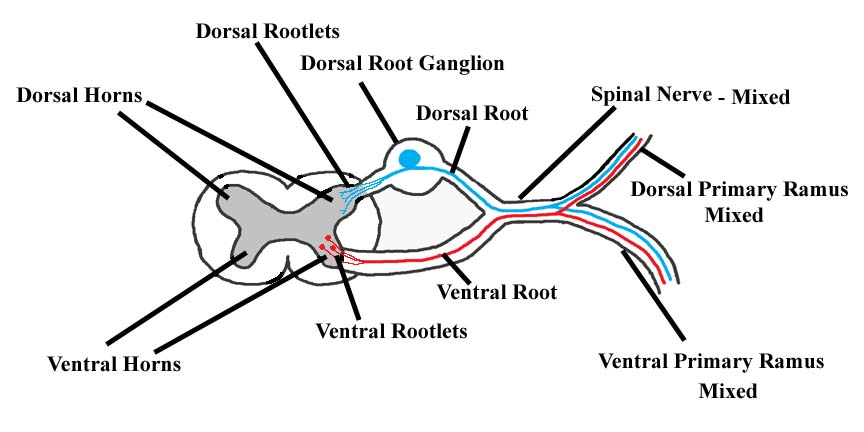
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots?
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots? Each spinal nerve is formed by the combination of nerve fibers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord. The dorsal roots carry afferent sensory axons, while the ventral roots carry efferent motor axons. How many dorsal root ganglion are there?
What is the difference between dorsal and ventral?
• Dorsal is the backside while ventral is the opposite of backside. • When a particular organ (A) is ventral to another (B), the organ-B lies dorsal to the organ-A. • Ventral side bears more external organs than the dorsal side usually does. • Usually, the dorsal side is hardy while the ventral side is tender.
What are the functions of the spinal nerves?
The Anatomy of Spinal Nerves
- Anatomy. The spine is made up of vertebrae (back bones) that protect and surround the spinal cord, which is a column of nerve tissue.
- Function. The spinal nerves have small sensory and motor branches. ...
- Associated Conditions. Spinal nerves can be affected by a number of conditions. ...
- Rehabilitation. ...
- Summary. ...
How to treat thoracic spinal nerve damage?
Treat Thoracic Pain Naturally
- Change your diet to speed up weight loss and decrease inflammation.
- Take an anti-inflammatory supplement like green-lipped mussel oil to decrease inflammation in your spine naturally and safely.
- Use heat treatment or cold therapy depending on whether you’re experiencing tightness or inflammation.

Where is the dorsal nerve root?
Each spinal nerve has two roots, a dorsal or posterior (meaning “toward the back”) one and a ventral or anterior (meaning “toward the front”) one. The dorsal root is sensory and the ventral root motor; the first cervical nerve may lack the dorsal root. Oval swellings, the spinal ganglia, characterize the dorsal roots.
What is the definition of dorsal root?
Medical Definition of dorsal root : the one of the two roots of a spinal nerve that passes posteriorly to the spinal cord separating the posterior and lateral funiculi and that consists of sensory fibers. — called also posterior root.
What are dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal nerves?
Spinal Nerve Roots Two pairs of nerve roots extend from each segment of the spinal cord. ventral roots (anterior roots) allow motor neurons to exit the spinal cord. dorsal roots (posterior roots) allow sensory neurons to enter the spinal cord.
What is the dorsal root made of?
The dorsal roots contain sensory fibers from the skin, subcutaneous and deep tissues, and viscera. Primary afferent fibers of the dorsal roots are either myelinated or unmyelinated. Cutaneous, joint and visceral afferents are composed of myelinated Aα/β, Aδ and unmyelinated C fibers.
What is the role of the dorsal root?
Tissue Engineering of the Nervous System Peripheral spinal nerves (Figure 17.2(a)) originate at the dorsal or ventral roots of the spinal cord, while cranial nerves originate from the brainstem. Dorsal roots contain sensory axons which carry signals into the CNS.
What is the role of dorsal root in spinal cord?
The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.
What is the difference between dorsal and ventral root?
