Vector data are excellent for capturing and storing spatial details, while raster data are well suited for capturing, storing, and analyzing data such as elevation, temperature, soil pH, etc. that vary continuously from location to location. Raster data formats also are used to store aerial and satellite imagery.
What is the difference between vector and raster data models?
What is the difference between raster and vector files?
- Resolution. One of the main differences between raster and vector files is their resolution. ...
- Uses. Digital photographs are usually raster files. ...
- File sizes. Raster files are generally larger than vector files. ...
- Compatibility and conversion. ...
- File and extension types. ...
- Raster file types.
What is better vector or raster?
Raster files are also commonly used for editing images, photos, and graphics. Vector files work better for digital illustrations, complex graphics, and logos. That’s because the resolution of vectors remains the same when resized, making them suitable for a wide variety of printed formats. Some projects combine both raster and vector images.
What is the difference between a raster and vector image?
Difference between Raster and Vector Image. 1. Raster images are made of pixels (tiny dots). Vector images are made of mathematical calculation that form objects and lines. 2. Raster image can be scaled at the cause of losing quality. Vector image can be scaled to any size with same quality and can be printed top any resolution. 3.
What's the difference between raster and vector mapping?
Important notice
- Raster map tiles are larger in size, less demanding on end-users hardware but more demanding on the server-side performance.
- Vector map tiles are faster to load, less demanding on the server-side performance but more demanding on end-users hardware.
- With MapTiler you can take advantage of both map data types. ...
Which is better raster or vector data?
Vector data are excellent for capturing and storing spatial details, while raster data are well suited for capturing, storing, and analyzing data such as elevation, temperature, soil pH, etc. that vary continuously from location to location. Raster data formats also are used to store aerial and satellite imagery.
What is the difference between raster data and?
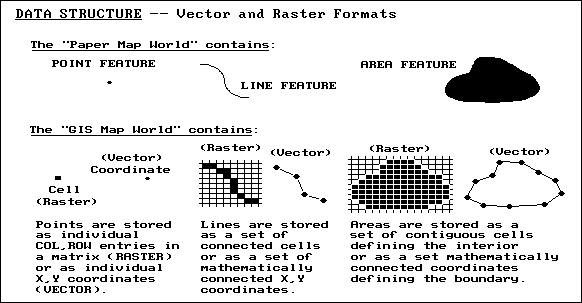
Raster data and vector data are two types of spatial data in GIS. The main difference between Raster and Vector Data is that the raster data represents data as a cell or a grid matrix while vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices.
What is the difference between vector model and raster model?
coordinates in a Cartesian coordinate systems. The raster model represents location as cells, also in a Cartesian coordinate system. The vector model represents feature shape accurately; the raster model represents rectangular areas and thus is more generalized and less accurate.
What are the raster and vector?
Raster (or bitmap) images are described by an array or map of bits within a rectangular grid of pixels or dots. Vector images are described by lines, shapes, and other graphic image components stored in a format that incorporates geometric formulas for rendering the image elements.
What is an example of raster data?
Rasters are digital aerial photographs, imagery from satellites, digital pictures, or even scanned maps. Data stored in a raster format represents real-world phenomena: Thematic data (also known as discrete) represents features such as land-use or soils data.
Which is an example of a vector dataset?
Vector data is represented as a collection of simple geometric objects such as points, lines, polygons, arcs, circles, etc. For example, a city may be represented by a point, a road may be represented by a collection of lines, and a state may be represented as a polygon.
What is raster data used for?
Raster datasets are commonly used for representing and managing imagery, digital elevation models, and numerous other phenomena. Often rasters are used as a way to represent point, line, and polygon features. In the example below, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as a raster dataset.
What is raster image example?
Examples of raster image file types are: BMP, TIFF, GIF, and JPEG files.
What is vector data used for?
Vector data is extremely useful for storing and representing data that has discrete boundaries, such as borders or building footprints, streets and other transport links, and location points. Ubiquitous online mapping portals, such as Google Maps and Open Street Maps, present data in this format.
Why is it called raster?
The word "raster" has its origins in the Latin rastrum (a rake), which is derived from radere (to scrape). It originates from the raster scan of cathode ray tube (CRT) video monitors, which paint the image line by line by magnetically or electrostatically steering a focused electron beam.
What is called raster?
raster graphics, also called bitmap graphics, a type of digital image that uses tiny rectangular pixels, or picture elements, arranged in a grid formation to represent an image.
