What are the six types of generalized seizures?
What are the six types of generalized seizures?
- Absence seizures ( petit mal seizures)
- Myoclonic seizures.
- Clonic seizures.
- Tonic seizures.
- Tonic-clonic seizures ( grand mal seizures)
- Atonic seizures (drop attacks)
What are the symptoms of tonic seizures?
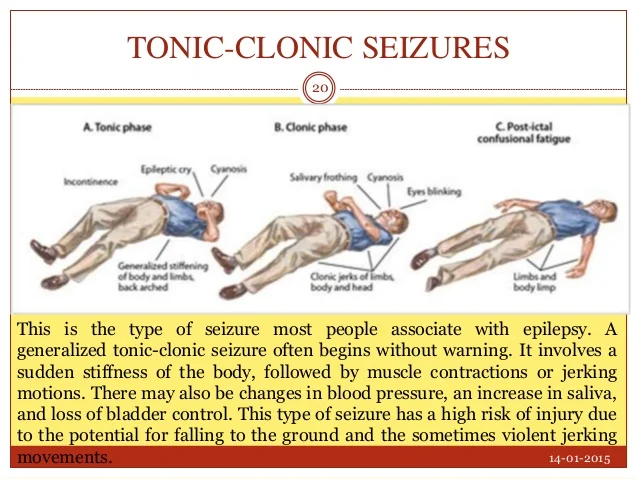
Tonic-clonic seizures—formerly known as "grand mal" seizures—come with the seizure symptoms people are most familiar with, per the Epilepsy Foundation. During the first phase (tonic), a person's muscles stiffen and they may cry out or groan ...
What are all the types of seizures?
Some types include:
- Simple focal seizures affect a small part of the brain. ...
- Complex focal seizures may make an individual feel confused or dazed. ...
- Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, then spread to both sides of the brain. ...
- Unknown onset seizures may later be diagnosed as focal or generalized seizures. ...
What is the first aid for seizures?
First aid for a seizure is aimed at keeping the person safe until the seizure stops on its own. Most seizures last from 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Stay calm and reassure bystanders. Loosen anything around the person's neck (clothing, ties, jewelry, etc.) that may impede breathing.

What are the 4 types of seizures?
The four different types of epilepsy are defined by the type of seizure a person experiences. They are: generalized epilepsy....Types of epilepsygeneralized seizures.focal seizures.unknown seizures.
What triggers a tonic-clonic seizure?
It's the type of seizure most people picture when they think about seizures. A grand mal seizure — also known as a generalized tonic-clonic seizure — is caused by abnormal electrical activity throughout the brain. Usually, a grand mal seizure is caused by epilepsy.
What happens during a tonic-clonic seizure?
Tonic-clonic seizures tonic stage – you lose consciousness, your body goes stiff, and you may fall to the floor. clonic stage – your limbs jerk about, you may lose control of your bladder or bowel, you may bite your tongue or the inside of your cheek, and you might have difficulty breathing.
What are the 3 main types of seizures?
Tonic, Clonic and Tonic-Clonic (Formerly called Grand Mal) Seizures.
What should you not do during a tonic-clonic seizure?
Do not attempt to hold the person still. Do not put anything in the person's mouth. It is physically impossible to swallow one's tongue, and putting things in the mouth may lead to injury. Time the seizure.
Can you be conscious during a tonic-clonic seizure?
