
Difference Between Pronation and Supination
- In the forearm, supination of the radio-ulna joint makes the palm facing forward or upward, whereas pronation of the same joint makes the palm facing backward or downward.
- Supination is stronger than pronation.
- In the forearm, the muscles called pronator teres and pronator quadratus are active in pronation. ...
How to tell if you over or under pronate?
- Stand with your heels together and your feet turned out like a duck.
- Try your best to move your legs outward using your glute muscles and tilting your pelvis under your body. ...
- You may hold this position for 30 seconds.
How to tell if you pronate?
- Stand a few feet away from a wall.
- Bend your front knee as you place one of your feet behind you to stretch your calf muscle.
- Rest your hands on the wall in front of you.
- If you haven’t already, try to slowly lower your back heel to the ground.
- Hold this position for up to 20 seconds before repeating on the other side.
How to determine pronation?
WHAT IS PRONATION AND WHY DOES IT MATTER?
- Underpronators (supinators) need a lot of cushioning to avoid strong impact
- Neutral pronators can wear a wide variety of shoes
- Overpronators should look for support or structured cushioning shoes
Do you pronate or supinate?
Pronation Vs. Supination. Generally speaking, pronation and supination are two common terms used to identify the upward and downward direction of your foot, arm, or hand. For example, when your forearm and palm are facing up, then it is supinated. On the other hand, you have pronation when your forearm and palm are facing down.
What is the difference between Overpronation and pronation?
Pronation is natural and happens because your feet naturally roll inward when walking. It becomes a problem when you overpronate, meaning your feet roll in excessively. This causes the arches of your feet to flatten out over time. Overpronation is shown by uneven wear on the inside part of a shoe's sole.
How do you know if you are a pronator or Supinator?
Look at the soles of your shoes and identify the areas where the wear is most pronounced. If the outer part of your sole is the most worn out, then you are a supinator, like about 10% of the population. If it is the inner part of your sole that is the most worn out, then you are a pronator, like 45% of the population.
What is supination example?
Supination is the movement in which a person turns their hand, wrist, and forearm upward. Turning your hand over to receive money is an example of supination.
What is pronation movement?
Pronation is the natural movement of the foot when it rolls inward. Thus, when walking, the foot tends to roll in a way that the weight of the body is more on the inner side of the foot. It is the normal side-to-side movement of the foot while running or walking.
How do I know my pronation?
A quick and easy way to see if you overpronate is to look at the bottom of your shoes for signs of wear and tear. If most of the wear is on the inside sole near the ball of the foot and near the big toe, there's a good possibility that you overpronate.
How do I know my pronation type?
Here are three simple ways to test for pronation that won't cost a dime: Look at your running shoes. If they show a lot of wear along the inner edge of the sole, you likely have flat feet and overpronate. If the wear is worse along the outside edge, you may have high arches and supinate (underpronate).
What is pronation example?
Supination and pronation are terms used to describe the up or down orientation of your hand, arm, or foot. When your palm or forearm faces up, it's supinated. When your palm or forearm faces down, it's pronated.
What is a pronation shoe?
Finding yours is the first step towards finding the right running shoes. Pronation refers to the way your foot rolls inward for impact distribution upon landing.
What is a pronated foot?
Pronation is a natural and normal movement of the foot that occurs during foot landing while running or walking. Simply put, it's your ankle and arch rolling or tipping inwards slightly, creating some shock absorption as your foot hits the ground after each step.
What is supination of foot?
Foot supination happens when you don't use the proper muscles to walk correctly. People who develop this issue struggle with pushing or activating the right muscles in their feet as they walk. It could be due to a number of factors, but usually, it's caused by a muscle imbalance in the feet.
How do you remember pronation and supination?
0:291:21Supination vs Pronation of the Hand - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou're turning it so your palm is facing upwards. Pronation. You are turning your hands to your palmMoreYou're turning it so your palm is facing upwards. Pronation. You are turning your hands to your palm faces downwards. This would be a pronated hand and this would be a supinated. Hand.
What causes supination?
What causes supination of the foot? Supination is usually a result of an inherited problem with the structure of your foot. In other words, it may run in families. Supination may also be caused by weakness in certain muscles of your foot, ankle, and leg.
