The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known fo…RNA
What are the pentose sugars present in DNA and RNA?
The pentose sugars that are present in DNA are deoxyribose. And RNA has ribose sugar, which is a pentose sugar. Ribose sugar is one more –OH group than deoxyribose. Phosphate residues are attached to a 5’ carbon hydroxyl group of sugar and a subsequent nucleotide to a 3’ carbon hydroxyl group of sugar, forming a 5’-3’ phosphodiester (1). 1.
What type of sugar is present in DNA and RNA?
The sugar present in DNA and RNA is mainly pentose sugar. There are mainly two bases of nucleic acids. These are DNA and RNA. The pentose sugars that are present in DNA are deoxyribose. And RNA has ribose sugar, which is a pentose sugar. Ribose sugar is one more –OH group than deoxyribose.
What is the difference between nucleotide and RNA?
The nucleotide is composed of nucleic acid, a phosphate, and lastly a sugar. The sugar that is found in the DNA is called deoxyribose while the sugar found inside the RNA is called as ribose. The sugar portion of the DNA and RNA are the same.
What is the difference between DNA RNA and ribose?
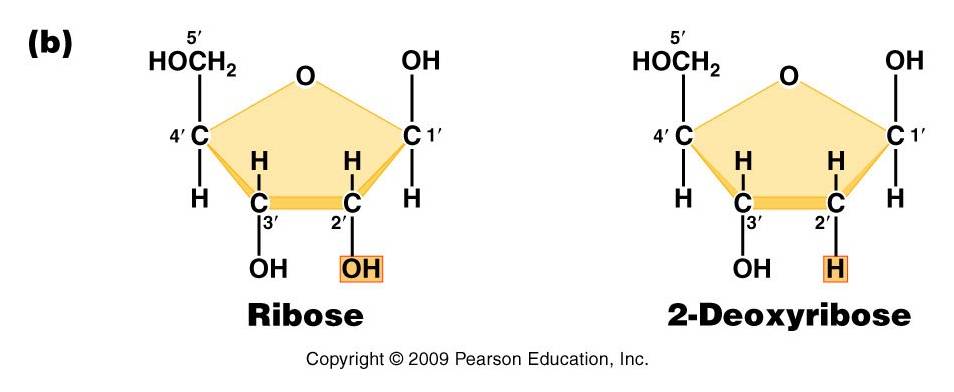
Summary of Differences Between DNA and RNA. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. The only difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that ribose has one more -OH group than deoxyribose, which has -H attached to the second (2') carbon in the ring.

What pentose sugar does RNA have?
β-d-riboseThe sugar portion of oligonucleotides is a five-carbon pentose occurring in one of two forms. In RNA, it is β-d-ribose in a ring structure. In DNA, the monosaccharide is β-d-2-deoxyribose, wherein the number 2′ carbon of the ring lacks a hydroxyl group.
What is the difference between the sugar in DNA deoxyribose and RNA ribose )?
DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. The only difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that ribose has one more -OH group than deoxyribose, which has -H attached to the second (2') carbon in the ring. DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
Do DNA and RNA have the same pentose?
DNA contains A, T, G, and C whereas RNA contains A, U, G, and C. The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, and in RNA, the sugar is ribose (Figure 2.7. 1). The difference between the sugars is the presence of the hydroxyl group on the second carbon of the ribose and hydrogen on the second carbon of the deoxyribose.
What type of pentose sugar is found in DNA?
DeoxyriboseDeoxyribose is the pentose sugar found in this type of polynucleotide, hence its name Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA. The nitrogenous bases found in DNA are, adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
What type of sugar is in DNA and RNA?
Sugar. Both DNA and RNA are built with a sugar backbone, but whereas the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (left in image), the sugar in RNA is called simply ribose (right in image).
What are the basic difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its own.
What type of sugar does RNA use?
Unlike DNA, RNA is usually single-stranded. Additionally, RNA contains ribose sugars rather than deoxyribose sugars, which makes RNA more unstable and more prone to degradation. RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase during a process called transcription.
How does RNA differ from DNA quizlet?
How is RNA different from DNA? RNA is different from DNA is three ways: (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose not dioxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded and not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
Which of the following best describes a structural difference between DNA and RNA?
Which of the following best describes a structural difference between DNA and RNA? The backbone of DNA contains deoxyribose, whereas the backbone of RNA contains ribose.
