
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction where only one parent is involved. The offspring produced is identical to the parent morphologically and genetically. Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, wherein a new plant is produced from the vegetative parts of a plant.
...
Difference between Vegetative Propagation and Spore Formation.
| Vegetative Propagation | Spore Formation |
|---|---|
| Vegetative propagation occurs through non-motile structures | Spores may be flagellated and motile |
What is vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative reproduction is an asexual reproduction method in plants. It uses parts of the parent plant to produce a new plant. Therefore, the newly developed plants are genetically identical to the parent plant.
What are the different types of vegetative propagation?
Different types of vegetative propagation include: This occurs when plants grow and develop naturally without any human interference. Natural vegetative propagation can be enabled by the development of adventitious roots. Thus, new plants may emerge from the roots, stem and leaves of the parent plant.
What are the disadvantages of vegetative reproduction in plants?
Thus, the new plants may become less healthy compared to the ones derived from sexual reproduction. One interesting fact of vegetative reproduction is that the plants that reproduce in this manner tend to reproduce sexually too and produce fruits and seeds. What is Asexual Reproduction?
How do plants propagate?
Plants propagate by stems, leaves or roots in this method. In simple words, vegetative reproduction refers to the plant propagation method which involves the use of a fragment or a part of a parent plant such as a leaf, a stem part or a root to make a new plant.
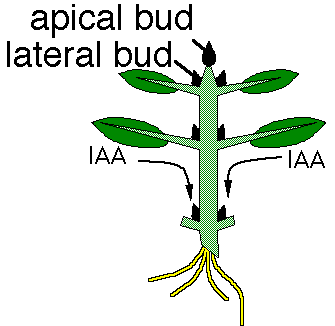
Is vegetative reproduction the same as vegetative propagation?
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules.
What is the difference between vegetative and?
The key difference between vegetative reproduction and asexual reproduction is that the vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction that uses a vegetative part of the parent to propagate while asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction that involves a single parent.
What are the 2 types of vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative propagation is grouped into the following two types: Natural vegetative propagation including reproduction by stem, leaf, and root. Artificial vegetative propagation includes reproduction by cutting, layering, grafting, and micro-propagation.
What is the difference between vegetative reproduction and budding?
Answer- Vegetative propogation- In this method, a new plant can be grown by the vegetative parts of a plant (stem, root, leaves). For eg- Bryophyllum plant can be grown by leaves, Rose plant from stem. Budding- In this method, a bud grows on the parent organisms and then it grows to a new organisms.
What is the difference between reproduction and propagation?
Sexual reproduction is the union of the pollen and egg, drawing from the genes of two parents to create a new, third individual. Sexual propagation involves the floral parts of a plant. Asexual propagation involves taking a part of one parent plant and causing it to regenerate itself into a new plant.
What is vegetative reproduction example?
Answer: The asexual reproduction where the vegetative part of the plant which give rise to a new plant is known as vegetative reproduction. Ginger is propagated by the rhizome. Chrysanthemum is propagated by stem cutting. Roots are used in vegetative propagation of sweet potato.
What is called vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of plant reproduction that occurs in its leaves, roots and stem. This can occur through fragmentation and regeneration of specific vegetative parts of plants.
What are the 3 types of vegetative propagation?
The most common types of artificial vegetative reproductive techniques include cutting, layering, grafting, suckering, and tissue culturing. These methods are employed by many farmers and horticulturists to produce healthier crops with more desirable qualities.
What are the 5 vegetative propagation?
The most common forms of vegetative propagation are grafting, cutting, layering, tuber, bulb or stolon formation, suckering and tissue culture.
Why is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is performed in the plants which do not have viable seeds or seeds which are dormant. Plants which have desirable superior traits are also vegetatively propagated because it results in producing identical plants.
What is the difference between vegetative and asexual?
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction where only one parent is involved. The offspring produced is identical to the parent morphologically and genetically. Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, wherein a new plant is produced from the vegetative parts of a plant.
What is vegetative and generative?
The generative cell produces two sperm cells, or male gametes, whereas the vegetative cell produces an elongated pollen tube, a gametophytic cell, to deliver the male gametes to the embryo sac.
What is generative and vegetative cells?
The generative cell undergoes a second mitosis to generate two sperm cells. The vegetative cell forms the pollen tube that delivers the sperm to the embryo sac. One sperm cell fertilizes the egg to produce the zygote, and the second sperm cell fuses with the central cell to produce the endosperm (3).
Is vegetative reproduction same as asexual?
vegetative reproduction, any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant or grows from a specialized reproductive structure (such as a stolon, rhizome, tuber, corm, or bulb).
What is vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction that takes place in plants. Plants propagate by stems, leaves or roots in this method. In simple words, vegetative reproduction refers to the plant propagation method which involves the use of a fragment or a part of a parent plant such as a leaf, a stem part or a root to make a new plant. ...
What is the difference between asexual and vegetative reproduction?
The key difference between vegetative reproduction and asexual reproduction is that the vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction that uses a vegetative part of the parent to propagate while asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction that involves a single parent. Reproduction ensures the continuation of living organisms.
What is the Difference Between Vegetative Reproduction and Asexual Reproduction?
It uses parts of the parent plant to produce a new plant. Therefore, the newly developed plants are genetically identical to the parent plant. Similarly, asexual reproduction too produces offsprings that are genetically identical to the parent. However, though both methods involve a single parent, in vegetative reproduction, the reproduction of offsprings occurs mainly through stems, roots, and leaves. Whereas, asexual reproduction can take place either via binary fission, budding, vegetative reproduction, spore formation, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, or agamogenesis. Hence, this is the key difference between vegetative reproduction and asexual reproduction.