Can Overpronation or Underpronation Be Fixed?
There are exercises that can help you to avoid injuries related to overpronation or underpronation. For instance, those who pronate can do calf rai...
Is There a Test That Indicates If I Excessively Pronate or Supinate?
The wet foot test can help you to determine if you overpronate or underpronate. Wet your foot and step onto an absorbent surface, like concrete or...
Can Overpronation or Underpronation Be a Problem in the Forearm?
When pronation or supination is a problem in the forearm, it’s usually due to a limitation of rotation, rather than an excess. Normal forearm rotat...
Overpronation Foot Definition
According to WebMD, overpronation is an abnormal movement where the foot rolls too far inwards with each step. It predisposes one to injuries on the medial side of the foot. It also causes alignment issues of the body from the foot, ankle, knees, hips and back.
Supination Foot Definition
Now supination is a movement where the foot rolls outward or moves outward. With each step, it’s rolling your bodies weight to the outer edges (pinky toe side) of your feet.
How do I know if I have Supination vs Pronation?
The most common way to understand these movements is by how much pressure you feel on your foot. Where do you feel this pressure at?
Symptoms of both overpronation and supination
Plantar Fasciitis This is a medical condition where the plantar fascia tendons becomes damaged or inflamed due to excess use or repeated use on one side of the foot or heel causing the tendons to become over stretched or over used.
Orthotics for Over Pronation
Custom orthotics ARE RECOMMENDED for people who need to correct mild to moderate pronation as well as for people who need more pronounced correction of pronation.
Supination vs Pronation Conclusion
To end, if you suffer from either over pronation or supination know you are not alone. These affect millions of your neighbors. Both are issues that can be improved upon with custom orthotics. Millions of people have received relief going this route.
What is the opposite of pronation?
Supination, quite simply, is the opposite of pronation. Whereas pronation refers to an inward rolling of the foot, supination is an outward rolling that causes the foot to rise above the ground as you walk. Oversupination can place excessive strain on the ankle and outer toes, causing the ankle to roll or sprain.
What does "pronation" mean in a foot?
If you’ve never had a foot injury before, you might not be familiar with the terms “pronation” and “supination,” which refer to the foot’s natural inward and outward movements when walking or running. These movements enable the feet and ankles to move properly and absorb the forces imposed upon them without injury.
Why does my foot roll inward?
If the foot rolls inward at a greater degree, it can places excessive weight on the side of the foot, increasing your risk of injury. Overpronation can have a number of causes, but it’s often related to the shape of your foot’s arch. People with flat feet, for example, are much more likely to suffer from overpronation than people with higher arches.
What is the tendency of the foot to roll inward?
PRONATION. From a medical perspective, pronation is the foot’s tendency to roll inward as it makes contact with the ground. For most people, the foot should roll inward by 15% or less, so that the entire foot briefly touches the ground before you push off from it.
Why does my ankle roll?
Oversupination can place excessive strain on the ankle and outer toes, causing the ankle to roll or sprain. Oversupination is usually associated with high runner’s arches and other hereditary traits. Weak, underdeveloped, misaligned muscles can also contribute to excessive supination, as can ill-fitting footwear.
Can wearing shoes cause overpronation?
Wearing the wrong type of shoes can exacerbate overpronation, though it’s rarely a cause of it. Overpronation can make you more prone to chronic conditions like Achilles tendonitis , plantar fasciitis, or bunions, particularly if you’re an avid runner. Be sure to thoroughly stretch your feet before running or exercising, ...
Do feet pronate or supinate?
Some people, however, may find that their feet pronate or supinate more than they should, leaving them with an awkward or painful gait. Here’s what you need to know about the differences between pronation and supination, and how to seek appropriate care. PRONATION. From a medical perspective, pronation is the foot’s tendency to roll inward as it ...
What is pronation in running?