What is the role of pentose sugar in DNA?
Introduction. Pentose sugar is a component of nucleotides. Nucleotides are biological molecules that act as monomers and as subunits of DNA and RNA. These biological molecules carry energy packets to the cell in the form of nucleoside triphosphate (ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP), which play a key role in metabolic processes.
What are the roles of pentose in DNA and RNA molecules?
Pentoses are carbohydrates made of five carbons. The DNA molecule is made of a sequence of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is formed by the association of one pentose called deoxyribose with phosphoric acid and a nitrogen-containing base A T C or G. RNA is also formed by a sequence of nucleotides.
Which of the following is found in RNA but not in DNA?
. uracilAnswer and Explanation: The nitrogenous base that is found in RNA but not in DNA is c. uracil. Additionally, RNA contains a sugar known as ribose.
What is the difference between a deoxyribose sugar and a ribose sugar?
The structure of Ribose and Deoxyribose is almost identical with just one difference. Ribose sugar has a hydroxyl (OH) group at position 2, whereas deoxyribose sugar has a hydrogen (H) atom at position 2. Due to this, deoxyribose sugar is more stable than ribose sugar.
What is the primary difference between ribose sugar and deoxyribose sugar quizlet?
what is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose? Both are sugars the only difference is deoxyribose is lacking oxygen. Can tell the difference by looking at the 2' carbon. If there is an OH bonded to it is ribose and deoxyribose has just a H.
What is ribose sugar in DNA?
ribose, also called D-ribose, five-carbon sugar found in RNA (ribonucleic acid), where it alternates with phosphate groups to form the “backbone” of the RNA polymer and binds to nitrogenous bases.
Is ribose in DNA or RNA?
Unlike DNA, RNA in biological cells is predominantly a single-stranded molecule. While DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose, characterised by the presence of the 2′-hydroxyl group on the pentose ring (Figure 5).
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
1.Deoxyribose is the sugar found in DNA while ribose is the sugar found in RNA. 2.Ribose has more hydroxyl atoms than deoxyribose. 3.Ribose is also called D-ribose while deoxyribose is also called 2-deoxyribose and dideoxyribose. 4.Ribose was discovered in 1891 while deoxyribose was discovered in 1929.
What is DNA information?
As our basic knowledge regarding genetics increases, DNA holds the necessary information about our genes. It contains the genetic makeup that we inherited from our parents, grandparents, great-grandparents, and so on and so forth.
Why is ribose important?
Ribose is also needed by ATP and NADH. These compounds need Ribose for phosphorilation. In the process of phosphorilation, ribose is turned into a functional sugar. Our human body forms ribose through sugar.
When was deoxyribose discovered?
Deoxyribose, on the other hand, was discovered by Phoebus Levene during 1929. Deoxyribose is also called as 2-deoxyribose and dideoxyribose. Deoxyribose is considered a monosaccharide. Ribose is available in the market. It is manufactured in the form of tablets, powders, and other forms.
How is DNA arranged in a cell?
It is arranged into chromosomes. Each cell contains a DNA plus the genetic information. Before a cell undergoes division or replication, the DNA also divides. Then the protein that is required undergoes the process of transcription in the form of RNA.
Which molecule contains more oxygen, hydrogen, and hydroxyl?
However, ribose contains more oxygen, hydrogen atoms also known as hydroxyl. This is the major difference between the two. Ribose was discovered in 1891 by Emil Fisher. Ribose is also known as D-ribose. Ribose is very needed in the process of transcription which is stated in the second paragraph.
Is DNA the same as RNA?
The DNA and RNA have reoccurring nucleotide units. The nucleotide is composed of nucleic acid, a phosphate, and lastly a sugar. The sugar that is found in the DNA is called deoxyribose while the sugar found inside the RNA is called as ribose. The sugar portion of the DNA and RNA are the same.
What are the bases of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA base pairing is slightly different since DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine; RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Uracil differs from thymine in that it lacks a methyl group on its ring.
Why is RNA more reactive than DNA?
The O-H bond in the ribose of RNA makes the molecule more reactive, compared with DNA. RNA is not stable under alkaline conditions, plus the large grooves in the molecule make it susceptible to enzyme attack. RNA is constantly produced, used, degraded, and recycled.
Why does DNA evolve if RNA exists?
