How might you calculate elasticity of supply?
the more accurate way to compute the price elasticity of supply; the formula divides the change in quantity supplied and price by their average values (Qs2 – Qs1)/ [ (Qs2+Qs1)/2] and (P2 – P1)/ [ (P2+P1)/2]. Thus, the formula for the mid-point elasticity approach is (Qs2 – Qs1)/ [ (Qs2+Qs1)/2] / (P2 – P1)/ [ (P2+P1)/2]. point elasticity approach:
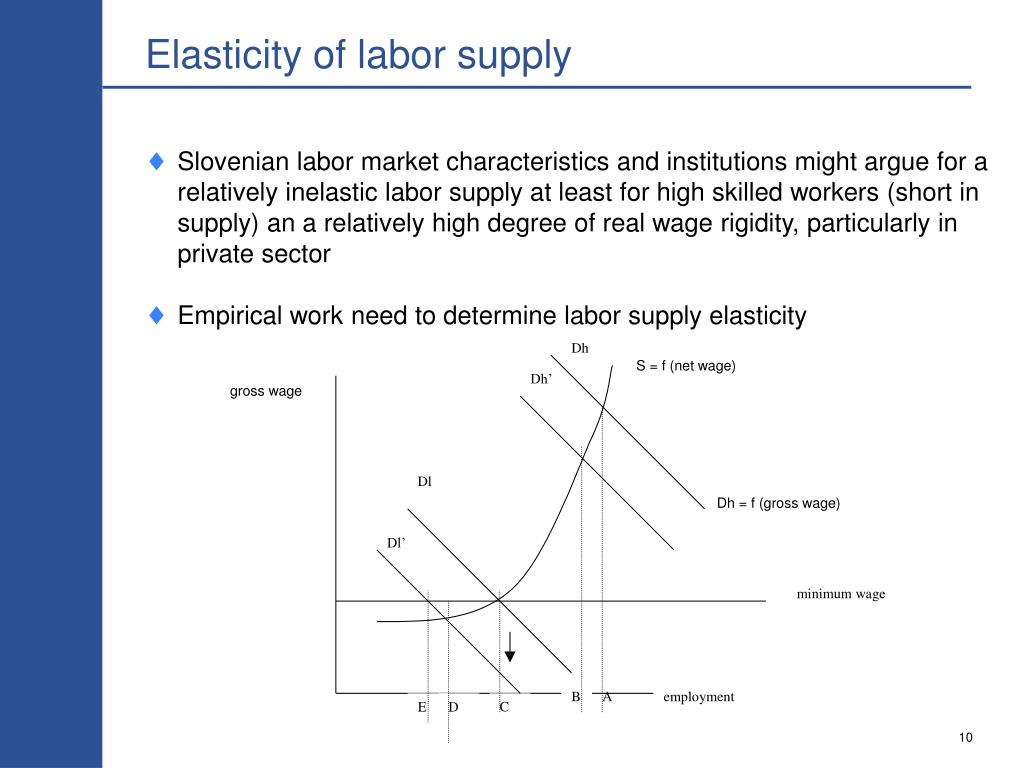
Is supply of Labor elastic or inelastic?
The supply of labor is generally said to be more elastic in lower-skilled jobs that require less training. For more skilled jobs, the supply of labor cannot change very quickly.
What is the importance of elasticity of demand and supply?
What is the importance of elasticity in demand and supply? The concept of price elasticity of demand is important for formulating government policies, especially the taxation policy. Government can impose higher taxes on goods with inelastic demand, whereas, low rates of taxes are imposed on commodities with elastic demand. ...
What are the elasticities of demand and supply?
The price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. Elasticities can be usefully divided into five broad categories: perfectly elastic, elastic, perfectly inelastic, inelastic, and unitary. An elastic demand or elastic supply is one in which the elasticity is greater than one ...

What is the elasticity of labor supply measure?
Elasticity of labour supply measures the extent to which labour supply responds to a change in the wage rate in a given time period.
Is the labor supply elastic or inelastic?