Each spinal nerve has two roots, a dorsal or posterior (meaning “toward the back”) one and a ventral or anterior (meaning “toward the front”) one. The dorsal root is sensory and the ventral root motor; the first cervical nerve may lack the dorsal root. Oval swellings, the spinal ganglia, characterize the dorsal roots.
What happens if dorsal root of spinal nerve is damaged?
Spinal root avulsion injuries typically affect ventral and well as dorsal roots, causing paralysis of denervated muscles, loss of sensory and autonomic function, and, most often, neuropathic pain.
What does dorsal mean in medical terms?
On a human body, dorsal (i.e., posterior) refers to the back portion of the body, whereas ventral (i.e., anterior) refers to the front part of the body. The terms dorsal and ventral are also often used to describe the relative location of a body part.
What is the dorsal nerve?
The dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris is a smaller terminal branch of the pudendal nerve. It runs forward first in the pudendal canal above the internal pudendal vessels and then in the deep perineal space between these vessels and the pubic arch.
Where do dorsal roots enter spinal cord?
Dorsal and ventral roots enter and leave the vertebral column respectively through intervertebral foramen at the vertebral segments corresponding to the spinal segment.
When the dorsal root of a spinal nerve is cut?
If the dorsal root of a spinal nerve is severed, output to skeletal muscles would be blocked. the spinal cord would not be able to process information at that level. output to visceral organs would be blocked.
What is a ventral root Definition?
Definitions of ventral root. one of two the two roots of a spinal nerve that passes ventrally from the spinal cord and that consists of motor fibers.
What does dorsal mean in medical terms?
On a human body, dorsal (i.e., posterior) refers to the back portion of the body, whereas ventral (i.e., anterior) refers to the front part of the body. The terms dorsal and ventral are also often used to describe the relative location of a body part.
What is dorsal nerve?
The dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris is a smaller terminal branch of the pudendal nerve. It runs forward first in the pudendal canal above the internal pudendal vessels and then in the deep perineal space between these vessels and the pubic arch.
Where is the ventral root?
the spinal cordEach ventral root (also named the anterior root, radix anterior, radix ventralis, or radix motoria) is attached to the spinal cord by a series of rootlets that emerge from the ventrolateral sulcus of the spinal cord in the anterior root exit zone.
What nerves join to form the spinal nerve proper?
The anterior and posterior roots join to form the spinal nerve proper, containing a mixture of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers. One of the great ways to learn anatomy effectively is to repeat as much as you can. Check out our free anatomy quizzes and guides to do this in a fun and interactive way!
What is the function of spinal nerves?
They are the structures through which the central nervous system (CNS) receives sensory information from the periphery, and through which the activity of the trunk and the limbs is regulated. Also they transmit the motor commands from the CNS to the muscles of the periphery.
How many spinal nerves are there?
Therefore, there are 12 pairs of thoracic spinal nerves, 5 pairs of lumbar spinal nerves, 5 pairs of sacral spinal nerves, and a coccygeal nerve. The cervical spinal nerves differ from this pattern.
Why do spinal nerves impinge?
These are mostly due to issues relating to the bony and cartilaginous structures surrounding the nerves as they emerge, as with the natural aging process.
How many spinal nerves are there in the cervical spine?
C1-C7 spinal nerves emerge from the vertebral canal above the corresponding vertebra, with an eighth pair of cervical spinal nerves emerging below the C7 vertebra, meaning there are a total of 8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves while there are only 7 cervical vertebrae.
How many pairs of nerves are there in the spinal cord?
They are composed of both motor and sensory fibres, as well as autonomic fibres, and exist as 31 pairs of nerves emerging intermittently from the spinal cord to exit the vertebral canal. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the spinal nerves.
What is the posterior root?
The posterior/dorsal root contains afferent nerve fibres, which return sensory information from the trunk and limbs to the CNS. The cell bodies of the posterior root neurons are not located in the central grey matter in the spinal cord, but instead in a structure called the spinal/ dorsal root ganglion . The anterior and posterior roots join to form the spinal nerve proper, containing a mixture of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers.
What is the dorsal nerve?
A dorsal nerve root is a bundle of nerve fibers responsible for transmitting sensory signals from the body to the brain. A dorsal root is paired with a ventral root, and together these form what are called the mixed segmental spinal nerves.
