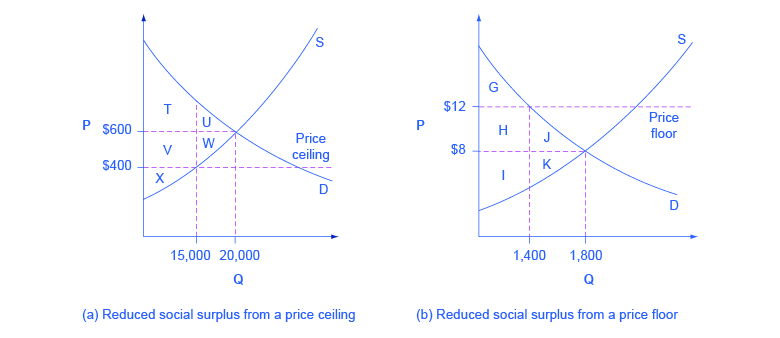
The direct economic effect of a price floor is a surge in supply and a reduction in demand also known as a surplus. A surplus can mean many different things, for goods that take up relatively low space it may not be significantly hard to store them until the market can handle the supply.
What is the impact of an effective price floor?
The impact of an effective price floor is generally surplus of inventory, but only if the market equilibrium price falls below that floor. A price floor acts as a safety net accessed only if the price falls low enough.
What are the consequences of price floor?
- Shortage. If price ceiling is set above the existing market price, there is no direct effect.
- Government rationing and queuing.
- Black market.
- Degradation of quality.
- Supply surplus.
- Government intervention.
- Minimum wage and unemployment.
What is a real life example of a price floor?
What is a real life example of a price floor? An example of a price floor is minimum wage laws, where the government sets out the minimum hourly rate that can be paid for labour. In this case, the wage is the price of labour, and employees are the suppliers of labor and the company is the consumer of employees’ labour. How does minimum wage affect price floor?
What does a price floor do?
A price floor is a regulation that prevents buying and selling a good or service below a specified price. Price floors are often implemented with one or more of the following goals in mind: To push the price of a good or service above the market price. To reduce the demand for goods or services thought to be harmful.

What is a price floor and what are its economic effects quizlet?
Terms in this set (4) Price Floor. keeps the price from going lower; minimum; causes a surplus; above the equilibrium. Surplus. the leftovers if something is over produced. Price Ceiling.
What causes price floor economics?
A price floor in economics is the minimum price that can be set for a good or service while still adhering to the traditional concept of supply and demand. Some price floors are set naturally by the laws of supply and demand while others are set by government regulation or intervention.
How do price floors affect consumers?
Producers are better off as a result of the binding price floor if the higher price (higher than equilibrium price) makes up for the lower quantity sold. Consumers are always worse off as a result of a binding price floor because they must pay more for a lower quantity.
What effects do price ceilings have on economic activity?
While they make staples affordable for consumers in the short term, price ceilings often carry long-term disadvantages, such as shortages, extra charges, or lower quality products. Economists worry that price ceilings cause a deadweight loss to an economy, making it more inefficient.
What is a price floor and what are its economic effects give an example?
A price floor is the lowest price that one can legally charge for some good or service. Perhaps the best-known example of a price floor is the minimum wage, which is based on the view that someone working full time should be able to afford a basic standard of living.
Why is price floor important?
Price floors and price ceilings are government-imposed minimums and maximums on the price of certain goods or services. It is usually done to protect buyers and suppliers or manage scarce resources during difficult economic times.
What is a price floor economics?
Definition: Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply. By observation, it has been found that lower price floors are ineffective. Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour-wage market.
Does price floor create surplus or shortage?
Price floors create surpluses by fixing the price above the equilibrium price. At the price set by the floor, the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. In agriculture, price floors have created persistent surpluses of a wide range of agricultural commodities.
What is the price floor give example?
A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. The most important example of a price floor is the minimum wage. A price ceiling is a maximum price that can be charged for a product or service.
What are the economic and social consequences of a price ceiling?
A price ceiling can increase the economic surplus of consumers as it decreases economic surpluses for the producer. The lower price will result is a shortage of supply and hence decreased sales.
Do price ceilings and floors change demand or supply?
