What could cause the SRAS curve to shift?
increase the amount people buy because of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the foreign price effect. These are triggered by a decline in the average price level, not by a decline in a single price (as is the case for a single market demand curve). Name some factors that could cause the SRAS curve to shift, and say
What are the economic reasons why the AD curve slopes down?
What are the economic reasons why the AD curve slopes down? There are three reasons why the AD curve has a negative slope: 1. The wealth effect. All else equal, as the price level rises, the value of
Why is the real GDP curve on the horizontal axis?
Real GDP is on the horizontal axis. The price level, as measured by the GDP deflator, is on the vertical axis What is the economic reason why the SRAS curve slopes up? All else the same (especially resource prices), it becomes more profitable to produce as the price level rises.
Why does the average value curve have a negative slope?
There are three reasons why the AD curve has a negative slope: 1. The wealth effect. All else equal, as the price level rises, the value of money falls. People who have money in any form become less wealthy, and so buy less, which means consumption falls. 2. The interest rate effect. As the price level rises, it requires more money to buy things.
Why is the SRAS curve vertical?
What does the far left portion of the SRAS curve represent?
What is the highest sustainable level of real GDP?
Why does the AD curve have a negative slope?
What are the components of aggregate demand?
Does demand increase for the same reason in response to a decrease?
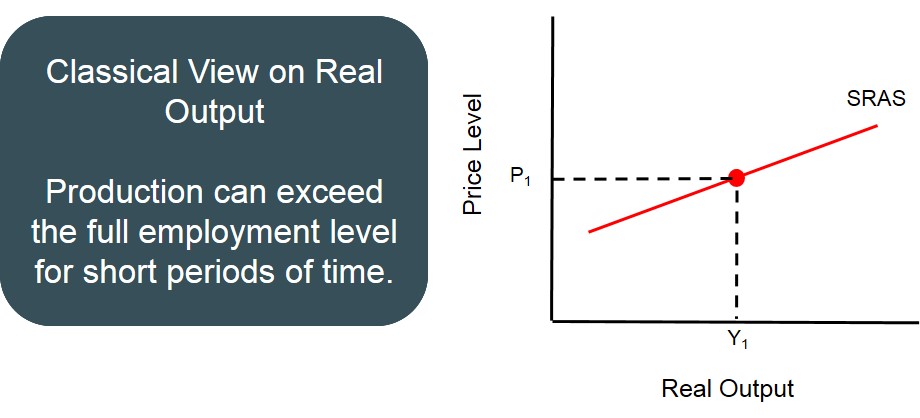
Can we produce beyond GDP?
See 4 more
About this website

What are the economic reasons why the AD curve slopes down?
It slopes downward because of the wealth effect on consumption, the interest rate effect on investment, and the international trade effect on net exports. The aggregate demand curve shifts when the quantity of real GDP demanded at each price level changes.
What causes short-run aggregate supply to increase?
In the short run, aggregate supply responds to higher demand (and prices) by increasing the use of current inputs in the production process. In the short run, the level of capital is fixed, and a company cannot, for example, erect a new factory or introduce a new technology to increase production efficiency.
What is short-run aggregate supply upward sloping?
An upward sloping curve is saying that if prices, aggregate prices - Now this isn't just prices in one good or service - if aggregate price is going down, it's saying in the economy as a whole people might be incented to work a little bit less. People might drop out of the labor pool.
What affects the short-run aggregate supply curve?
Along with energy prices, two other key inputs that may shift the SRAS curve are the cost of labor, or wages, and the cost of imported goods that are used as inputs for other products.
What increases short-run supply?
Changes in prices of factors of production shift the short-run aggregate supply curve. In addition, changes in the capital stock, the stock of natural resources, and the level of technology can also cause the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift.
What happens to short-run aggregate supply when wages increase?
A rise in the money wage rate makes the aggregate supply curve shift inward, meaning that the quantity supplied at any price level declines. A fall in the money wage rate makes the aggregate supply curve shift outward, meaning that the quantity supplied at any price level increases.
What causes the supply curve to shift in the short-run?
The short-run market supply curve can shift to the right (an increase in supply) in response to (1) existing firms acquiring new capital and (2) new firms entering the market.
Chapter 8 Macroeconomics Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is potential GDP?, labor productivity changes, suppose structural unemployment rate rises, what happens to the LRAS and more.