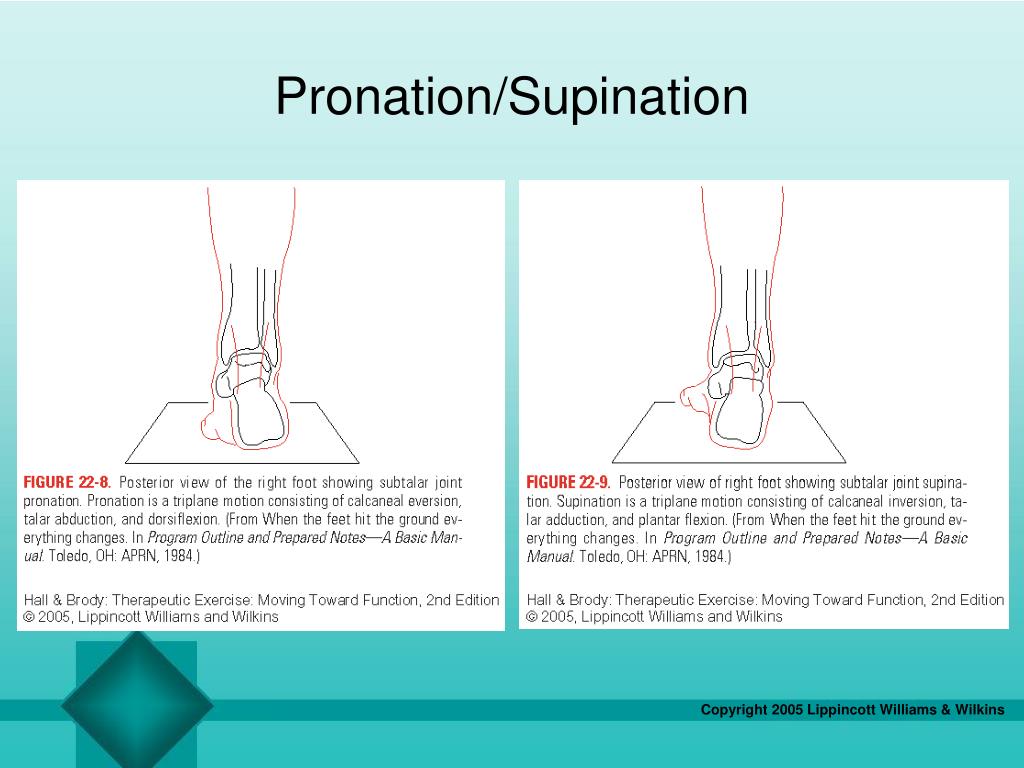
Anatomically, pronation of the foot is a combination of three movements—eversion, abduction, and dorsiflexion— in three different planes of motion (Norris, 2011). People frequently describe this combination of movements as the “rolling inward” of the foot while walking or running. This motion is a normal part of gait when walking and running, and individuals typically roll their feet inward about 15 percent ( What Every Runner Needs to Know About Pronation, 2018). Pronation is important because it assists with absorbing forces transmitted through the foot and aids in forefoot push-off (Dhillon et al., 2018; Every Runner Needs to Know, 2018).
Why is pronation important?
Pronation is important because it assists with absorbing forces transmitted through the foot and aids in forefoot push-off (Dhillon et al., 2018; Every Runner Needs to Know, 2018). However, if pronation occurs too quickly or too fast, this causes overpronation (Lowe & Chaitow, 2009).
Which is stronger, pronation or supination?
Pronation vs Supination. • In the forearm, supination of the radio-ulna joint makes the palm facing forward or upward, whereas pronation of the same joint makes the palm facing backward or downward. • Supination is stronger than pronation. • In the forearm, the muscles called pronator teres and pronator quadratus are active in pronation.
Where do pronation and supination occur?
In forearm, pronation and supination occur at synovial pivot joints at the proximal and distal ends of radius and ulna.
What muscles are involved in pronation?
Pronation involves two muscles; pronator teres and pronator quadratus. The pronator teres crosses the anterior forearm from the medial side of elbow and extends halfway down to lateral shaft of the radius. The pronator quadratus is located just above the wrist, passing transversely between the lower anterior shaft of the ulna and radius.
What is pronation in a hand?
Pronation rotates the hand to face downwards so that the radius and the ulna of the forearm are crossed. It puts the palm of the hand on a flat surface. For example, pronation involves when pouring something from a jug. Pronation involves two muscles; pronator teres and pronator quadratus.
Which muscle is involved in supination movements against resistance?
The biceps brachii is involved in supination movements against resistance by pulling on the radial turberosity to rotate the radius. The supinator is involved in slow movements of supination, such as when arms hang by sides.
