the rate they're paying on a loan. What matters is the inflation-adjusted interest rate, ...
What happens if the inflation rate turns out to be 10 percent?
But what if the inflation rate turns out to be 10 percent, the same as the interest rate charged on the loan, rather than zero? Then during the year, the price of an apple increases from $1 to $1.10. When the loan is paid off and the lender receives $110, he'll be able to buy only 100 apples, not the 110 as desired when he made the loan. In this case, the "real" return is zero instead of the expected 10 percent.
Why is the ex-ante rate called the ex-post rate?
This is called the "ex-ante" real interest rate because it's calculated before the actual inflation rate is known. Only after the loan is repaid, and the inflation rate for the loan's period is known, can we calculate the actual real return (meaning the "ex-post" real return on the loan.
What is the most important interest rate?
The most important of these interest rates for financial decisions is the ex-ante real rate . The nominal rate doesn't tell the borrower and lender what the actual return will be in terms of purchasing power, and the ex-ante real rate is unknown at the time the decision to make/take the loan is made.
Can researchers be sure of ex ante real rate?
But all of these approaches have problems, so researchers can never be sure about the accuracy of their ex-ante real rate calculations.
What is the difference between nominal and real interest rates?
The difference between nominal and real interest rates is that while nominal interests remain stable, the real interest rates are bound to change over time, meaning it is unstable. Nominal interest rates are fixed given the previous rate given, while real interest rates are freshly affected by the present situation.
What is Real Interest Rate?
Interest rates and inflation are set by central banks in a country at a specific level where it is considered to be a stable macroeconomic scenario . So, inflation is considered as one of the major economic indicators which indicate the stability of the country’s economy. It is the central bank’s responsibility to increase or decrease the interest rates based on their economy.
Why is nominal interest fixed?
It is decided at the time of transaction and does not change over time. This is because it does not take money or economic inflation into account.
How is inflation determined?
Inflation is a major determinant of the general price level of goods and services in an economy and is determined by monetary authorities through controlling the money supply. Inflation represents a loss of real value from the medium of exchange and all nominal assets, a loss that increases the purchasing power of money – a phenomenon that a price index measures.
What is the extra money that is paid to the bank called?
This extra amount of money paid to the bank is called interest. The amount of money to be paid as interest depends on the interest rates fixed by banks.
Do you have to pay back a nominal interest rate?
Thus with the nominal interest rate, you can be sure of the minimum payment that you have to pay back to the bank as the rates of interest do not change.
Is nominal interest rate accurate?
The market is a fluctuating entity, and inflation rates change from time to time. And hence nominal interest rates are also not an accurate rare of interest.
Nominal interest rate
The nominal rate of interest is the rate that is actually agreed and paid. For example, it’s the rate homeowners pay on their mortgage or the return savers receive on their deposits. Borrowers pay the nominal rate and savers receive it.
Real interest rate
It’s not only the nominal payment that is important to both borrowers and savers, but also how many goods, services or other things they could buy with that money. Economists call this the purchasing power of money. It usually decreases over time as prices rise due to inflation.
Development of nominal and real interest rates in the euro area
The real interest rate varies depending on the nominal rate and the rate of inflation. For example, in the early 1980s even though the average nominal interest rate in the euro area was high, inflation was also high. As a result, the average real interest rate was low.
What is nominal interest rate?
The nominal interest rate (or money interest rate) is the percentage increase in money you pay the lender for the use of the money you borrowed. For instance, imagine that you borrowed $100 from your bank one year ago at 8% interest on your loan. When you repay the loan, you must repay the $100 you borrowed plus $8 in interest—a total of $108.
What type of investment earns a real rate of return?
Also, for the unlikely event of deflation, there is a safeguard built into the TIPS system: the final payment of principal cannot be less than the original par value. I-bonds, issued by the U.S. Treasury, are another type of investment that earns a real rate of return.
What does 5% inflation mean?
Inflation is a rise in the general price level. A 5% inflation rate means that an average basket of goods you purchased this year is 5% more expensive when compared to last year. This leads to the concept of the real, or inflation-adjusted, interest rate. The real interest rate measures the percentage increase in purchasing power ...
Is nominal interest rate equal to real interest rate?
As shown, the nominal interest rate is equal to the real interest rate plus the rate of inflation 1. Fortunately, the market for U.S. Treasury securities provides a way to estimate both nominal and real interest rates.