Do price ceilings and floors change demand or supply? Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. Remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change.
What is price ceiling in economics example?
A price ceiling is a legal maximum price that one pays for some good or service. A government imposes price ceilings in order to keep the price of some necessary good or service affordable. For example, in 2005 during Hurricane Katrina, the price of bottled water increased above $5 per gallon.
What sets the floor of product prices?
Cost-based Pricing Costs determine the floor for the price that the business can charge. Thus, cost-based pricing sets the price based on the costs of production, distribution and also selling the product.
What is a price floor in economics?
Definition: Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply. By observation, it has been found that lower price floors are ineffective. Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour-wage market.
What is the price floor give example?
An example of a price floor is minimum wage laws, where the government sets out the minimum hourly rate that can be paid for labour.
When the government imposes a binding price floor it causes?
When the government imposes a binding price floor, it causes? a surplus of the good to develop.
What is price floor?
Like price ceiling, price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government. But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
What happens when the price floor is continued for a long time?
Government intervention. When price floor is continued for a long time, supply surplus is generated in a huge amount. In case of producer surplus, producers would have reduced the price to increase consumers’ demands and clear off the stock. But since it is illegal to do so, producers cannot do anything.
Why is price ceiling important?
Price ceiling is practiced in an attempt to help consumers in purchasing necessary commodities which government believes to have become unattainable for consumers due to high price. However, price ceiling in a long run can cause adverse effect on market and create huge market inefficiencies. Some effects of price ceiling are.
What is the price ceiling?
Price ceiling is a measure of price control imposed by the government on particular commodities in order to prevent consumers from being charged high prices. Price ceiling can also be understood as a legal maximum price set by the government on particular goods and services to make those commodities attainable to all consumers.
What is the effect of shortage of commodities on the black market?
Shortage of commodities encourages black market. Sellers begin trading commodities to relatives and friends, and they start charging other people prices multiple times higher than that of price ceiling.
What happens when the price ceiling is set below the market price?
But, if price ceiling is set below the existing market price, the market undergoes problem of shortage. When price ceiling is set below the market price, producers will begin to slow or stop their production process causing less supply of commodity in the market.
What happens to the demand of the consumers for such commodities with the fall in price?
On the other hand, demand of the consumers for such commodity increases with the fall in price. And with this imbalance between supply and demand of the commodity, shortage is created in the market.
Why do we have price floors?
The aim of price floors is to ensure suppliers achieve a minimum price which ensures the firm stays in business. Or, in the case of the minimum wage (an example of a price floor), to improve living standards.
What happens if the price floor is below the equilibrium?
This is because if the price floor is set below the equilibrium, then the price floor is set below the market value. In other words, the firm is able to sell at a higher price than the minimum price set. For example, the iPhone sells for around $699. Yet if the price floor was set at $500 (below the equilibrium), it would have no effect.
Why is there a black market?
When prices are set artificially above the market value, it can lead to black markets as producers seek to sell their production surplus. For instance, the NFL used to operate a price floor that set a minimum price on resold tickets. This meant season ticket holders and other resellers had to sell for a minimum price. However, this made it more difficult for them to sell as the price was in excess of what many were willing to pay. In turn, a black market was created to allow those who wanted to sell tickets to find buyers.
What happens when the price of bread increases?
With prices higher than they would be under a market equilibrium, customers will look to purchase substitute goods instead. For instance, if a price floor for a loaf of bread increases its price from $1.50 to $2, consumers may start to switch to cereal’s that are also $2 for a box.
Why did India put a price floor on steel imports?
In 2016, India set a price floor on steel imports – largely to deter foreign competitors such as China from dumping cheap steel into the market. With the country facing cheap steel from China, its domestic steel manufacturers came under significant pressure. Customers were opting for the cheaper Chinese option, which threatened the existence of Indian manufacturers. The government, therefore, stepped in to artificially inflate the price of Chinese steel and essentially make it uncompetitive. This protected its domestic steel industry as it saw demand return as Indian steel became comparatively cheap.
Why is the price floor set at $2.50?
