What is the difference between ventilation and breathing?
Apr 03, 2020 · Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing—inspiration (inhaling air) and expiration (exhaling air). External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the lungs and the blood. Oxygen diffuses into the blood, while CO 2 diffuses from the blood into the lungs. What is the difference between gas exchange and breathing? Breathing is the taking of air in …
What is the difference between intubation and ventilation?
As nouns the difference between breathing and ventilation is that breathing is the act of respiration; a single instance of this while ventilation is the replacement of stale or noxious air with fresh. As a verb breathing is .
Is intubation the same as ventilator?
Jan 27, 2022 · Breathing noun. Respiration; the act of inhaling and exhaling air. ‘Subject to a difficulty of breathing.’; Ventilation noun. The act of ventilating, or the state of being ventilated; the art or process of replacing foul air by that which is pure, in any inclosed place, as a house, a church, a mine, etc.; free exposure to air.
Are better breathing about breathing techniques?
Mar 18, 2020 · Breathing is a process of taking oxygen into the lungs while respiration is taking the oxygen from the lungs into the blood stream or to the cells. Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of lungs and gas exchange is the absorption of oxygen from the lungs and release of carbon dioxide.

Is ventilation the same as breathing?
What is the difference between ventilation rate and breathing rate?
What's the difference between ventilation and oxygen?
Why breathing is called ventilation?
What are the 4 types of breathing?
What is the difference between ventilation respiration and perfusion?
Should Covid 19 patients be ventilated?
What do ventilators do?
When should you ventilate a patient?
How do we ventilate our lungs?
Is ventilation the same as diffusion?
What is internal ventilation?
What is the process of breathing?
The bodily process of breathing; the inhalation of air to provide oxygen, and the exhalation of spent air to remove carbon dioxide.
Is breathing the same as ventilation?
is that breathing is the act of respiration; a single instance of this while ventilation is the replacement of stale or noxious air with fresh.
What is the difference between breathing and respiration?
Breathing is a process of taking oxygen into the lungs while respiration is taking the oxygen from the lungs into the blood stream or to the cells. Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of lungs and gas exchange is the absorption of oxygen from the lungs and release of carbon dioxide.
What is the exchange of air between the atmosphere and the lungs?
Ventilation: The exchange of air between the atmosphere and the lungs – achieved by the physical act of breathing. Gas Exchange: The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and bloodstream (via passive diffusion)
How is gas exchange maintained in the respiratory system?
Gas exchange is performed by the lungs by eliminating carbon dioxide, a waste product given off by cellular respiration.
How does ventilation work?
Simply put, ventilation is breathing – the physical movement of air between the outside environment and the lungs. Air travels through the mouth and nasal passages, then down the pharynx. Upon reaching the vocal cords, air flows into the trachea, transitioning from the upper airway into the lower airway. Here, it continues distally to the carina, then through the primary bronchi, various branches of bronchioles, and eventually arriving in the alveoli. This is inhalation. Air movement in a reverse pathway from alveoli to mouth and nose, is exhalation. Inhalation, followed by exhalation, equals one ventilation. This is what you observe (chest rise and fall) when determining the breathing rate.
What is the difference between inhalation and exhalation?
This is inhalation. Air movement in a reverse pathway from alveoli to mouth and nose, is exhalation. Inhalation, followed by exhalation, equals one ventilation. This is what you observe (chest rise and fall) when determining the breathing rate.
How does the volume of the lungs change?
So, how does the lung volume change? Quite simply, it is a combination of muscle contractions stimulated by the central nervous system, and the movement of a serous membrane within the thorax called the pleura. The pleura is made of two layers: a parietal layer that lines the inside of the thorax and a visceral layer that covers the lungs and adjoining structures (blood vessels, bronchi, and nerves). Between the visceral and parietal layers is a small, fluid-filled space, called the pleural cavity.
Why do we need to change the pressure in the alveoli?
These necessary changes in intrapulmonary pressure occur because of changes in lung volume.
Which structure is responsible for pulmonary ventilation?
Combining the function of all these structures, the pulmonary ventilation mechanism establishes two gas pressure gradients.
Where does the pleural cavity begin?
Between the visceral and parietal layers is a small, fluid-filled space, called the pleural cavity. The initiation of ventilation begins with the brainstem, where impulses (action potentials) generate within the medulla oblongata, then travel distally within the spinal cord.