What are the different types of asexual reproduction?
There are many types of asexual reproduction, and some of them are; binary fission, budding, vegetative reproduction, spore formation, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, and agamogenesis. Moreover, asexual reproduction is common in prokaryotes such as eubacteria and archaea. Besides, it is common among the fungi as well.
What is the purpose of reproduction?
Reproduction ensures the continuation of living organisms. There are two methods of reproduction; they are the sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves two organisms of opposite sex while asexual reproduction involves only a single parent. Plants show both sexual and asexual reproduction methods.
Is asexual reproduction genetically identical to the parent?
Similarly, asexual reproduction too produces offsprings that are genetically identical to the parent. However, though both methods involve a single parent, in vegetative reproduction, the reproduction of offsprings occurs mainly through stems, roots, and leaves.
Is asexual reproduction common in prokaryotes?
Moreover, asexual reproduction is common in prokaryotes such as eubacteria and archaea. Besides, it is common among the fungi as well. In adition to that, plants and some animals also show asexual reproduction together with sexual reproduction.
What is the same as vegetative propagation?
Vegetative forms of propagation in any type of living thing are basically the same as the ordinary growth and development of the organism, with the possibility of separation of the outgrowth.
What is vegetative reproduction?
vegetative reproduction is also known as asexual reproduction in which only a single parent is involved to give rise to new offSprings. these offsprings are so similar to their parents that they are termed as clones.
What is the difference between vegetative and sexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes whereas vegetative propagation is a asexual mode of reproduction by which new plants are produced by the old part of plant.
What is vegetative growth?
In single celled organisms vegetative growth is simply cell growth and division. The ploidy of the cell is maintained. There are organisms that can propagate apparently indefinitely as either haploids or diploids.
How do two parents contribute to sexual reproduction?
in sexual reproduction two parents are involved who give rise to different gamates which combine and give rise to an offspring. The offspring so produced has a different genetic makeup as well as is different in morphological features .
How does sexual reproduction work?
Sexual reproduction requires the doubling of the germ cell's DNA; then it divides into millions of body cells - a body which does its work.
What is the division of a cell to make another the same as itself?
All reproduction is division of a cell to make another the same as itself.
What is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, in which the cells do not split, but the reproduced organism grows from an extension of the parent plant, such as a runner or budding. Once a the reproduced plant is mature it can survive on its own without the the parent.
How does vegetative reproduction work?
The best example of vegetative reproduction is seen in the case of potato tubers which are the result of asexual reproduction. This is advantageous for those growing potatoes as they do not need any seeds for reproduction and can grow more potatoes to make more money from their business. However, one disadvantage of vegetative reproduction is that new plants grow close to the parent and also to each other fighting for nutrition from the soil. All of them have to share the same resources and also have to fight for light. This means that new plants become less healthy than is the case with sexual reproduction. In vegetative reproduction, a new plant grows from a vegetative part of the plant which is usually the stem. Bulbs, rhizomes, corms, runners are some of the examples of structures of vegetative reproduction.
What is the difference between asexual and vegetative reproduction?
vegetation reproduction is one of the type of asexual reproduction. in asexual reproduction there is no fusion of male nd female gametes.while in vegetation propagation reproduction takes place through vegetative parts like leaves, stem nd root .from these parts new individual can form.
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the formation of new individuals from the cell (s) of single parent . The offspring will be exact genetic copies of the parent except in specific cases of 'automixis'. It is very common in plants, less so in plants.
How does cell division work?
Cell division is how organisms grow and repair themselves. It is also how many organisms produce offspring. For many single-celled organisms, reproduction is a similar process. The parent cell simply divides to form two daughter cells that are identical to the parent. In many other organisms, two parents are involved, and the offspring are not identical to the parents. In fact, each offspring is unique. Look at the family in Figure below. The children resemble their parents, but they are not identical to them. Instead, each has a unique combination of characteristics inherited from both parents.
What happens when a parent cell splits into two identical daughter cells of the same size?
Binary fission occurs when a parent cell splits into two identical daughter cells of the same size.
What happens when a yeast cell breaks away from the parent cell?
Budding occurs when a parent cell forms a bubble-like bud. The bud stays attached to the parent cell while it grows and develops. When the bud is fully developed, it breaks away from the parent cell and forms a new organism. Budding in yeast is shown in Figure below.
What is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of plant reproduction that occurs in its leaves, roots and stem. This can occur through fragmentation and regeneration of specific vegetative parts of plants. Let us explore the different types of vegetative propagation and its examples in detail.
What is artificial vegetative reproduction?
Artificial Vegetative Propagation. This is a type of vegetative reproduction carried out by humans on the fields and laboratories. The most common types of vegetative reproduction occurring artificially include:
What are the structures of a plant that are vegetative?
The vegetative plant structures arising from the stem are known as rhizomes, bulbs, runners, tubers, etc.
What is the term for the stem of a plant that is bent to the ground and covered with soil?
Layering. In this, the stem of the plant is bent to the ground and covered with soil. Adventitious roots emerge from the plant parts covered with the soil. This attached stem with developing roots is known as a layer.
What is grafting in plants?
Grafting. In this, the cutting from some other plant is attached to the stem of plant rooted in the ground. The tissues of the graft become integrated with the tissues of the rooted plant and develop as a single plant over time.
Why are plant cells cultured?
In this, the plant cells from different parts of a plant are cultured in the laboratory to develop a new plant. This technique is helpful in increasing the number of rare and endangered plant species that are unable to grow under natural conditions.