Why is it called raster image?
The name derives from the early CRT video technology, which would “paint” an image on a screen line by line by magnetically steering a focused electron beam across a fluorescent viewing surface. This process of building an image was known as a Raster Scan, and the resulting pattern — or picture — was known as a Raster.
What is the difference between raster data and spatial data?
Spatial data types provide the information that a computer requires to reconstruct the spatial data in digital form. In the raster world, we have grid cells representing real-world features. In the vector world, we have points, lines, and polygons that consist of vertices and paths.
What is the difference between raster and vector GIS?
The vector model uses points and line segments to identify locations on the earth while the raster model uses a series of cells to represent locations on the earth. The figure represents vector (left) versus raster (right) data. One of the most common types of raster data is land cover derived from satellite imagery.
What are 3 different formats for raster graphics?
Popular types of raster files include JPEG, PNG, and GIF images. However, because their pixel number is fixed, raster images can become distorted or blurry when resized to fill a bigger or smaller space.
What is the difference between a raster and grid?
A grid is commonly used to refer to a raster data model. A grid is a fully integrated grid (cell-based) geoprocessing system for use with ArcInfo (another ESRI GIS program). The term grid cell is often used to refer to a single element of a raster data structure.
Why are raster models useful?
Raster models are useful for storing data that varies continuously. For example, elevation surfaces, temperature and lead contamination.
Why do rasters look pixelated?
They are usually regularly spaced and square but they don’t have to be. Rasters often look pixelated because each pixel has its own value or class.
What are the two primary types of spatial data in GIS?
Every house, every tree, every city has its own unique latitude and longitude coordinates. The two primary types of spatial data are vector and raster data in GIS. But what is the difference between raster and vector data?
What are vectors made of?
Vector data is not made up of a grid of pixels. Instead, vector graphics are comprised of vertices and paths. The three basic symbol types for vector data are points, lines, and polygons (areas). Because cartographers use these symbols to represent real-world features in maps, they often have to decide based on the level of detail in the map.
How does a raster depicting an oil spill show how the fluid moves from high concentration to low concentration?
At the source of the oil spill, concentration is higher and diffuses outwards with diminishing values as a function of distance.
Why do cartographers use polygons?
Cartographers use polygons to show boundaries and they all have an area. For example, a building footprint has a square-footage, and agricultural fields have acreage.
How do vector lines work?
Vector lines connect each vertex with paths. Basically, you’re connecting the dots in a set order and it becomes a vector line with each dot representing a vertex.
What is the difference between raster and vector data?
Vector data are excellent for capturing and storing spatial details, while raster data are well suited for capturing, storing, and analyzing data such as elevation, temperature, soil pH, etc. that vary continuously from location to location. Raster data formats also are used to store aerial and satellite imagery.
What is vector raster?
Raster and vector are two very different but common data formats used to store geospatial data.
What is raster data?
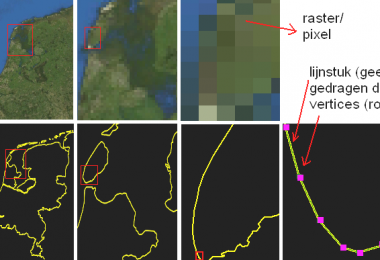
Raster data, on the other hand, use a matrix of square areas to define where features are located. These squares, also called pixels, cells, and grids, typically are of uniform size, and their size determines the detail that can be maintained in the dataset. Because raster data represent square areas, they describe interiors rather ...
What are the different types of GIS data?
There are three different types of GIS data, which include spatial, attribute, and metadata. Vector data, raster data, images, Triangular Irregular Networks (TINs), and terrain datasets are all apart of Spatial data. Attribute data is made up of details such as the information that explains “where”, “what”, and “why”. It provides characteristics about the spatial data. Metadata consists of information involving scale, accuracy, projection, data source, manipulations, and how the data is obtained.
What exactly is the vector type of data?
Definition: Vector data is the process of representing real world objects and features within the GIS field. This means that anything that you can visually see in a landscape, such as trees, houses, and rivers, can be represented in a GIS application.
What are the differences between vector and raster data?
