What is the effect of resonance in parallel circuit?
- The circuit impedance is purely resistive because there is no frequency term present in it.
- The value of Zr will be very high because the ratio L/C is very large at parallel resonance.
- The value of circuit current, Ir = V/Zr is very small because the value of Zr is very high.
Why do we need a parallel resonance circuit?
- The circuit impedance is purely resistive because there is no frequency term present in it. ...
- The value of Zr will be very high because the ratio L/C is very large at parallel resonance.
- The value of circuit current, Ir = V/Zr is very small because the value of Zr is very high.
What is the formula for parallel resonance?
- I = V/R
- I = VR
- I = VC/R
- I = VCR
How to determine the total resistance in a parallel circuit?
Calculate the total resistance of resistors in parallel with ease!
- Equations
- Applications. Resistors in series are equivalent to one resistor whose resistance is the sum of each individual resistor.
- Further Reading
How do you calculate resistance in a parallel circuit?
- Series Resistance = R1 + R2
- Parallel Resistance = (R1 * R2) / (R1 + R2)
- Ohms Law: V = I * R
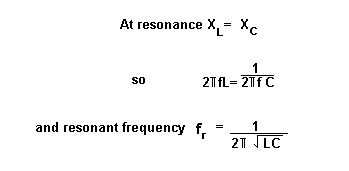
What is resonance effect in circuit?
Resonance can be defined as the sensitivity against a certain vibration frequency in mechanical structures. For an electronic circuit, the circuits with only one capacitor and coil are called the resonance circuits.
What is the effect of resonance in series RLC circuit?
At resonance in series RLC circuit, both inductive and capacitive reactance cancel each other and we know that in series circuit, the current flowing through all the elements is same, So the voltage across inductor and capacitor is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction and thereby they cancel each other.
What is resonance in series and parallel circuits?
Series resonance refers to the resonance that occurs in circuits where capacitors and inductors are connected in series, whereas parallel resonance refers to the resonance that occurs in circuits where the capacitors and inductors are connected in parallel.
What are the effects of series resonance?
Effects of Series Resonance i.e Zr = R. At the resonance condition, as the impedance of the circuit is minimum, the current in the circuit is maximum. i.e Ir = V/Zr = V/R. As the value of resonant current Ir is maximum hence, the power drawn by the circuit is also maximized.
What is the condition for parallel resonance?
Parallel resonance occurs when the supply frequency creates zero phase difference between the supply voltage and current producing a resistive circuit.
What is meant by parallel resonance circuit?
A parallel circuit consisting of inductor and capacitor in which the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance are equal and obtain maximum impedance at the frequency at which the circuit is resonant.
When a parallel circuit is in resonance which of the following of the circuit is maximum?
The total current in the parallel resonant circuit is zero otherwise, In series resonant circuit is maximum.
How does parallel resonance magnifies the current?
By means of the parallel resonant circuit, the current taken from the supply can be magnified. This type of resonance is called current resonance. Quality factor of R-L-C parallel circuit is the current magnification in the circuit at resonance.
What is the maximum frequency of resistance in parallel with C?
Resistance in parallel with C in series resonant circuit shifts curreent maximum from calculated 159.2 Hz to about 136.8 Hz.
What is the exception to the rule of circuit resistance causing a resonant frequency shift?
One notable exception to the rule of circuit resistance causing a resonant frequency shift is the case of series resistor-inductor-capacitor (“RLC”) circuits. So long as all components are connected in series with each other, the resonant frequency of the circuit will be unaffected by the resistance. (Figure below) The resulting plot is shown in (Figure below).
What happens to energy in a tank circuit?
In a perfect tank circuit (no resistance), this oscillation would continue forever, just as a frictionless pendulum would continue to swing at its resonant frequency forever. But frictionless machines are difficult to find in the real world, and so are lossless tank circuits. Energy lost through resistance (or inductor core losses or radiated electromagnetic waves or . . .) in a tank circuit will cause the oscillations to decay in amplitude until they are no more. If enough energy losses are present in a tank circuit, it will fail to resonate at all.