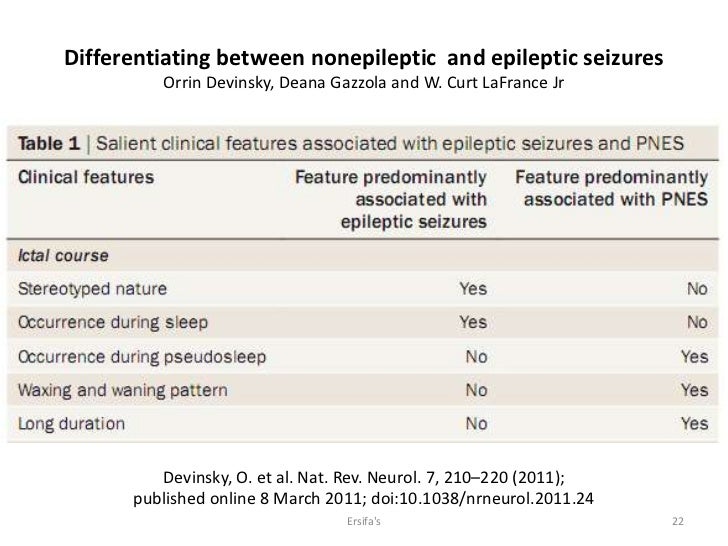
It is widely accepted that total amnesia and loss of consciousness occur during generalised tonic-clonic seizures. 1 2 Indeed, retention of memory, responsiveness, and the ability to speak during generalised seizures suggest a diagnosis of pseudoseizures.
What is the difference between a seizure and epilepsy or are they the same?
Epilepsy vs Seizures A seizure is a single occurrence, whereas epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by two or more unprovoked seizures.
What support is given during a tonic-clonic seizure?
Keep the person SAFE. Help the person lie down, and place something soft under the head and neck. Keep the person (especially the head) away from sharp or hard objects, such as the corner of a table. Loosen all tight clothing.
What are the 4 stages of a tonic-clonic seizure?
The four phases of seizure are:Prodromal.Early ictal (the “aura”)Ictal.Postictal.
What 3 things can cause seizures?
Fever, the physical stress of being sick, and dehydration (from not drinking or eating normally, or from vomiting) can all bring on seizures. It can also be hard to get a good night's sleep while sick, and lack of sleep can be a trigger. Plus, some of the medications used to treat these ailments may be triggers.
How can you tell the difference between focal and generalized seizures?
Focal seizures are divided into those in which the affected person is aware and those with impaired awareness; these events can be motor or non-motor. Generalized seizures are also categorized as motor and non-motor, but loss of awareness occurs with most events.
What are warning signs of a seizure?
General symptoms or warning signs of a seizure can include:Staring.Jerking movements of the arms and legs.Stiffening of the body.Loss of consciousness.Breathing problems or stopping breathing.Loss of bowel or bladder control.Falling suddenly for no apparent reason, especially when associated with loss of consciousness.More items...
What is the difference between a clonic seizure and a tonic seizure?
So ‘tonic clonic seizures’ are an alternate contraction and relaxation of muscles with an increased or heightened basal muscular tone or a spasm, whereas ‘tonic’ seizure is a continuous spasmodic state of heightened or increased muscular tone, and a clonic seizure is an alternate contraction and relaxation of the muscles with the basal resting tone at normal levels during the phase of relaxation !
What is a tonic seizure?
A Tonic seizure is when the muscles get stiff and contract very suddenly.
What is a tonic clonic?
Tonic clonic (old term: grand mal) yield pretty much matching stiffening & jerking of arms & legs and involves other muscle groups as well. This lasts for a few minutes and includes loss of awareness - bladder & bowel control is often lost. When the person returns to awareness there is a period of confusion.
What is the difference between epilepsy and non-epileptic seizures?
Many seizures are subtle and don't cause the individual to collapse or even lose consciousness. But the important difference with epileptic seizures is that it's usually a condition someone has to live with for a lifetime, whereas non-epileptic seizures are typically contained events.
Why do I have seizures when I'm young?
Some seizures are caused by conditions such as low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) or a change to the way the heart is working. Some very young children have ‘febrile convulsions (jerking movements) when they have a high temperature. These are not the same as epileptic seizures. When I used the word ‘seizure’ I mean an epileptic seizure.
How long does a seizure last?
Seizure types vary by where and how they begin in the brain. Most seizures last from 30 seconds to two minutes. A seizure that lasts longer than five minutes is a medical emergency.
What does it mean when you have two seizures?
If you have two or more seizures or a tendency to have recurrent seizures, you have epilepsy.
What is a tonic clonic seizure?
Tonic-clonic seizures involve sudden muscle stiffening and contraction, and rhythmic twitching or jerking. Read about their causes and how they can be treated.