Why do dorsal roots go untreated?
According to NCBI, surgeons do attempt to reconnect ventral roots to the spinal cord, while severed dorsal roots are usually left untreated because the latter do not regenerate central sensory axons in the spinal cord.
What nerves control temperature?
Dorsal nerv e roots control the sensation of temperature and pain; damage potentially causes an intensification of pain or an interruption of sensation. Thirty-one pairs of nerve roots branch out from the spinal column. A dorsal nerve root is a bundle of nerve fibers responsible for transmitting sensory signals from the body to the brain.
What is the dorsal root ganglion?
The dorsal root ganglion, more recently referred to as the spinal ganglion, is a collection of neuronal cell bodies of sensory neurons . It is the most common type of sensory ganglion in the human body . Each cell body in the ganglion belongs to what is considered to be a pseudounipolar neuron. A pseudounipolar neuron consists of a cell body bearing one short axon which bifurcates into two processes. The main function of the spinal ganglion cells is to transmit the sensory neural signals from the peripheral to the central nervous system .
Which type of neurons are found in the spinal ganglion?
All cell bodies contained in the spinal ganglion are considered to belong to pseudounipolar neurons, which are a variation of bipolar neurons. These neurons have specialized structures: cell bodies that extend a short axon that quickly terminates by bifurcating into two processes, central and peripheral. The peripheral process carries information from the periphery through the spinal nerve (together with motor fibers), while the shorter central process extends towards the posterior horns of the gray matter of the spinal cord.
What is the function of the spinal ganglion?
More specifically, its main function is to relay the sensory nerve impulses from the periphery to the peripheral nervous system. The cell bodies contain genetic information and organelles which direct and drive cellular activity, as well as maintain the structure of the neuron.
What is the ganglion in the nervous system?
The term ganglion refers to a cluster of the neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. The spinal ganglion contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons situated in the posterior root of each spinal nerve (except for spinal nerve C1). These neurons are known as first-order neurons of the somatosensory system and carry sensations related to touch, vibration, proprioception, pain and temperature. Their cell bodies are typically variable in size but all are encapsulated by satellite glial cells which prevent the impulse transmission between them.
Which neuron is T-shaped?
Because of this specific ‘T-shaped’ structure of pseudounipolar neurons, impulses generated in the periphery bypass the cell bodies in the spinal l root ganglion and continue directly to the spinal cord through the central process of the neuron.
Which nerves transmit motor, sensory, and autonomic signals?
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that transmit motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the central nervous system and the periphery. Each spinal nerve carries afferent (sensory) fibers and efferent (motor) fibers to and from the spinal cord , the former of which comprise the posterior/dorsal roots. Each posterior root presents a ganglion as it emerges from the intervertebral foramen.
Where do sensory impulses travel?
These impulses then travel to the spinal cord either directly (bypassing the cell bodies) or through the neuronal cell body in the dorsal root ganglion. It has been long believed that these cell bodies acted as storage "helpers" in transmitting impulses, such as pain impulses (nociception). However, it has been shown that these neural bodies are indeed active participants in the regulation of this signaling process.
How does a neurosurgeon access the spinal cord?
During the actual procedure, the neurosurgeon gains access to the spinal cord by creating an opening in the spine called a laminectomy. The surgeon opens the dura, the membrane covering the cord. Using a surgical microscope, the surgeon carefully isolates the area of the spinal cord damaged by the avulsed nerve roots.
What percentage of people with spinal cord trauma have chronic nerve pain?
The procedure itself involves a neurosurgeon entering the spinal cord and silencing the damaged areas of pain-signaling nerve cells. Between 10 and 30 percent of people with spinal cord trauma and brachial plexus injuries suffer from unrelenting chronic nerve pain, which can be severe and debilitating both physically and mentally. ...
Can a neuroma cause pain?
Damage to a peripheral nerve can lead to neuroma formation. Rarely, these neuromas can cause severe pain. This is treated with surgical resection of the neuroma if non-operative management fails. Peripheral nerves can be torn away (avulsed) from the spinal cord, which damages the dorsal root entry zone of the cord, ...