Thus, we find that, while the short-run supply curve of the industry always slopes upwards to the right, the long-run supply curve may be a horizontal straight line, sloping upwards or sloping downwards depending upon the fact whether the industry in question is a constant cost industry, increasing cost industry or decreasing cost industry.
How do you find the short run supply curve?
Short-Run Supply
- Total revenue and marginal revenue. If a firm decides to supply the amount Q of output and the price in the perfectly competitive market is P, the firm's total revenue ...
- Short‐run profit maximization. ...
- Graphical illustration of short‐run profit maximization. ...
- Short‐run losses and the shut‐down decision. ...
- average fixed costs. ...
- Short‐run supply curve. ...
What is the difference between short run and long run?
the Long Run in Microeconomics
- Short Run vs. Long Run. ...
- Example of Short Run vs. Long Run. ...
- Variable Inputs and Fixed Inputs. Suppose the demand for hockey sticks has greatly increased, prompting the company to produce more sticks.
- Implications of Short Run vs. Long Run. ...
- Short Run vs. Long Run in Macroeconomics. ...
What is a short run industry supply curve?
The short-run market supply curve is the horizontal sum of each individual firm's supply curve. That is, the amount supplied by the total market equals the sum of what each firm in the industry supplies at a given price.
What is short run market supply curve?
- $1: 0
- $3: 0
- $5: 1,000
- $7: 1,300
- $9: 1,800
- $11: 2,500

What is the difference between short run and long run?
"The short run is a period of time in which the quantity of at least one input is fixed and the quantities of the other inputs can be varied. The long run is a period of time in which the quantities of all inputs can be varied.
What is the difference between long run and short run equilibrium?
Short-run equilibrium is when the aggregate amount of output is the same as the aggregate amount of demand. Long-run equilibrium is when prices adjust to changes in the market and the economy functions at its full potential.
What is the long run supply curve?
Summary. The long-run supply is the supply of goods available when all inputs are variable. The long-run supply curve is always more elastic than the short-run supply curve. The long-run average cost curve envelopes the short-run average cost curves in a u-shaped curve.
What is the difference between long run and short run in economics?
The long run is a period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable. In the long run, firms are able to adjust all costs, whereas in the short run firms are only able to influence prices through adjustments made to production levels.
What are the two main differences between the short run and long run?
Differences. The main difference between long run and short run costs is that there are no fixed factors in the long run; there are both fixed and variable factors in the short run. In the long run the general price level, contractual wages, and expectations adjust fully to the state of the economy.
What is the difference between the short run and the long run quizlet?
What is the difference between the short run & the long run? In the short run: at least one input is fixed. In the long run: the firm is able to vary all its inputs, adopt new technology, & change the size of its physical plant.
What is a short run supply curve?
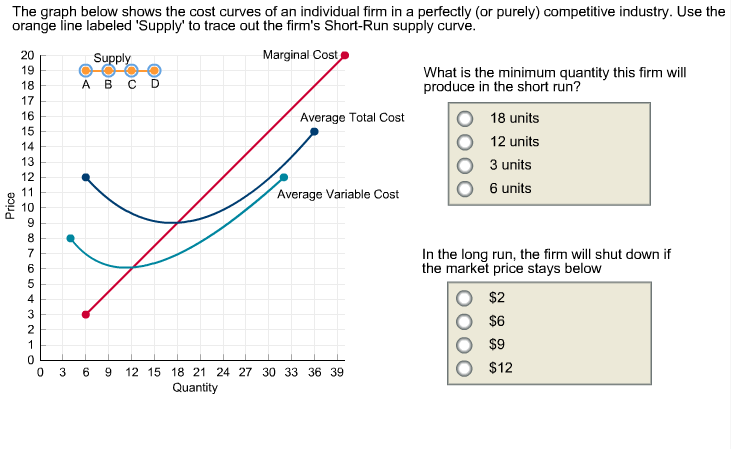
The short-run individual supply curve is the individual's marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. It holds true because a firm will not produce if the market price is lesser than the shut-down price.