Does nominal interest rate take inflation into account?
But the nominal interest rate doesn’t take inflation into account. In other words, it is unadjusted for inflation. To continue our scenario, suppose on your way to the bank a newspaper headline caught your eye stating: “Inflation at 5% This Year!” Inflation is a rise in the general price level. A 5% inflation rate means that an average basket of goods you purchased this year is 5% more expensive when compared to last year. This leads to the concept of the real, or inflation-adjusted, interest rate. The real interest rate measures the percentage increase in purchasing power the lender receives when the borrower repays the loan with interest.. In our earlier example, the lender earned 8% or $8 on the $100 loan. However, because inflation was 5% over the same time period, the lender actually earned only 3% in real purchasing power or $3 on the $100 loan.
Do TIPS bonds have real interest?
Unlike other investments that pay a nominal interest rate, TIPS earn a real interest rate. The TIPS securities earn a fixed rate of interest just like many other types of government bonds. But, in addition to the fixed rate, the principal value of your TIPS bond is adjusted for inflation. So, at maturity, TIPS investors receive an ...
What is nominal interest rate?
Nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate before taking inflation into account. Nominal can also refer to the advertised or stated interest rate on a loan, without taking into account any fees or compounding of interest.
Why do central banks set nominal rates?
Nominal interest rates may be held at artificially low levels after a major recession to stimulate economic activity through low real interest rates, which encourage consumers to take out loans and spend money. 1 However, a necessary condition for such stimulus measures is that inflation should not be a present or a near-term threat. In the United States, the federal funds rate, the interest rate set by the Federal Reserve, can also be referred to as a nominal rate.
Why Do Investors Care More About Real Interest Rates?
To avoid purchasing power erosion through inflation, investors consider the real interest rate, rather than the nominal rate. One way to estimate the real rate of return in the United States is to observe the interest rates on Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS). The difference between the yield on a Treasury bond and the yield on TIPS of the same maturity provides an estimate of inflation expectations in the economy.
What Is Difference Between Nominal Rate and APY?
To that end, the effective rate (APY) is often higher than the nominal rate.
How Do You Calculate the Effective Rate If Nominal Rate Is Known?
The formula for effective interest rate (e) is:
What is APR in accounting?
Rather, the consumer pays an effective rate that varies based on fees and the effect of compounding. To that end, annual percentage rate (APR) differs from the nominal rate, as it takes fees into account, and annual percentage yield (APY) takes both fees and compounding into account.
How to find real interest rate?
The equation that links nominal and real interest rates can be approximated as nominal rate = real interest rate + inflation rate, or nominal rate - inflation rate = real interest rate.
What is nominal interest rate?
The nominal interest rate is the stated interest rate of a bond or loan, which signifies the actual monetary price borrowers pay lenders to use their money. If the nominal rate on a loan is 5%, borrowers can expect to pay $5 of interest for every $100 loaned to them. This is often referred to as the coupon rate because it was traditionally stamped ...
Why is real interest rate called real interest rate?
The real interest rate is so named, because unlike the nominal rate, it factors inflation into the equation, to give investors a more accurate measure of their buying power, after they redeem their positions. If an annually compounding bond lists a 6% nominal yield and the inflation rate is 4%, ...
What Are the Different Interest Rates?
The different types of interest rates, including real, nominal, effective, and annual, are distinguished by key economic factors, that can help individuals become smarter consumers and shrewder investors.
What do shrew investors look for in bond interest rates?
When it comes to a bond’s interest rates, shrew investors know to look beyond nominal or coupon rates when considering their overall investment objectives. A qualified financial advisor can help investors navigate interest rates that keep up with inflation.
How much interest does a $1,000 bond pay?
Investors and borrowers should also be aware of the effective interest rate, which takes the concept of compounding into account. For example, if a bond pays 6% annually and compounds semiannually, an investor who places $1,000 in this bond will receive $30 of interest payments after the first 6 months ($1,000 x .03), and $30.90 of interest after the next six months ($1,030 x .03). In total, this investor receives $60.90 for the year. In this scenario, while the nominal rate is 6%, the effective rate is 6.09%.
Can real interest rates be negative?