These points, lines, and polygons declare the location of objects such as fire hydrants, roads, walkways, and more. Raster data uses squares, which are known as pixels or cells, to mark where certain features are located. These pixels look like grids, and they are usually the same size. The size controls how much detail is shown and can be updated and altered in the dataset. In simple terms, vector data focuses on declaring boundaries and locations, whereas raster data focuses on describing what is within the area.
What is point in GIS?
Point: Using point for your vector data is your decision to make. Point works best depending on how far you are from the specific feature, how much time you have, and the type of feature that you are wanting to put on your GIS application. Point features consist of X, Y, and, sometimes, Z coordinates. If you do not have a lot of time, point is the data type that takes the least amount of time, but it is not recommended for large scale maps.
Why is spatial data important?
Spatial data is important, as it is data that contains information about locations on the surface of the Earth. This data is continuously being assessed and evaluated in a variety of different fields, but GIS experts are more prominent users of the term.
What are the advantages of vector data?
Advantages: An advantage of vector data is that it can be used to map out an entire landscape as well as its features. It also can be used to answer difficult questions without going to the landscape site.
What is a line of lines?
A line makes sense when you would like to show features such as roads, walking paths, and rivers. When more than two vertices are joined, you will then have what is called a “line of lines,” or a polyline.
What is the difference between raster and vector?
Do you use raster or vector images? Raster images are made up of pixels, while vector images are formed by mathematical curves and paths. Being comfortable with the ins and outs of both formats and how they translate when exported is an essential skill for every designer. Let’s get started.
Why is a raster image larger?
Due to the abundance of pixels in a raster image, the file sizes can be substantial. An illustration with higher DPI (dots per inch) or PPI (pixels per inch) will be larger in size and data, which can be worrisome when there are limits to image storage or restrictions on uploaded file sizes.
Why are vectors so scalable?
Due to their algorithmic makeup, vectors are infinitely scalable and remain smooth and crisp even when sized up to massive dimensions. Even when scaled to substantial proportions, this pattern below remains clean and exact. Elements like fonts render the same way: When sized up or down, they retain their quality.
How to reduce file size of online photos?
Tip: You can quickly cut down file size by reducing the resolution to 72 PPI for online images.
What is vector art?
Vectors use a different approach to image renderings. They are made of paths and curves dictated by mathematical formulas. These paths and curves are produced exclusively through design softwares designed for vectors, like Adobe Illustrator or Sketch. Due to their algorithmic makeup, vectors are infinitely scalable and remain smooth and crisp even when sized up to massive dimensions.
What is Shutterstock Flex?
Shutterstock FLEX gives you the flexibility to download different types of content in one subscription.
What does it mean when a tropical pattern is pixelated?
Notice how the edges of the tropical pattern below become pixelated and jagged when magnified. This is a key indicator of a raster-based image. Obvious pixels make an image look unprofessional and unsightly. As a rule of thumb, it is best to only downsize a raster image to avoid heavy pixelation.
What are the two common data types used in GIS?
Vector and raster are the two common data types used in GIS. Knowing their structure provides insights on their usage.
What is raster data?
Raster data stores information of features in cell-based manner. Satellite images, photogrammetry and scanned maps are all raster-based data. Raster models are used to store data, which varies continuously as in aerial photography, a satellite image or elevation values (DEM- Digital Elevation Model).
What is the purpose of vector models?
Vectors models are used to store data, which have discrete boundaries like country borders, land parcels and roads. Vector models are useful for storing data that has discrete boundaries , such as country borders, land parcels, and streets. Points Lines Polygons.
What is GeoJSON used for?
GeoJSON – a lightweight format based on JSON, used by many open source GIS packages
Which is easier to update, vector or raster?
Vector data are easier to update like adding river stream but has to be recreated for the raster image.
Who developed the shapefile?
Shapefile – Most popular vector data developed by Esri
Why is raster used in remote sensing?
For example due to the nature of its collection, raster is often the only choice when working with remote sensing data captured by cameras on planes or satellites. The spatial resolution of such data will be determined by the capabilities of the sensor used to take an image which is why it can be subject to a pixelated look when using a low resolution.
What are vectors in math?
Rather than working with a matrix of cells, vector data stores basic geometries (made up of one or more interconnected vertices), with three key types: 1 Points - single vertex, e.g. a house. 2 Lines - two or more vertices where the first and last vertex are not equal, e.g. a road. 3 Polygons - three or more vertices with the last vertex equal to the first, e.g. a boundary.
What is a line in geometry?
