
Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, unlike prokaryotes, which have no membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes belong to the domain Eukaryota or Eukarya. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ and κάρυον. Eukaryotic cells also conta…
Prokaryote
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό "before" and κάρυον "nut or kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species wit…
What does the plasma membrane do in a prokaryotic cell?
What does the cell membrane do in a prokaryotic cell? The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that surrounds the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell. It physically separates the cytoplasm from the outside environment. The plasma membrane also works as a selectively permeable, or semipermeable, barrier that controls what enters and exits the cell.
Does a prokaryotic cell have a plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a double layer of lipids that separates the cell interior from the outside environment. This double layer consists largely of specialized lipids called phospholipids.
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Well, to summarise, prokaryotic cells are unicellular micro-organisms, whereas eukaryotic cells are multi-cellular organisms. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells, while there is no nuclei present in prokaryotic cells.
What are the functions of the plasma membrane in eukaryotes?
What is Plasma Membrane?
- Structure of Plasma Membrane. A plasma membrane is mainly composed of carbohydrates, phospholipids, proteins, conjugated molecules, which is about 5 to 8 nm in thickness.
- Functions of the Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane functions as a physical barrier between the external environment and the inner cell organelles.
- Facts about Plasma Membrane. ...
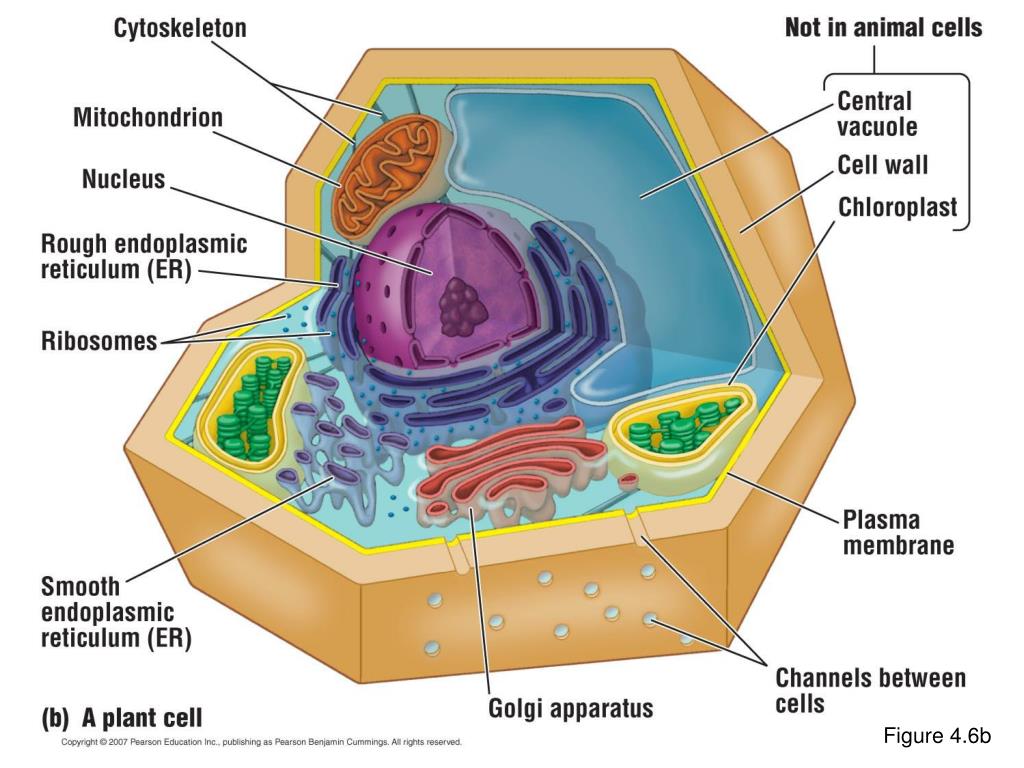
What is the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
1: Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane: The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids. Cholesterol, also present, contributes to the fluidity of the membrane.