The time period under consideration is also a factor affecting the supply: in the short run, the supply curve of labour tends to be inelastic as it takes time for people to respond to changes in relative wages.
Why is labour supply perfectly elastic?
In a perfectly competitive labour market, where the wage rate is determined in the industry, rather than by the individual firm, each firm is a wage taker. This means that the actual equilibrium wage will be set in the market, and the supply of labour to the individual firm is perfectly elastic at the market rate.
Is labor supply more elastic than demand?
Labor demand will be more elastic the easier it is to substitute capital (mechanical equipment, computers, etc.) for workers. The higher the percentage labor costs are of total costs, the more elastic labor demand will be because an increase in wage rates will have a large impact on overall production costs.
Is labour price elastic?
Ease and cost of factor substitution: Labour demand is more elastic when a firm can substitute easily and cheaply between labour & capital inputs. Price elasticity of demand for the final product: This determines whether a firm can pass on higher labour costs to consumers in higher prices.
What is labor supply equal to?
The labour supply is the number of hours people are willing and able to supply at a given wage rate.
What is perfectly elastic and inelastic supply?
Perfectly elastic means the response to price is complete and infinite: a change in price results in the quantity falling to zero. Perfectly inelastic means that there is no change in quantity at all when price changes.
What is the meaning of perfectly elastic supply?
A perfectly elastic supply represents a case in which the quantity supplied of a commodity responds by an infinite amount to a very small change in price.
What does elastic Labour demand mean?
An elastic demand for labor means that firms will respond to a small change in the wage by laying off a large number of workers, so the employment effect will be large. The elasticity of labor supply is not relevant if we are concerned only with employment effects.
Is demand for Labour elastic or inelastic?
Labour demand is defined as the amount of labour that employers seek to hire during a given time period at a particular wage rate. The demand for labour as a factor of production is a derived demand, in that labour is demanded not for its own sake but for its contribution to the production of goods and services.
Is elastic supply less than 1?
When the elasticity is less than one, the supply of the good can be described as inelastic; when it is greater than one, the supply can be described as elastic. An elasticity of zero indicates that quantity supplied does not respond to a price change: the good is "fixed" in supply.
How do you calculate elasticity of demand for labor?
Wage elasticity of demand for labour measures the sensitivityof employment to a change in wage rates. The formula is % change in labour demand / % change in wages.
Is demand for labor inelastic?
Demand for the good or service produced by the labour may, itself, be inelastic. Given that demand for labour is derived from the demand for the good or service produced, it is likely that how firms respond to a change in the wage rate is mirrored by how consumers respond to a change in price.
Is labor a supply or demand?
The firm's demand for labor is a derived demand; it is derived from the demand for the firm's output. If demand for the firm's output increases, the firm will demand more labor and will hire more workers. If demand for the firm's output falls, the firm will demand less labor and will reduce its work force.
How does the demand for labor become inelastic and elastic?
When the demand for labour is elastic this means that a slight change in wages leads to a greater change in employment levels. Conversely, if the demand for labour is inelastic, this means that a big change in wage rates will lead to a smaller change in employment levels.
How do you know if a supply curve is elastic or inelastic?
If the supply changes little with a change in price, then supplies are considered inelastic. Supply is elastic if there are large changes in supply for a small change in price. If the percentage change in price is equal, though opposite, to the percentage change in quantity, then supply elasticity is unit elastic.
What is the elasticity of labor supply?
What is the elasticity of labor supply? Discuss why economists disagree about the magnitude of the elasticity of labor supply.
What is the elasticity of labor supply?
Elasticity of labor supply refers to the degree to which the quantity supplied of labor will go up or down as wages increase or decrease. If there is a high degree of elasticity, the quantity supplied of labor will change a great deal as wages change. If the supply is inelastic, the quantity supplied will not change much as wages change.
What is the degree to which the quantity supplied of labor will go up or down as wages increase or decrease?