For instance, doughnuts sell for $2 each. If the price floor is set at $2.50, this means that the customer must now pay the extra 50 cents for each doughnut. So whilst the baker may potentially benefit, the customer does not, which is why price floors are often seen as corporate welfare. 3. Lower Demand.
What would happen if the iPhone price floor was $800?
If the price floor was set at $800 instead, it would benefit Apple as it would be selling at a higher price. However, fewer customers will purchase the iPhone as a result – meaning the actual profit it receives may in fact be lower. This results in an economic surplus, whereby more goods are supplied than demanded.
How does price floor affect producers?
Changes in producer surplus. Price floors have a mixed effect on producers. The reduction in the number of goods sold is a loss for some producers. This is reflected in the deadweight loss. On the other hand, the higher price charged for the goods that are sold is a benefit. This benefit is reflected in the portion of surplus that is reallocated from the consumers to the producers.
What can happen as a result of a price floor?
As we have already seen, a binding price floor raises the price of a good above the equilibrium price. This leads to a reduction in demand and an increase in supply. Quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded, which leads to a surplus of goods in the market.
What is the effect of price floor on consumer surplus?
An overall reduction in consumer surplus. When a price floor is implemented, consumers are harmed more than suppliers. Consumers who remain in the market are charged a higher price, while consumers who exit the market lose the entire benefit of purchasing the good. In other words, total consumer surplus falls because of deadweight loss and because a portion of the consumer surplus is reallocated to the producers.
What is a price floor that is set below the equilibrium price called?
A price floor that is set below the equilibrium price is called a non-binding price floor . A non-binding price floor has no effect in a competitive market, because the equilibrium price already exceeds the price floor. In the non-binding case, market participants will continue to buy and sell at the equilibrium price and quantity.
What is the opposite of a price floor?
Price floors are just one form of price control. The opposite of a price floor is a price ceiling. Price floors and price ceilings are both intended to move prices away from the market equilibrium, but they are designed to do so in opposite directions.
What is price ceiling?
For a price ceiling to be binding, it must be below the equilibrium price rather than above it. Price ceilings are typically implemented to keep prices low for the benefit of consumers. These regulations increase demand and reduce supply resulting in a shortage of goods, and they tend to benefit the demand side of the market more than the supply side.
What would happen if the minimum wage was raised?
If you believe that the market for low-wage labor is competitive, then a price floor on wages would create unemployment due to a reduction in the demand for labor and an increase in the supply. Low-wage workers who remain employed under a minimum wage would benefit from a higher wage, but many other workers might lose their jobs and struggle to find work.
How do price floors affect the market?
Price floors distort markets in a number of ways. For example, they promote inefficiency. Some suppliers that could not compete at a lower market equilibrium price can survive and prosper at the higher government-mandated price level. Consumers pay more for the product, and in doing so, subsidize the inefficiencies.
How does price floor affect surplus products?
Surplus product is just one visible effect of a price floor. Price floors distort markets in a number of ways. For example, they promote inefficiency. Some suppliers that could not compete at a lower market equilibrium price can survive and prosper at the higher government-mandated price level. Consumers pay more for the product, and in doing so, subsidize the inefficiencies. Because of the higher price, consumers purchase less, so some would-be buyers cannot afford the product or simply elect not to purchase it.
What happens when the price is low?
Conversely, if the price is low, consumers will want to purchase more than suppliers produce . The excess demand bids up the market price. An equilibrium is reached when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded and there is neither surplus ...
Why do consumers pay more for products?
Consumers pay more for the product, and in doing so, subsidize the inefficiencies. Because of the higher price, consumers purchase less, so some would-be buyers cannot afford the product or simply elect not to purchase it.
What would happen if artificial prices were higher?
Artificial higher prices create a surplus, subsidizing farmers at the expense of consumers. If the government purchases the surplus crop, it is at taxpayer expense. And if the excess production is done on marginal farmland, the result could be environmental damage. References.
What happens when you don't work at equilibrium wage?
The result is more workers chasing fewer jobs.
When the price of a commodity is too low, what happens?
When society or the government feels that the price of a commodity is too low, policymakers impose a price floor, establishing a minimum price above the market equilibrium. When the price is above the equilibrium, the quantity supplied will be greater than the quantity demanded and there will be a surplus.