What is plasma membrane in prokaryotic cell?
The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that surrounds the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell. It physically separates the cytoplasm from the outside environment. The plasma membrane also works as a selectively permeable, or semipermeable, barrier that controls what enters and exits the cell.
Do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a plasma membrane?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a double layer of lipids that separates the cell interior from the outside environment. This double layer consists largely of specialized lipids called phospholipids.
Is a cell membrane prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Instead, their DNA floats around inside the cell. Eukaryotes are single-celled (unicellular) organisms. Bacteria and Archaea are the only prokaryote....Prokaryotic Cells.Prokaryotic CellsEukaryotic CellsMembrane-Bound OrganellesNoYesExamplesBacteriaPlants, animals, fungi2 more rows•May 24, 2021
What are the plasma membrane?
Definition. The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface.
What is the function of plasma membrane?
The main function of plasma membrane is that it acts as a physical barrier between the external environment and the inner cell organelles. The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane, which permits the movement of only certain molecules both in and out of the cell.
Why is plasma membrane called?
The plasma membrane is called as selectively permeable membrane because it regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It means that the plasma membrane allows some material to pass through it while at the same time it blocks other material from entering through it.
What is plasma membrane structure?
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments.
What is a Prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-...
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucle...
Define Cell?
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organ...
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes ar...
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells have several unique features. Listed below are some important features: In structure, both animal and plant cells are q...
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and are involv...
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was first discovered in the year 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and...
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Scientists speculate that these organisms gave rise to the eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.
What is the meaning of eukaryotic cell?
The term “ Eukaryotes ” is derived from the Greek word “ eu “, (meaning: good) and “ karyon ” (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to “ good or true nu clei .”. Eukaryotes are more complex and much larger than the prokaryotes. They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
What are the structures that help in cellular respiration?
It is also one of the smallest components within the cell. Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assist in cellular respiration.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
The nucleus contains DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial role in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the creation of energy, which is then utilized by the cell.
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Right below the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides strength and rigidity to the cell. Further down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside environment. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also one of the smallest components within the cell.
What are the biotic components of the environment?
Biotic components of the environment include all forms of life from minute bacteria to towering giant Sequoias. However, at the microscopic level, all living organisms are made up of the same basic unit – the cell.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic plasma membranes?
There are many differents in between eukaryotic and prokaryotic plasma membranes;They are, 1)The size of prokaryotic cells is typically 0.2-2.0 micrometer in diameter while eukaryotic cell is 10-100 micrometer in diameter. 2)Eukaryotes are called to have ‘true nucleus’ because it contains membrane-bound nuclei and consists ...
What is the cell membrane of an eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cell membrane is basically trilamellar with double layer of phospholipid. It is asymmetrical. It has intrinsic and extrinsic proteins that also help in transport across membrane. It has other components like cholesterol to maintain fluidity of membrane.
What are the structures in the prokaryotic cell wall?
Prokaryotic cell wall have structures called mesosomes in them which are somewhat like enfolding so. They are involved in some physiological functions of prokaryotes too
Why are eukaryotes called true nuclei?
2)Eukaryotes are called to have ‘true nucleus’ because it contains membrane-bound nuclei and consists of other organelles while prokaryotes does not have nuclear membrane or other membrane enclosed organelles.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane:-. The cell membrane is a type of plasma membrane that encloses the entire contents of a cell, including the cytoplasm and all the organelles. The cell membrane is not always the outermost layer of the cell since plant cells also have a cell wall that further encloses the cell membrane.
How does cell division occur in prokaryotes?
3)In prokaryotes, the cell division occurs via binary fission and no meiosis takes place but only transfer of DNA fragments occurs via conjugation. Cell division in eukaryotes occurs through mitosis and sexual reproduction occurs through meiosis.
Which cell has a cell envelope?