Macroeconomics Chapter 8 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The short-run aggregate supply curve was constructed assuming that as the price of outputs increases, the price of inputs stays the same. How would an increase in the prices of important inputs, like energy, affect aggregate supply?, In the AD/AS model, what prevents the economy from achieving equilibrium at the potential output ...
Solved What is meant by the Phillips Curve “tradeoff”? | Chegg.com
What is meant by the Phillips Curve “tradeoff”? High inflation results in high unemployment. High unemployment eventually returns to normal.
Solved: Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) has the potential to signi ...
Principles of Macroeconomics for AP® Courses 2e (0th Edition) Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 10 Problem 46CTQ: Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) has the potential to significantly increase the amount of natural gas produced in the United States. If a large percentage of factories and utility companies use natural gas, what will happen to output, the price level, and employment as ...
OpenEd CUNY - Shifts in Aggregate Supply
The original equilibrium in the AD/AS diagram will shift to a new equilibrium if the AS or AD curve shifts. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right, then at every price level, producers supply a greater quantity of real GDP.
Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) has the potential to...open 3
Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) has the potential to significantly increase the amount of natural gas produced in the United States. If a large percentage of factories and utility companies use natural gas, what will happen to output, the price level, and employment as fracking becomes more widely used?
Why is the SRAS curve vertical?
On the far right the SRAS curve is nearly vertical because the economy is
What does the far left portion of the SRAS curve represent?
The far left portion of the SRAS curve represents the economy when it is
What is the highest sustainable level of real GDP?
Potential GDP is the highest sustainable level of real GDP that an
Why does the AD curve have a negative slope?
There are three reasons why the AD curve has a negative slope: 1. The wealth effect. All else equal, as the price level rises , the value of. money falls. People who have money in any form become less wealthy, and so buy less, which means consumption falls. 2.
What are the components of aggregate demand?
The components of aggregate demand are consumption, (intended)
Does demand increase for the same reason in response to a decrease?
demand does not increase for the same reason in response to a decrease
Can we produce beyond GDP?
many hours), but we cannot produce beyond potential GDP for long.
Why does the SRAS curve shift to the left?
If firms are required to use less efficient technology, the SRAS curve will shift to the left because productivity will be lower. That will reduce real GDP, increase the price level, and reduce employment. Note that GDP will be smaller, but that the standard of living might improve because of a cleaner environment.
Why does the AD curve have a negative slope?
There are three reasons why the AD curve has a negative slope: 1. The wealth effect. All else equal, as the price level rises , the value of. money falls. People who have money in any form become less wealthy, and so buy less, which means consumption falls. 2.
What would happen if the labor force was smaller?
A smaller labor force would be reflected in a leftward shift in both short run aggregate supply and potential GDP. That would lead to a lower equilibrium level of GDP and a higher price level.
What would happen if the EU economy increased?
Higher EU growth would increase demand for U.S. exports, reducing our trade deficit. The increased demand for exports would show up as a rightward shift in AD, causing GDP to rise (and the price level to rise as well). Higher GDP would require more jobs to fill, so U.S. employment would also rise.
How would immigration reform affect GDP?
That would lead to a higher equilibrium GDP and a lower price level. It would also increase potential GDP.
What happens if Mexico goes into recession?
If Mexico goes into recession, its GDP declines. With less income, it will import less. A fall in Mexican imports means a fall in U.S. exports. The decline in our exports can be shown as a leftward shift in AD, leading to a decrease in our GDP and price level.
What does higher input prices mean?
Higher input prices make output less profitable, decreasing the desired supply. This is shown graphically as a leftward shift in the AS curve.
Why is the SRAS curve vertical?
On the far right the SRAS curve is nearly vertical because the economy is
What does the far left portion of the SRAS curve represent?
The far left portion of the SRAS curve represents the economy when it is
What is the highest sustainable level of real GDP?
Potential GDP is the highest sustainable level of real GDP that an
Why does the AD curve have a negative slope?
There are three reasons why the AD curve has a negative slope: 1. The wealth effect. All else equal, as the price level rises , the value of. money falls. People who have money in any form become less wealthy, and so buy less, which means consumption falls. 2.
What are the components of aggregate demand?
The components of aggregate demand are consumption, (intended)
Does demand increase for the same reason in response to a decrease?
demand does not increase for the same reason in response to a decrease
Can we produce beyond GDP?
many hours), but we cannot produce beyond potential GDP for long.