What is the short run supply curve of a firm explain?
Short‐run supply curve. The firm's short‐run supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply.
What is the short run supply function?
In words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The short run supply function of a firm with "typical" cost curves is shown in the figure. Note: At the output it chooses, the firm may make a loss.
What is a long run equilibrium?
Long Run Equilibrium of the Firm In the long run, a firm achieves equilibrium when it adjusts its plant/s to produce output at the minimum point of their long-run Average Cost (AC) curve. This curve is tangential to the market price defined demand curve. In the long run, a firm just earns normal profits.
What is a short run equilibrium?
An economy is in short-run equilibrium when the aggregate amount of output demanded is equal to the aggregate amount of output supplied.
What do you mean by the equilibrium of a firm in the short run?
Short-Run Equilibrium of the Firm: A firm is in equilibrium in the short-run when it has no tendency to expand or contract its output and wants to earn maximum profit or to incur minimum losses. The short-run is a period of time in which the firm can vary its output by changing the variable factors of production.
What is the long run equilibrium price?
The long-run equilibrium requires that both average total cost is minimized and price equals average total cost (zero economic profit is earned).
Why does the short run aggregate supply curve slope upwards?
The short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upwards because businesses supply more due to the increase in prices. Usually, firms are limited in the short-run because they can't expand their premises or buy new machinery to cater for the increased supply needs; therefore, they produce as much as they can using the available resources.
Why is the LRAS curve vertical?
It is vertical because, in the long run, there is no correlation between price level and the real level of production in the economy. Approved by eNotes Editorial Team.
Why do businesses want to maintain the same profit level?
Businesses want to maintain the same profit level, and cannot risk increasing the quantity supplied due to competition. If they increase supply , others might do the same; leaving them with more unsold goods despite spending on production.
Is the short run AS curve long run?
The first is that one is short run and the other is long run. The short run AS curve is based on the assumption that all of the things that determine aggregate supply are being held constant. In the long run, these determinants of AS are not held constant. That leads to the second difference, which is the shapes of the curves.
How do economists differentiate between the short run and the long run?
Economists differentiate between the short run and the long run with regard to market dynamics as follows: Short run: The number of firms in an industry is fixed (even though firms can "shut down" and produce a quantity of zero). Long run: The number of firms in an industry is variable since firms can enter and exit the marketplace.
What is the short run?
In contrast, economists often define the short run as the time horizon over which the scale of an operation is fixed and the only available business decision is the number of workers to employ. (Technically, the short run could also represent a situation where the amount of labor is fixed and the amount of capital is variable, ...
Why do firms exit the market?
Firms will exit a market if the market price is low enough to result in negative profit. If all firms have the same costs, firm profits will be zero in the long run in a competitive market. (Those firms that have lower costs can maintain positive profit even in the long run.)
What is the long run of a firm?
Firms' profits can be positive, negative, or zero. The Long Run: Firms will enter a market if the market price is high enough to result in positive profit.
Why are output prices more flexible than input prices?
prices of materials used to make more products) because the latter is more constrained by long-term contracts and social factors and such.
Is there a sunk cost in the long run?
In addition, there are no sunk costs in the long run, since the company has the option of not doing business at all and incurring a cost of zero. In summary, the short run and the long run in terms of cost can be summarized as follows: Short run: Fixed costs are already paid and are unrecoverable (i.e. "sunk").
Is the quantity of capital and production processes variable?
Short run: Quantity of labor is variable but the quantity of capital and production processes are fixed (i.e. taken as a given). Long run: Quantity of labor, the quantity of capital, and production processes are all variable (i.e. changeable).
Why does the long run aggregate supply curve not increase profits?
When the price rises, it does not increase profits because wages and other input prices will also increase proportionally. Therefore, an increase in price does not affect the profit and quantity supplied. As a result, the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
What is short run equilibrium?