How are tonic-clonic seizures treated?
The best treatment for tonic-clonic seizures depends on the cause. In some cases, tonic-clonic seizures can be controlled with anti-epileptic drugs . Secondarily generalized seizures are slightly less likely to respond to anti-epileptic drugs. The ketogenic diet, vagus nerve stimulation or surgery may all be considered in certain cases.
How can you tell if your child has tonic, clonic or tonic-clonic seizures?
src="https://akhpub.aboutkidshealth.ca/Style%20Library/akh/swfanimations/swf.html?swffile=Seizure_tonic_clonic_MED_ANI_EN.swf"
How many children have tonic-clonic seizures?
Tonic-clonic seizures are the most common type of generalized seizure. Studies have seen tonic-clonic seizures in up to 27 per cent of children with epilepsy.
What is the outlook for a child with tonic-clonic seizures?
Some children have only one tonic-clonic seizure provoked by illness, fever, or medication, and never have another. These children are not considered to have epilepsy.
How long do tonic clonic seizures last?
Tonic-clonic seizures last for about a minute on average, but they can last far longer. The length and severity of a tonic-clonic seizure, the muscles involved and the amount of autonomic involvement (flushing, sweating, heart rate changes) can all vary from person to person.
What happens to a child during a tonic phase of a seizure?
In the tonic phase of the seizure, the child becomes rigid, their teeth clench, they may stop breathing and turn blue, and saliva or foam may drip from their mouth. Their heart rate and blood pressure rise and they may sweat or tremble.
What is a tonic clonic seizure?
Tonic-clonic seizures, also called grand mal seizures, can make a person. Cry out. Lose consciousness. Fall to the ground. Have muscle jerks or spasms. The person may feel tired after a tonic-clonic seizure. Focal seizures are located in just one area of the brain. These seizures are also called partial seizures.
What are the two types of seizures?
Seizures are classified into two groups. Generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain. Absence seizures, sometimes called petit mal seizures, can cause rapid blinking or a few seconds of staring into space. Tonic-clonic seizures, also called grand mal seizures, can make a person. Cry out.
How do you know if you have a seizure?
A person having a seizure may seem confused or look like they are staring at something that isn’t there. Other seizures can cause a person to fall, shake, and become unaware of what’s going on around them.
What are the words used to describe seizures?
These words are used to describe generalized seizures: Tonic: Muscles in the body become stiff. Atonic: Muscles in the body relax. Myoclonic: Short jerking in parts of the body. Clonic: Periods of shaking or jerking parts on the body.
Where do secondary seizures occur?
Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, but then spread to both sides of the brain. In other words, the person first has a focal seizure, followed by a generalized seizure.
Can epilepsy cause a strange taste?
These seizures can cause twitching or a change in sensation, such as a strange taste or smell. Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confused or dazed. The person will be unable to respond to questions or direction for up to a few minutes.
What is the tonic phase of a seizure?
The tonic phase of the seizure, which is typically of short duration (few second) is the period during which the subject looses consciousness. The subject may cry or moan during this phase. The muscle may tense and hence the patient can fall down during this phase.
What happens during the tonic phase of a seizure?
During this seizure the subject looses consciousness and may jerk continuously. The tonic phase of the seizure, which is typically of short duration (few second) is the period during which the subject looses consciousness. The subject may cry or moan during this phase.
What is a myoclonic twitch?
Myoclonic seizures are usually muscle twitches or jerks that do not necessarily indicate a medical issue. An example of a non-medical myclonic twitch is when one is just about to fall asleep, and your leg jumps. Technically, any spontaneous involuntary muscle twitch, jerk or spasm can be considered a myoclonic seizure.
What is the difference between a tonic and a myochlonic?
However, Tonic-Clonic usually involves all/most muscle major muscle groups during the seizure (breathing, vocal cord, hands, arms, fingers etc.) While a Myochlonic usually involves only arms, or maybe legs. Both can have repetitive jerking (stiffening and relaxing).
How long does a myochlonic seizure last?