The elasticity of the supply of labor refers to the degree to which the quantity supplied of labor will go up or down as wages increase or decrease. If there is a high degree of elasticity , the quantity supplied of labor will change a great deal as wages change.
What is labor supply elasticity?
Share Link. Labor supply elasticity refers to what happens to the supply of workers when the overall compensation for a job changes. If a job is very elastic, the number of people willing to work will increase if the compensation increases. If the compensation decreases, the number of people willing to work will decrease.
What are some examples of elastic labor supply?
A very good example of an elastic labor supply is in the field of education. As pay and benefit packages either have been cut or have remained flat, many school districts are having a difficult time finding teachers to work in their schools. For various reasons, including flat or lower salaries and lower benefit packages, people are opting to do other jobs instead of working in the classroom. These people are showing their dissatisfaction by not taking open positions, not going into the profession, or leaving the profession. If compensation and benefit packages improved, the supply of teachers should increase.
Why is the supply of labor elastic?
The supply of labor is generally said to be more elastic in lower-skilled jobs that require less training. For more skilled jobs, the supply of labor cannot change very quickly. For example, if the wages of doctors went up, there would be no great change in the number of doctors working because it takes a long time to get ...
How long is the free trial for eNotes?
Start your 48-hour free trial to unlock this answer and thousands more. Enjoy eNotes ad-free and cancel anytime.
What is a certified educator?
Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
Did You Know?
Alfred Marshall, a British economist, gave the concept of elasticity of demand and supply in his book “Principles of Economics” in 1890. He was the one to define elasticity of supply and deduced the price elasticity of supply formula. He also explained that the prices of some goods such as medications, salt, gasoline, etc. can increase without reducing their demand in the market, which means that their prices are inelastic. This is because these goods are crucial to the everyday lives of the consumers.
What is less than unit elastic supply?
In such a case, the price elasticity of supply is less than 1.
How does a commodity become elastic?
Perfectly Elastic Supply: A commodity becomes perfectly elastic when its elasticity of supply is infinite. This means that even for a slight increase in price, the supply becomes infinite. For a perfectly elastic supply, the percentage change in the price is zero for any change in the quantity supplied. More than Unit Elastic Supply: When the ...
What does ES mean in a supply?
Here, ES denotes the elasticity of supply which is equal to the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in the price of the commodity.
What does elasticity of supply mean?
Ans: According to the elasticity of supply definition, the supply of a product depends upon its market price. So, if the price of that commodity is less than its cost of production, its supply will be less as the supplier will not earn enough profit by selling that product. However, when its value in the market increases, ...
When is the price elasticity of a commodity greater than 1?
More than Unit Elastic Supply: When the percentage change in the supply is greater than the percentage change in price, then the commodity has the price elasticity of supply greater than 1.
Which axis is the quantity supplied on?
Keeping the quantity supplied on the X-axis and the price of the commodity on the Y-axis, we can draw certain conclusions from the different values of elasticity of supply formula.
Why is Frisch elasticity important?
The Frisch elasticity of labor supply is important for economic analysis and for understanding business cycle fluctuations. It also controls intertemporal substitution responses to fluctuations of wage. Moreover it determines the reaction of effects to fiscal policy interventions, taxation or money transfers. [1]
What is the Frisch elasticity of labor supply?
In other words, the Frisch elasticity measures the substitution effect of a change in the wage rate on labor supply. This concept was proposed by the economist Ragnar Frisch after whom the elasticity of labor supply is named.
What is the effect of Frisch Elasticity?
The overall effect of the Frisch elasticity, however, can be distinguished into extensive and intensive. The extensive effect can be explained as a decision whether to work at all. The intensive effect refers to a decision of an employee on the number of hours to work. . Under certain circumstances, a constant marginal utility ...
Who proposed the Frisch elasticity?
This concept was proposed by the economist Ragnar Frisch after whom the elasticity of labor supply is named. The value of the Frisch elasticity is interpreted as willingness to work when wage is changed. The higher the Frisch elasticity, the more willing are people to work if the wage increases. The Frisch elasticity can be also refers as “ ...