Economists divide the macroeconomic equilibrium into two: Short-run equilibrium is when aggregate demand equals short-run aggregate supply. Shifts in both cause actual real GDP to fluctuate around potential GDP.
What is macroeconomic equilibrium?
What’s it: A macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when aggregate supply equals aggregate demand. Aggregate supply represents the total output of goods and services. Meanwhile, aggregate demand represents the total goods and services demanded in the economy. Changes in aggregate supply or aggregate demand affect inflation, real GDP, ...
What determines the price level of the economy?
The intersection of short-run aggregate demand and supply determines the economy’s price level and actual real GDP. Because nominal wages do not change to achieve full employment, a short-run equilibrium can occur below, just right, or above potential GDP.
Why does aggregate demand decrease?
Producers raise prices to make more profit. And at the same time, aggregate demand decreases because of the tendency of the price level to rise. The economy will go to its new equilibrium, and aggregate demand equals aggregate supply. Long-run equilibrium.
Why does aggregate supply change?
Furthermore, long-run aggregate supply occurs to change only because of changes in production factors’ quantity and quality. It will increase when the amount of labor, natural resources, and capital increases.
When the price level declines, what happens to real wealth?
When the price level declines, real wealth increases and encourages households to increase their consumption (wealth effect). The opposite effect also applies when the price level rises. You can read about it in the aggregate demand curve article. All right, back to macroeconomic equilibrium.
What is the difference between a short run and a long run aggregate supply curve?
The difference between the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve is assumed to be that there is a period after the price of a good or service increases but the factor inputs have not adjusted yet to this increase. A basic example would be a service provider raising prices, but not yet raising the pay of the employee providing that service. In the short run, consumers are going to pay for more goods due to the higher prices, and this will suppress demand. The workers or providers of other factor inputs like suppliers will increase prices or wages in line with the increase in the retail price of the good. Thus, the employee who provides the service, in order to maintain his or her standard of living, will demand a wage increase when the price of goods in the economy increases. The long-run aggregate supply curve "describes the period when input prices have completely adjusted to changes in the price level of final goods." This curve occurs when the short-run aggregate supply curve reaches equilibrium. The short-run aggregate supply curve approaches the long-run aggregate supply curve. Represented graphically, this distinction is clear. The short-run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve where an increase in the price level will result in an
What is the demand curve?
The demand curve that an individual firm faces is called the residual demand curve: the market demand that is not met by other sellers at any given price. The firm 's residual demand function, Dr (p), shows the quantity demanded from the firm at price p. A firm sells only to people who have not already purchased the good from another seller. We can determine how much demand is left for a particular firm at each possible price using the market demand curve and the supply curve for all other firms in
What is supply side economics?
Supply-Side Economics: Its History and Relevance Today. “Supply-side economics provided the political and theoretical foundation for a remarkable number of tax cuts in the United States and other countries during the eighties. Supply-side economics stresses the impact of tax rates on the incentives for people to produce and to use resources efficiently .” -James D. Gwartney Introduction The theory of supply-side economics has several labels associated with it, some positive and

Production Decisions
Measuring Costs
Market Entry and Exit
- Economists differentiate between the short run and the long run with regard to market dynamics as follows: 1. Short run: The number of firms in an industry is fixed (even though firms can "shut down" and produce a quantity of zero). 2. Long run: The number of firms in an industry is variable since firms can enter and exit the marketplace.
Microeconomic Implications
- The distinction between the short run and the long run has a number of implications for differences in market behavior, which can be summarized as follows: The Short Run: 1. Firms will produce if the market price at least covers variable costs, since fixed costshave already been paid and, as such, don't enter the decision-making process. 2. Firms' profitscan be positive, negative, …
Macroeconomic Implications
- In macroeconomics, the short run is generally defined as the time horizon over which the wages and prices of other inputs to production are "sticky," or inflexible, and the long run is defined as the period of time over which these input prices have time to adjust. The reasoning is that output prices (i.e. prices of products sold to consumers) are ...