Lines - two or more vertices where the first and last vertex are not equal, e.g. a road. Polygons - three or more vertices with the last vertex equal to the first, e.g. a boundary. Below we can see vector data (specifically polygons representing the evolution of Manhattan’s building footprints over time) within a map created using CARTO VL.
What is the power of vector data?
The power of vector data becomes evident when we start to move from simply asking where something occurs to why. This is true spatial analysis and allows us to gain deeper insights from the data as GIS evolves to Spatial Data Science. Some questions that can be answered leveraging vector data include:
What is raster data?
Raster data is made up as a matrix of pixels, also referred to as cells in much the same way as you might find when working within a spreadsheet. They are often square and regularly spaced but don’t have to be.
Is Vector Data supported by Carto?
Vector data is fully supported across the CARTO platform since Location Intelligence relies on the ability to analyze and visualize data in such a format.
Can raster data be added to a basemap?
Raster data can be added as a basemap within the CARTO platform which by default uses vector graphics for map rendering.
What is the difference between a fine raster and a vector?
At this scale, there is very little difference between the vector representation and the "fine" (small pixel size) raster representation. However, if you zoomed in closely, you'd see the polygon edges of the fine raster would start to become pixelated, whereas the vector representation would remain crisp. In the "coarse" raster the pixelation is already clearly visible, even at this scale.
What is raster data?
Raster data is made up of pixels (or cells), and each pixel has an associated value. Simplifying slightly, a digital photograph is an example of a raster dataset where each pixel value corresponds to a particular colour. In GIS, the pixel values may represent elevation above sea level, or chemical concentrations, or rainfall etc. The key point is that all of this data is represented as a grid of (usually square) cells. The difference between a digital elevation model (DEM) in GIS and a digital photograph is that the DEM includes additional information describing where the edges of the image are located in the real world, together with how big each cell is on the ground. This means that your GIS can position your raster images (DEM, hillshade, slope map etc.) correctly relative to one another, and this allows you to build up your map.
How are latitude and longitude displayed in raster?
Latitudes and Longitudes in Raster data are displayed in the form of closed shapes where each pixel has a particular latitude and longitude associated with it.
What is vector raster?
In GIS, vector and raster are two different ways of representing spatial data. However, the distinction between vector and raster data types is not unique to GIS: here is an example from the graphic design world which might be clearer. Raster data is made up of pixels (or cells), and each pixel has an associated value.
What is vector data model?
vector data model: [data models] A representation of the world using points, lines, and polygons. Vector models are useful for storing data that has discrete boundaries, such as country borders, land parcels, and streets.
Do vectors need to be regularly spaced?
Note that whereas raster data consists of an array of regularly spaced cells, the points in a vector dataset need not be regularly spaced.

Vectors Models Are Points, Lines, and Polygons
Raster Types: Discrete vs Continuous
- Raster datais made up of pixels (also referred to as grid cells). They are usually regularly spaced and square but they don’t have to be. Rasters often look pixelated because each pixel has its own value or class. For example: Each pixel value in a satellite image has a red, green, and blue value. Alternatively, each value in an elevation map represents a specific height. It could represent anyt…
Vector Data Advantages and Disadvantages
- What are the advantages of using vector data?
Because vector data have vertices and paths, this means that the graphical output is generally more aesthetically pleasing. Furthermore, it gives higher geographic accuracy because data isn’t dependent on grid size. Topology rules can help data integrity with vector data models. Not only … - What are the disadvantages of using vector data?
Continuous data is poorly stored and displayed as vectors. If you want to display continuous data as a vector, it would require substantial generalization.Although topology is useful for vector data, it is often processing intensive. Any feature edits require updates on topology. With a lot of featu…
Vector vs Raster: Spatial Data Types
- It’s not always straightforward which spatial data type you should use for your maps. In the end, it really comes down to how the cartographer conceptualizes the feature on their map. 1. Do you want to work with pixels or coordinates?Raster data works with pixels. Vector data consists of coordinates. 2. What is your map scale?Vectors can scale objects up to the size of a billboard. B…
Spatial Data Structures
- Spatial data types provide the information that a computer requires to reconstruct the spatial data in digital form. In the raster world, we have grid cells representing real-world features. In the vector world, we have points, lines, and polygons that consist of vertices and paths. Vector and raster data both have their advantages and disadvantages. But don’t sweat it: Because you can conver…