Which muscle is most active in supination?
This motion is more powerful than pronation. Turning a screw is an example for supination. There are two basic muscles active in supination; namely, biceps brachii and supinator.
Where is the pronator quadratus located?
The pronator quadratus is located just above the wrist, passing transversely between the lower anterior shaft of the ulna and radius. Many pronation movements are made by the pronator quadratus alone. However, pronator teres is involved especially when an extra power is needed against resistance.
What are some examples of functional movements that utilise pronation and supination?
Turning a screwdriver and turning a key are two examples of the functional movements that utilise pronation and supination. There are a number of muscles involved in each of these movements, which work synergistically. Key facts about pronation and supination. Pronation. Palm facing downwards.
Which joint is involved in pronation?
Involved joints. Proximal radioulnar joint - between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna. Distal radioulnar joint - between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius. Acting muscles. Pronator teres muscle - enables pronation.
What is the pronation of the radius?
Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint. The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament, that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna. The wheel like rotation of the head of the radius enables supination (palm facing upwards), and pronation (palm facing downwards).
Which nerve innervates the pronator quadratus?
Pronator quadratus. The anterior interosseus nerve, a branch of the median nerve, innervates this square-shaped muscle in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It arises from the distal anterior surface of the ulna and inserts onto the distal anterior shaft of the radius to cause pronation when it contracts.
Where is the pivot joint located?
This pivot joint is located distally near the wrist joint, and is formed between the head of the ulna, and the ulnar notch of the radius. The anterior and posterior radioulnar ligaments, as well as a triangular fibrocartilaginous plate support this joint. This triangular fibrocartilage connects the bones and ensures they remain together during pronation and supination. It is thicker at its periphery than at its centre. The thick apex of the triangle attaches to the ulnar styloid process, and its thin base attaches to the prominent edge of the radius, just proximal to the radiocarpal articulation. The triangular fibrocartilage also separates the wrist joint (radiocarpal joint) from the lunate and triquetrum bones. The ulnar notch of the radius slides over the head of the ulna during pronation and supination.
Which ligament is lined with a synovial membrane that ensures smooth action during pronation and supination
The superior fibers of the ligament blend with the ligaments of the elbow, and the lower fibers contribute to the quadrate ligament. The inner ligament is lined with a synovial membrane that ensures smooth action during pronation and supination.
Which muscle expands out as the bicipital aponeurosis, which attaches to the shaft of
The tendon of the muscle inserts onto the radial tuberosity. The muscle also expands out as the bicipital aponeurosis, which attaches to the shaft of the ulna. Biceps brachii acts primarily as an elbow flexor, and secondarily as a supinator. It is able to supinate when the elbow is flexed.
How to do pronation vs supination?
In this way, you can choose which muscles get targeted based on hand position or grip. To demonstrate, hold your elbow at your side and bend your arm 90 degrees with your palm facing down. Now place the other hand on your bicep ...
What is a pronated back?
Pronated Back Exercises. Most often, back exercises are performed with a pronated overhand grip. Such as traditional pullups, lat pulldowns, bent-over barbell rows, and deadlifts. With this hand position, your back is taking on most of the load, which is good for muscle and strength gains. YouTube.
What is a pronated tricep extension?
Pronation Tricep Exercises. A standard tricep extension is usually performed using a pronated hand position. This is an overhand grip on exercises like skull crushers or cable press downs. And it tends to target more of the inner and mid heads of the tricep.
What is a supinated bicep?
Supination Bicep Exercises. An example of an exercise performed with a supinated hand position is the standard bicep curl. This includes and variation where your palms are mostly facing up. Such as barbell, cable, or machine curls performed with an underhand grip.
What does "up" mean in pronated hand?
While a pronated hand position is when your palm is facing down. An easy way to remember this is that s up ination contains the word up, as in palm up. It also sounds like the word soup. So I picture a cupped hand as if it’s holding a bowl of soup.
Is supination a function of the tricep?
While supination vs pronation is not a direct function of the tricep muscle, it does affect which part of the tricep gets used most during a particular exercise. Again, it’s important to start by pointing out that the “tri” in tricep means there are three muscle heads on the back of your arm.
