
What is the effect of increasing the KVP on IR?
A 15% increase in kVp has the same effect as doubling the mAs. A 15% decrease in kVp has the same effect as decreasing the mAs by half. Increasing the kVp by 15% increases the exposure to the IR, unless the mAs is decreased. Also, decreasing the kVp by 15% decreases the exposure to the IR, unless the mAs is increased.
What is the 15 percent KVP rule?
- Answers What is 15 percent Kvp rule? An increase in kVp by 15% must be accompanied by a reduction in mAs by 50% in order to maintain radiographic density. Inversely, a reduction of 15% in kVp must be accompanied by an increase in mAs by a factor of 2 (Doubling). What 15 percent percent of 450? 15 percent percent of 450 = 0.675.
How does KVP affect the number of X-rays?
The number of x-rays is proportional to kVp^2. This is more strong than the mA or the time (s) which are both linearly proportional to the number of x-rays. The number of x-rays incident on the patient is the first of two major factors which are responsible for the 15% Rule. How does the kVp influence the X-ray Penetration and the Remnant beam?
What is a high KVP range for radiography?
A greater change in the kVp is needed when operating at a high kVp (greater than 90) compared with operating at a low kVp (less than 70) (Figure 10-5). FIGURE 10-5kVp Range and Radiographic Density. Produced at 50 kVp (A)and produced at 90 kVp with the mAs adjusted to maintain radiographic density (C).
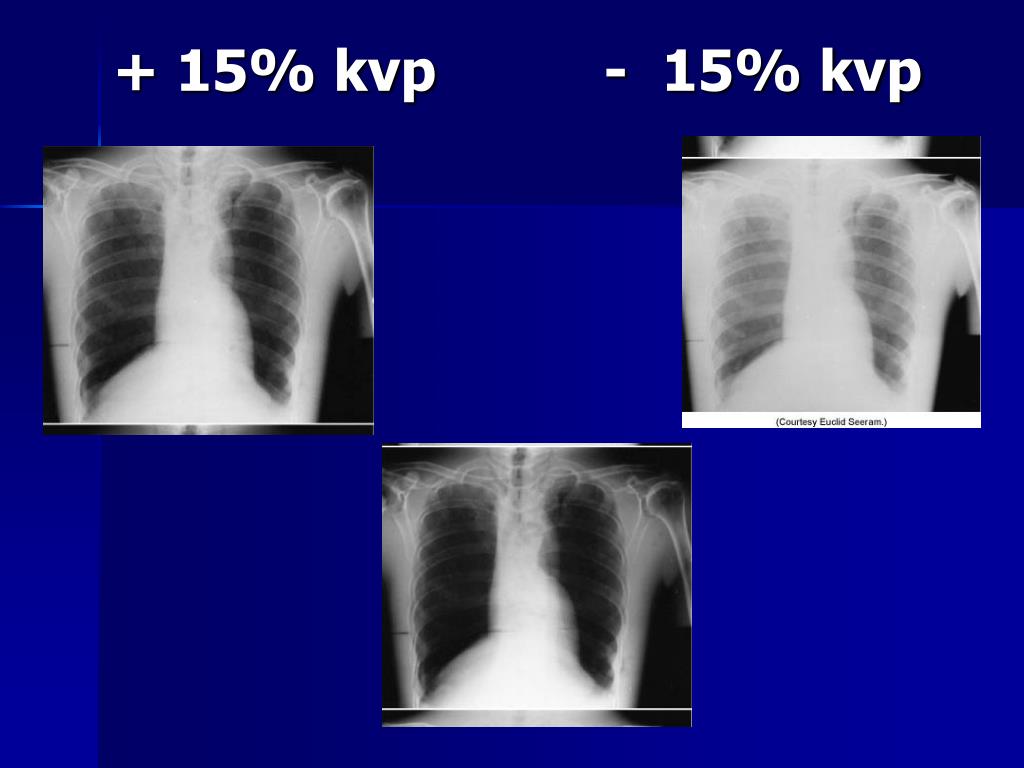
How does the 15% rule affect image quality?
The 15% Rule in x-ray radiography comes from the fact that (1.15)^5 ~2. This means that a 15% increase in the kVp will lead an exposure approximately 2 times higher at the image receptor (e.g. the detector or film).
What is the 15% rule in radiography?
The 15% Rule is a useful approximation for Radiologic Technologists / Radiographers to adjust the mAs when changes to the kVp are desired in the x-ray protocol. The 15% Rule states: when the kVp is lowered by 15% the mAs needs to be increased by a factor of 2, and when the kVp is increased …
What is the 15% rule?
After the carbohydrate is eaten, the person should wait about 15 minutes for the sugar to get into their blood. If the person does not feel better within 15 minutes more carbohydrate can be consumed. Their blood sugar should be checked to make sure it has come within a safe range.
How does kVp affect radiographic image?
kVp controls the penetrating strength of an x-ray beam (beam quality). Whenever an exposure is made, the x-rays must be energetic (strong enough) to adequately penetrate through the area of interest. The higher the kVp, the more likely the x-ray beam will be able to penetrate through thicker or more dense material.
How does kVp affect image quality?
The first experiment showed that, when the film density is kept constant, the higher the kVp, the lower the resolution and image contrast percentage; also, the higher the mAs, the higher the resolution and image contrast percentage.
What is kVp rule?
A longstanding 'rule of thumb' suggests that increasing kVp by 10 whilst halving the time gives similar perceptual image quality when compared to the original exposure factors.