However, Myochlonic may be so quick it is only noticeable to the person having it. Maybe 2 or 3 jerks. While a Tonic-Clonic seizure is usually 30 seconds or more. (5 minutes is uncommon but can be life threatening to person).
What muscle group is involved in a seizure?
Both have jerking movements of body parts. However, Tonic-Clonic usually involves all/most muscle major muscle groups during the seizure (breathing, vocal cord, hands, arms, fingers etc.) While a Myochlonic usually involves only arms, or maybe legs.
What is it called when a person remains conscious?
If a person remains conscious it is called Tonic-Clonic W/retained awareness. However, that is very rare. A Myochlonic Epileptic seizure always retains awareness. Although many people have Myochlonic seizures just as they are falling asleep and their body quickly jerks, even though they do not have a seizure disorder.
How to treat tonic clonic seizures?
Treatment for tonic-clonic seizures can involve medication, surgery, nerve stimulation, dietary therapy or a combination of these approaches.
What is a tonic clonic?
Tonic-Clonic (Grand Mal) Seizures. Tonic-clonic seizures, formerly known as grand mal seizures, comprise two stages: a tonic phase and a clonic phase. These intense seizures can be frightening to experience or observe, as extreme muscle spasms may temporarily arrest breathing.
How long does it take for a tonic clonic to resolve?
Witnessing a person having a tonic-clonic seizure can be upsetting, but it’s important to remember that most seizures resolve on their own after one to three minutes. To offer assistance:
What is the name of the sensation that a person experiences when they have a seizure?
Aura. The seizure may start with a simple or complex partial seizure known as an aura. The person may experience abnormal sensations such as a particular smell, vertigo, nausea, or anxiety. If the person is familiar with having seizures, they may recognize the warning signs of a seizure about to begin.
What is the best treatment for epilepsy?
A range of therapies, including anti-seizure medication, nerve stimulation, dietary therapy and surgical procedures can address the seizures and, in many cases, bring them under control.
What to do after a seizure?
After a person’s first seizure, it is important to consult with a physician. Parents or family members who observe the seizure can note the details and help create a written report that the person can take to the doctor. A video recording of the event (if available) can also aid in diagnosis.
Can a person remember having a seizure?
Gradually the person regains awareness and may feel confused, exhausted, physically sore, sad or embarrassed for a few hours. The person may not remember having a seizure, and may have other memory loss. Occasionally, people may have abnormal or combative behavior after a tonic-clonic seizure while the brain is recovering.
What is a tonic clonic seizure?
A tonic-clonic seizure, formerly called a grand mal seizure, is the "classic" type of seizure most people are familiar with. It involves loss of consciousness or awareness, plus uncontrolled jerking and stiffness of the arms, legs, or body.
How long does a tonic clonic seizure last?
It generally lasts just a few seconds to a couple of minutes. 1 .
Why do people have seizures?
Most people who are prone to recurrent tonic-clonic seizures can experience a seizure due to a fever, infection, sleepiness, or no known trigger at all. Anti-seizure medications, which are also referred to as anticonvulsants, are often recommended to prevent or reduce recurrent seizures.
What is the best medication for epileptic status?
Medications used to treat status epilepticus include intravenous forms of lorazepam, diazepam, and midazolam. 3
Why do people develop epilepsy?
Epilepsy: This is the most common cause. You can be born with it or develop it later in life due to brain damage. Brain injury: Head trauma, brain injury, strokes, aneurysms, brain tumors, and brain infections may cause long-term epilepsy.
Is a tonic clonic seizure a primary or secondary seizure?
Due to impaired consciousness, you may not be aware that you're having such a seizure. A tonic-clonic seizure can be classified as either a primary or secondary generalized seizure. 2 . Secondary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure. Starts in one part of the brain, but spreads to both sides.
Can epilepsy prevent seizures?
There is a high likelihood that you will reduce the number of tonic-clonic seizures you have once doctors find the cause and get you on anticonvulsant medication. Most people with epilepsy can prevent seizures and have a good quality of life. That said, tonic-clonic seizures can pose some social and emotional challenges.