Is internal respiration negatively influenced by disease?
Unfortunately, external and internal respiration can also be negatively influenced and inhibited by various disease processes. At the time of this article, the most notable respiratory pathology is caused by COVID-19, the coronavirus. View the YouTube video from the Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Sanjay Mukhopadhyay (found in the reference listings) to get a first-hand view of what COVID-19 does to the alveolar-capillary membrane.
What is the difference between respiration and ventilation?
The main difference between ventilation and respiration is that ventilation is the provision of fresh air into the lungs while respiration is the gas exchange between the body and the external environment. Lungs are the organs involved in both ...
What is the purpose of ventilation?
Ventilation is the provision of fresh air into the lungs. The conducting zones of the lungs are involved in ventilation. It includes nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchi, bronchial tree, and terminal bronchioles. Inspiration and expiration are the two events of ventilation. Inspiration and expiration are shown in figure 1.
How does respiration occur?
Respiration refers to the gas exchange between the body and the external environment. It occurs by diffusion based on the partial pressure differences of the respiratory gases – oxygen and carbon dioxide. The internal and and external respiration are the two types of respiration in the body. External respiration occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. When compared to the air in the alveoli, the partial pressure of oxygen is less, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is high in the blood. Therefore, oxygen from the atmospheric air diffuses into the blood while carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the air in the alveoli. Oxygen External respiration is shown in figure 2.
What is respiration based on?
Respiration: Respiration occurs based on the partial pressure differences of respiratory gases between blood and the atmospheric air or tissues.
What is atmospheric pressure?
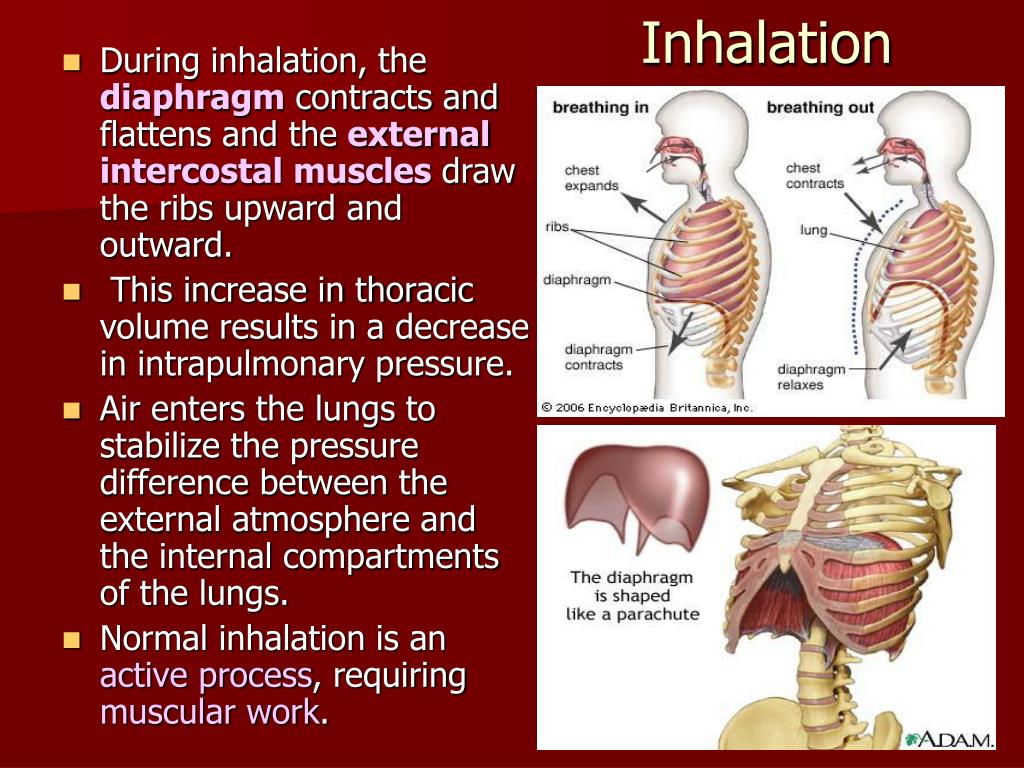
The atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. The increased volume of the lungs causes the reduction of pressure. It is achieved by the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. When the pressure goes down to 758 mm Hg, the atmospheric air comes into the lung. This is called inspiration.
Where does external respiration occur?