Does increasing kVp increase contrast?
A higher kVp will make the x-ray beam more penetrating. It will also result in less difference in attenuation between the different parts of the subject, leading to lower contrast.
What is high kVp technique?
High tube potential, or 'high-kVp' techniques, which were established using traditional film-screen technology, are well-known and widely documented methods of reducing patient radiation doses. 2-7. The high kVp concept for dose reduction has since been carried over to digital imaging.
What are the advantages of using high kVp techniques?
A high kilovoltage technique enhances the visibility of the lungs by reducing the contrast of the bony thorax and also has the advantage of better penetration of the mediastinum (4,6).
How does kVp affect quantity?
Factors influencing x-ray quantity includes: peak voltage (kVp): beam quantity is approximately proportional to the square of the tube potential. generator type/voltage waveform: reducing ripple increases beam quantity. beam filtration: increasing filtration reduces beam quantity.
What is the reason for decreasing the mAs when kVp is increased?
In reality, so as to not increase dose unnecessarily, the mAs setting is typically adjusted down to compensate for the increased photon quantity caused by increasing kVp.
What does kVp mean in radiology?
kilovoltage peakkVp. The kilovoltage peak (kVp) is the difference in potential applied to the X-ray tube.[11][14] kVp is directly proportional to the average energy of the X-ray spectrum produced, referred to as X-ray quality.[14] kVp plays a role in adjusting the amount of penetration and exposure in an acquisition.
What is the grid ratio formula?
Grid Ratio Formula The following formula is used to calculate the Grid Ratio. GRD = HLS / DS. Where GRD is the Grid Ratio. HLS is the height of lead strips (in) DS is the distance between strips (in)
What is the reciprocity law in radiography?
The reciprocity law constitutes one of the fundamental rules of photography and of radiography. It states that the quality of a series of photographic or radiographic films will be uniformly constant if the exposure times with which the films are made vary reciprocally with the intensities of the exposing radiation.
What happens when you increase mAs?
Changes in mAs affect radiation dose, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrast. [14] Increasing mAs produces more electrons in an X-ray tube and subsequently increases the amount of radiation exposure. [11] High mAs will increase SNR but will decrease image contrast.
What is the relationship between kVp and mAs?
The first experiment showed that, when the film density is kept constant, the higher the kVp, the lower the resolution and image contrast percentage; also, the higher the mAs, the higher the resolution and image contrast percentage.
Why should a radiographer be diligent in monitoring exposure indicator values?
The radiographer should be diligent in monitoring exposure indicator values to ensure that quality images are obtained with the lowest possible radiation dose to the patient.
How to correct density error on repeat radiograph?
In general, for repeat radiographs necessitated by density errors, the mAs is adjusted by a factor of 2; therefore a minimum change involves doubling or halving the mAs. This typically brings the optical densities back within the straight-line portion of the film’s sensitometric curve to best visualize the anatomic area of interest. As mentioned previously, it may take more than doubling the mAs to correct for a density error. If the radiograph necessitates an adjustment greater than a factor of 2, the radiographer should multiply or divide the mAs by 4 (Figure 10-3).
Why are radiographs not repeated?
Radiographs that have sufficient but not optimal density usually are not repeated. If a radiograph must be repeated because of another error, such as positioning, the radiographer may also use the opportunity to make an adjustment in density to produce a radiograph of optimal quality. Making a visible change in radiographicdensity requires that the minimum amount of change in mAs be approximately 30% (depending on equipment, this may vary between 25% and 35%). Radiographic images generally are not repeated to make only a slight visible change. A radiographic image repeated because of insufficient or excessive density requires a change in mAs by a factor of at least 2.
Why is it important for a radiographer to determine the amount of mAs needed to produce a?
This is not an easy task because there are so many variables that can affect the amount of mAs required. For example, single-phase generators produce less radiation for the same mAs when compared with a high-frequency generator.
What are the primary exposure techniques?
The primary exposure technique factors the radiographer selects on the control panel are milliamperage, time of exposure, and kilovoltage peak (kVp). Depending on the type of control panel, milliamperage and exposure time may be selected separately or combined as one factor, milliamperage/second (mAs). Regardless, it is important to understand how changing each separately or in combination affects the radiation reaching the IR and the radiographic image.
How does mAs affect radial density?
The mAs has a direct effect on the amount of radiographic density produced when using a film-screen IR. The minimum change needed to correct for a density error is determined by multiplying or dividing the mAs by 2. When a greater change in mAs is needed, the radiographer should multiply or divide by 4, 8, and so on.
When a greater change in mAs is needed, should the radiographer multiply or divide by?
When a greater change in mAs is needed, the radiographer should multiply or divide by 4, 8, and so on. Digital IRs can detect a wider range of radiation intensities (wider dynamic range) exiting the patient and therefore are not as dependent on the mAs as film-screen IRs.
What is the kVp of an AP abdomen radiograph?
An AP abdomen radiograph was taken using 95 kVp and 30 mAs. The EI shows excessive IR exposure and the image has very little contrast. What should be done to reduce exposure and improve image quality?
What does S# mean on a radiograph?
A radiograph is taken at 80 kVp & 30 mAs. The S# indicates overexposure and the IR exposure should be reduced by half.
Can generator mAs be increased?
However, generator mAs cannot be increased be casue of patient radiation exposure, is not desirable. Increasing kVp by 10 (90 kVp) would double the IR exposure and reduce noise. An AP abdomen radiograph on an obese patient was taken using 80 kVp and 500 mAs.