It’s feasible for real interest rates to be in negative territory if the inflation rate exceeds the nominal rate of an investment. For example, a bond with a 3% nominal rate will have a real interest rate of -1%, if the inflation rate is 4%. A comparison of real and nominal interest rates can be calculated using this equation:
Is a loan with frequent compounding periods more expensive than one that compounds annually?
For example, a loan with frequent compounding periods will be more expensive than one that compounds annually, which is a vital consideration when shopping for mortgages. Furthermore, a bond that pays just a 1% real interest rate may not adequately grow an investor’s assets over time.
What is nominal interest rate?
The nominal interest rate is the rate you pay on a loan. Firms, households, and governments use the credit market for borrowing. The credit demand curve shows the relationship between the quantity of credit demanded and the real interest rate.
Which rate always exceeds the real rate?
The nominal interest rate always exceeds the real interest rate.
When to use real interest rate in optimizing economic agents?
Optimizing economic agents use the real interest rate when thinking about the economic costs and returns of a loan. Suppose the average rate paid by banks on savings accounts is 0.8% at a time when inflation is around 1.85%.
What happens to a lender's ability to make loans?
a lender's ability to make loans falls as the real interest rate rises.
What is nominal interest rate?
Nominal Interest Rate. Also known as simple interest rate. Nominal interest is calculated on the original principal only. If you borrow $100,000 for one year at 7% , you end up paying back $107,000. Effective Interest Rate. Also known as compound interest.
What is the difference between nominal and effective interest?
Nominal vs. Effective Interest Rate: What’s the Difference? 1 Nominal Interest Rate. Also known as simple interest rate. Nominal interest is calculated on the original principal only. If you borrow $100,000 for one year at 7%, you end up paying back $107,000. 2 Effective Interest Rate. Also known as compound interest. With effective interest, the interest rate is applied to the original principal AND all the accumulated interest. If you borrow $100,000 for one year at 7% and the interest is compounded semi-annually, you end up paying back $107,122.50. Therefore, the effective interest rate is actually 7.1225%. In Canada, this is known as the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and it’s the rate that Canadian mortgage lenders are required to quote.
What is the effective interest rate?
With effective interest, the interest rate is applied to the original principal AND all the accumulated interest. If you borrow $100,000 for one year at 7% and the interest is compounded semi-annually, you end up paying back $107,122.50. Therefore, the effective interest rate is actually 7.1225%. In Canada, this is known as the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and it’s the rate that Canadian mortgage lenders are required to quote.
Is the effective interest rate higher than the nominal interest rate?
But the result is still the same: the effective interest rate is slightly higher than the nominal interest rate.

What’s The Difference Between Nominal and Real Interest Rates?
- Simply put, the real interest rate is the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. For example, if a nominal interest rate was 2% and the inflation rate was 1%, the real interest rate would be 1%.
What It Means For Investors
- When nominal interest rates are higher than inflation rates, real interest rates are positive. When nominal interest rates are lower than inflation rates, real interest rates are negative. This is important to understand when looking at interest rates on investments in comparison to current inflation rates. For example, between March 2020 and December 2021, real interest rates as me…
The Bottom Line
- Nominal and real interest rates are important because they play different roles in your financial decisions. If a real interest rate is positive, it means you have more purchasing power. If the real interest rate is negative (nominal rate minus the inflation rate), then it means you have less purchasing power—at least when it comes to investments and earning interest on your money. …
Nominal vs Real Interest Rate
What Is Nominal Interest Rate?
What Is Real Interest Rate?
Main Differences Between Nominal and Real Interest Rate
- The nominal interest rate is usually stable over time and adjusted only at the end of the loan, while the real interest rate, due to its flexibility, changes by the market inflation.
- Nominal interest rates can never be of a negative value, while real interest rates can become a negative value if inflation occurs in the market, which makes the prices go much below normal.
- Nominal interest rate is not an accurate markerof the market price of goods and services, wh…
- The nominal interest rate is usually stable over time and adjusted only at the end of the loan, while the real interest rate, due to its flexibility, changes by the market inflation.
- Nominal interest rates can never be of a negative value, while real interest rates can become a negative value if inflation occurs in the market, which makes the prices go much below normal.
- Nominal interest rate is not an accurate markerof the market price of goods and services, whereas real interest rate is an accurate market price marker.
- Nominal interest rate is made without taking inflation into account, whereas real interest rates are determined keeping inflation in mind.
Conclusion
References