Most prokaryotic cells especially bacterial cells have cell envelope which consists of tightly bound three layered structure ,- glycocalyx,cell wall and plasma membrane which all together serve as protective unit
What is the cell membrane of a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell membrane is actually a fluid phospholipid bi-layer submerged with proteins. The cell membranes of prokaryotic cells have two phospholipid layers. A prokaryotic cell membrane is a thin lipid bilayer. The thickness of the prokaryotic cell membrane is about 7 nm.
How small is a prokaryotic cell?
4. The size of the prokaryotic cell is very small (0.05 to 10µm).
What are the cells of an organism?
There are many species of organisms on earth. The body of all these organisms is made up of tiny billions of cells that cannot be seen with the naked eye. In 1665 scientist Robert Hooke first discovered the cell. The cells are arranged one on top of the other to form organisms. The size of a cell is about 0.1 micrometer to 100 micrometers. The unicellular smallest cell is mycoplasma galliseticum. The diameter of the smallest cell is about 10 micrometers. Cells are the building blocks of an organism’s body. On the basis of the nucleus, the cells are classified into two types eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. The structure of all cells is different. As an example, eukaryotic cells are composed of cell walls, cell membranes, nucleus, cytoplasm, and some cell organelles located in the cytoplasm. On the other hand, prokaryotic cells are composed of capsules, cell walls, cell membranes, cytoplasm, genetic material, pili, and flagella. Each cell has a specific cell membrane. The cell membrane of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is the topic of the discussion below (3).
What is the plasma membrane?
The plasma or cell membrane is semipermeable, quasi-fluid, and dynamic. This plasma membrane separates the prokaryotic cell from the surrounding environment. The prokaryotic cell membrane is made of 40% lipids and 60% proteins and no cholesterol. The prokaryotic cell membrane consists of monounsaturated fatty acids. The phospholipid layer has two ends, the head part is of glycerol and the tail part consists of two molecule fatty acids. The head is called polar hydrophilic ends and the tail is called non-polar hydrophobic ends. The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells folds inwards to form mesosomes (4) & (3).
What is the meaning of the word "eukaryotic"?
The eukaryotic word comes from two Greek words Eu and karyon. The word Eu means, “well” or “good” and the karyon means, “nut” or “kernel”.
Which type of cell has ribosomes?
5. The ribosomes of eukaryotic cells are large in size. And ribosomes of both 70s and 80s types are present in eukaryotic cells.
Which cell membrane controls diffusion and osmosis?
2. The process of diffusion and osmosis of cells is controlled by the prokaryotic cell membrane.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Differences in Organization. Prokaryotic cells engage in reproduction through a process of cell division called binary fission. Eukaryotic cells use a different process of cell division called mitosis, which involves a constant cycle of cell growth and development.
Why are prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells?
The reason for the difference in cell sizes between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells belongs to the different structure and organization between the two types of cells. The lack of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotes might be the most noticeable difference. While eukaryotic cells contain organelles enclosed in membranes – two examples ...
What are the two main categories of cells?
All of these cells, whether they operate as a solitary bacterial cell or as part of a complex system such as the human body, can be sorted into two main categories: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells .
How do eukaryotes reproduce?
Eukaryotes reproduce sexually through meiosis, which allows for genetic variance. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, copying themselves. Despite this, gene transfer processes still allow for genetic variance. One of these is transduction in which viruses move DNA from one bacterium to another.
Which is larger, prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes include larger, more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis.
How is genetic variance transferred?
In this process, genes are transferred from one bacterial cell to another by means of viral cells. The viruses grab the plasmids from one bacterium and transfer it to another bacterial cell.
Which domain has eukaryotic cells?
Eukarya. The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotes, while the organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells. The Archaea domain has subcategories, but scientific sources differ on whether these categories are phyla or kingdoms. They are:
Answer
eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not
New questions in Biology
Fill in the missing words Typos are created as a cell copies its dna before dividing. A base could be added or ____ Our cells can fix most typos befor … e cell division.