The most likely answer for this is that having a double-stranded molecule helps protect the genetic code from damage. If one strand is broken, the other strand can serve as a template for repair.
What is double stranded RNA?
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) sometimes occurs. It is similar to DNA, except thymine is replaced by uracil. This type of RNA is found in some viruses. When these viruses infect eukaryotic cells, the dsRNA can interfere with normal RNA function and stimulate an interferon response.
What is the molecule that stores genetic blueprints?
RNA is used to transmit genetic information in some organisms and may have been the molecule used to store genetic blueprints in primitive organisms. B-form double helix. DNA is a double-stranded molecule consisting of a long chain of nucleotides. A-form helix.
What is the function of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA perform different functions in humans. DNA is responsible for storing and transferring genetic information, while RNA directly codes for amino acids and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins.
What is the most common form of DNA?
While the most common form of DNA is a double helix. there is evidence for rare cases of branched DNA, quadruplex DNA, and molecules made from triple strands. 2 Scientists have found DNA in which arsenic substitutes for phosphorus. 3
What is the difference between pentose sugars and RNA?
The difference between the pentose sugars of DNA and RNA is that ribonucleic acids contain one hydroxyl group, whereas deoxyribonucleic acid contains only one hydrogen atom.
What are the two types of pentose sugars?
There are two types of pentose sugar found in nucleic acid. These are ribose sugar and deoxyribose sugar. They have a five-membered ring in their structure. In addition to pentose sugar, a nucleic acid contains a nitrogenous base and phosphorus group. When the base is combined with this sugar, a nucleoside is formed, such as deoxyadenosine, adenosine guanosine, etc.
What are the bases of nucleic acids?
There are mainly two bases of nucleic acids. These are DNA and RNA. The pentose sugars that are present in DNA are deoxyribose. And RNA has ribose sugar, which is a pentose sugar. Ribose sugar is one more –OH group than deoxyribose. Phosphate residues are attached to a 5’ carbon hydroxyl group of sugar and a subsequent nucleotide to a 3’ carbon hydroxyl group of sugar, forming a 5’-3’ phosphodiester (1).
What is ribose sugar?
2. Ribose sugar, a type of pentose sugar, is very important for photosynthesis, respiration, and nucleic acid synthesis.
What is the link between nitrogen and carbon in purine nucleoside?
On the other hand, in purine nucleoside, the link is between nitrogen atom 9 of purine and carbon atom 1’ of the pentose sugar. When a pentose sugar residue of a nucleoside is esterified with phosphoric acid then nucleotide is formed (1) & (2).
How are nucleotides formed?
Nucleotides are formed by combining a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group with pentose sugar. The main polymer of nucleotides is nucleic acid. This sugar is found only after the hydrolysis of nucleic acids.
Why are nucleic acids important?
Nucleic acids naturally act as molecules that carry primary information in cells. In nucleic acids, this sugar and phosphates are connected to each other in an alternative chain (sugar-phosphate backbone) by phosphodiester connection. So it is very important as a component of nucleotides. Below is a description of its structure and function (3) & (4).
What is the sugar in DNA called?
Both DNA and RNA are built with a sugar backbone, but whereas the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (left in image), the sugar in RNA is called simply ribose (right in image).
What are the bases of DNA?
Bases. The nitrogen bases in DNA are the basic units of genetic code, and their correct ordering and pairing is essential to biological function . The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
What is the process of bringing amino acids to the protein factories?
Transfer RNA ( tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation.
What is the purpose of DNA?
DNA encodes all genetic information, and is the blueprint from which all biological life is created. And that’s only in the short-term. In the long-term, DNA is a storage device, a biological flash drive that allows the blueprint of life to be passed between generations 2. RNA functions as the reader that decodes this flash drive.
How many strands does DNA have?
DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands.
What is the most important molecule in cell biology?
December 18 2020. | by Ruairi J Mackenzie, Editor for Technology Networks. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA) are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. They are both linear polymers, consisting of sugars, phosphates and bases, ...
What are the different types of RNA?
What are the three types of RNA? 1 Messenger RNA ( mRNA) copies portions of genetic code, a process called transcription, and transports these copies to ribosomes, which are the cellular factories that facilitate the production of proteins from this code. 2 Transfer RNA ( tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation. 3 Finally, Ribosomal RNA ( rRNA) is a component of the ribosome factory itself without which protein production would not occur 3.