External respiration occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. When compared to the air in the alveoli, the partial pressure of oxygen is less, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is high in the blood.
Where do respiration and ventilation occur?
Both ventilation and respiration occur in lungs of most vertebrates.
What is the difference between intubation and ventilation?
Another difference between intubation and ventilation is that intubation can be a single step in the ventilation process.
What is the purpose of ventilation?
In common use, ventilation refers to any system that allows the replacement of gaseous substances with new gases, such as fresh air replacing stuffy air inside a building. In a healthy person's body, ventilation occurs when the lungs swap waste carbon dioxide for new oxygen-containing air. Artificial ventilation is any medical intervention that makes this process more efficient in people who are having trouble breathing. As a healthy person uses muscles to contract and relax the lungs to pull in and exhale breath, artificial ventilators need to produce some air under pressure to push the air in and take the waste gases back out again.
Why do doctors intubate the lungs?
For example, in the case of people who have lung conditions that make it hard to breathe, the intubation procedure can help doctors to remove excess mucus and other substances that block the lungs from getting enough oxygen. Often, the crossover between intubation and ventilation occurs when the doctor places a tube into the lungs with one end outside the body in order to use it as a channel for air to get into the body. This may be placed through an incision in the airway itself, or through natural openings such as the mouth.
What is the purpose of an intubation tube?
Other common areas of intubation include the hollow tunnel from the nose to the gastrointestinal tract, or the mouth to the gastrointestinal tract. The purpose of the tube may be to insert medicinal substances into a particular area, take samples from suspected areas of disease, or remove substances that are dangerous to health.
Do you need to intubate for ventilation?
Although intubation and ventilation may be included in the same medical procedure, some forms of ventilation do not necessitate intubation. In these cases, the patient does not have to have a tube inserted down through the entire airway, but can receive air through a different mechanism. A mask that covers the face and produces enough air pressure to fill and empty the lungs is one option, but this form of ventilation does not allow the patient to breathe as well if he or she tends to choke on vomit from the stomach.
What is the act of inhaling and exhaling?
Ventilation is the act or process of inhaling and exhaling. To evaluate the adequacy of ventilation , a provider must exercise eternal vigilance. Chest rise, compliance (as assessed by the feel of the bag-valve mask), and respiratory rate are qualitative clinical signs that should be used to evaluate the adequacy of ventilation.
When monitoring ventilation and oxygenation in the prehospital environment, should capnography be combined with pulse oximetry?
Ideally, when monitoring ventilation and oxygenation in the prehospital environment, capnography should be combined with pulse oximetry. With capnography, providers are able detect respiratory insufficiency early and are able to institute early interventions, thereby preventing arterial oxygen desaturation.
What is the process of adding oxygen to the body system?
Oxygenation refers to the process of adding oxygen to the body system. There is no way to reliably measure arterial oxygenation via clinical signs alone. Cyanosis, pallor and other physical findings are not reliable.
What is the difference between a respirator and a ventilator?
Typically, a ventilator is a a device used to maintain artificial breathing or circulate fresh air, while a respirator is a mask used to protect the wearer from particulates in the air.
What is a ventilator?
The first definition we give for ventilator is the word's original sense, in use since the first half of the 18th century: "a device for introducing fresh air or expelling foul or stagnant air.".
What does a respirator mean?
However (and here we should note that however, although not defined as such, often functions as a word signifying that confusion is soon upon us), the second definition we give for respirator is "a device for maintaining artificial respiration; ventilator (sense b)." Why would we do such a thing? Because people have been using respirator to mean ventilator for a very long time. The 'mask' sense of respirator is older, dating to the first half of the 19th century, but the 'device' (or 'ventilator') sense of this word is almost as old, in use since the 1850s.
Why do people use respirators?
Because people have been using respirator to mean ventilator for a very long time. The 'mask' sense of respirator is older, dating to the first half of the 19th century, but the 'device' (or 'ventilator') sense of this word is almost as old, in use since the 1850s.
What is the numerical rating of a respirator?
A numerical rating (such as 95 or 99) is sometimes assigned to such a respirator to indicate the percentage of particles filtered.
Is it confusing to use a respirator and a ventilator?
It can be confusing, as both words are concerned with breathing, or respiratory functions, and there is quite a bit of semantic overlap. If you are concerned about misuse simply restrict your use of respirator to the mask that protects the wearer (and others), and that of ventilator to the device that assists in breathing .