What is antiresonance in electronics?
Antiresonance is an effect that resonant circuit designers must be aware of. The equations for determining antiresonance “shift” are complex, and will not be covered in this brief lesson. It should suffice the beginning student of electronics to understand that the effect exists, and what its general tendencies are.
Why does an inductor ring?
Inductor ringing due to resonance with stray capacitance.
How does resistance work in mechanical systems?
Interestingly enough, the principle of employing resistance to eliminate unwanted resonance is one frequently used in the design of mechanical systems, where any moving object with mass is a potential resonator . A very common application of this is the use of shock absorbers in automobiles. Without shock absorbers, cars would bounce wildly at their resonant frequency after hitting any bump in the road. The shock absorber’s job is to introduce a strong antiresonant effect by dissipating energy hydraulically (in the same way that a resistor dissipates energy electrically).
Why add a series resistor?
SPICE can’t handle an inductor connected directly in parallel with any voltage source or any other inductor, so the addition of a series resistor is necessary to “break up” the voltage source/inductor loop that would otherwise be formed.
What is parallel resonance?
If the resonance occurs in parallel RLC circuit, then it is called as Parallel Resonance. Consider the following parallel RLC circuit, which is represented in phasor domain. Here, the passive elements such as resistor, inductor and capacitor are connected in parallel.
What is parallel resonance RLC circuit?
Note − Parallel resonance RLC circuit is called as current magnification circuit. Because, the magnitude of current flowing through inductor and capacitor is equal to Q times the input sinusoidal current I.
What is the voltage across all the elements of parallel RLC circuit at resonance?
Therefore, the voltage across all the elements of parallel RLC circuit at resonance is V = IR.
What is the current flowing through a resistor at resonance?
Therefore, the current flowing through resistor at resonance is I R = I.
Is resonance frequency the same in parallel RLC?
The above resonance condition is same as that of series RLC circuit. So, the resonant frequency, fr will be same in both series RLC circuit and parallel RLC circuit.
When does resonance occur?
Resonance occurs when capacitive and inductive reactances are equal to each other.
What is resonance in a tank circuit?
Resonance in a Tank Circuit. A condition of resonance will be experienced in a tank circuit when the reactance of the capacitor and inductor are equal to each other. Because inductive reactance increases with increasing frequency and capacitive reactance decreases with increasing frequency, there will only be one frequency where these two ...
What happens when capacitive and inductive reactances equal to each other?
What happens at resonance is quite interesting. With capacitive and inductive reactances equal to each other, the total impedance increases to infinity, meaning that the tank circuit draws no current from the AC power source!

Resonant Frequency
Series LC Circuits
- Switching our attention toseries LC circuits, (Figure below) we experiment with placing significant resistances in parallel with either L or C. In the following series circuit examples, a 1 Ω resistor (R1) is placed in series with the inductor and capacitor to limit total current at resonance. The “extra” resistance inserted to influence resonant frequency effects is the 100 Ω resistor, R2. The …
Antiresonance in LC Circuits
- The tendency for added resistance to skew the point at which impedance reaches a maximum or minimum in an LC circuit is called antiresonance. The astute observer will notice a pattern between the four SPICE examples given above, in terms of how resistance affects the resonantpeak of a circuit: Parallel (“tank”) LC circuit: 1. R in series with L: re...
RLC Circuits
- One notable exception to the rule of circuit resistance causing a resonant frequency shift is the case of series resistor-inductor-capacitor (“RLC”) circuits. So long as allcomponents are connected in series with each other, the resonant frequency of the circuit will be unaffected by the resistance. (Figure below) The resulting plot is shown in (Figure below). Series LC with resistanc…
Antiresonance’S Dampening Effect
- It is noteworthy that antiresonance has the effect of dampening the oscillations of free-running LC circuits such as tank circuits. In the beginning of this chapter we saw how a capacitor and inductor connected directly together would act something like a pendulum, exchanging voltage and current peaks just like a pendulum exchanges kinetic and potential energy. In a perfect tank …