
What is the true purpose of the Electoral College?
The United States Electoral College is the group of presidential electors required by the Constitution to form every four years for the sole purpose of electing the president and vice president.Each state appoints electors pursuant to the methods described by its legislature, equal in number to its congressional delegation (senators and representatives).
What is the Electoral College and what is its purpose?
Electoral college is a body of officials who formally elect the nation's president every four years. The Electoral College is made up of 538 electors who`s purpose is to cast votes to decide the President and Vice-President of the United States.
What is the biggest problem with the Electoral College?
The first problem with the Electoral College is that it gives more weight to voters in small states than those in more populous ones, says DeRosa. Every state gets a minimum of three electoral votes. However, each state’s total allotment is based on its representation in the Senate (always two people) and the House (varies by population).
What are the pros and cons of the Electoral College?
- The system tends to represent more the diversity of the country. ...
- The Electoral College is also the reflection of the federal character of the United States. ...
- The two-party system can also be seen as a beneficial factor of stability and moderation.
Is the Electoral College based on popular vote?
There is no Constitutional provision or Federal law that requires electors to vote according to the results of the popular vote in their States. Some States, however, require electors to cast their votes according to the popular vote.
How Electoral College is determined?
Step 3: The Electoral College The number of electors each state gets is equal to its total number of Senators and Representatives in Congress. A total of 538 electors form the Electoral College. Each elector casts one vote following the general election. The candidate who gets 270 votes or more wins.
What formed the Electoral College and its purpose?
Originally, the Electoral College provided the Constitutional Convention with a compromise between two main proposals: the popular election of the President and the election of the President by Congress. About this object The 1953 electoral vote count declared Dwight D. Eisenhower the winner.
What is the Electoral College simple definition?
The Electoral College is how we refer to the process by which the United States elects the President, even though that term does not appear in the U.S. Constitution. In this process, the States (which includes the District of Columbia just for this process) elect the President and Vice President.
Can electors vote anyway they wish?
Specifically, the opinion held that electors have a constitutional right to vote for the presidential candidate of their choice and are not bound by any prior pledges they may have made.
What is a major criticism of the Electoral College?
Three criticisms of the College are made: It is “undemocratic;” It permits the election of a candidate who does not win the most votes; and. Its winner-takes-all approach cancels the votes of the losing candidates in each state.
What problem did the Electoral College solve?
This arrangement, it was thought, would prevent bribery, corruption, secret dealing, and foreign influence. own State, each Elector was required to cast two votes for president, at least one of which had to be for someone outside their home State.
How did the 12th Amendment change the Electoral College?
Passed by Congress December 9, 1803, and ratified June 15, 1804, the 12th Amendment provided for separate Electoral College votes for President and Vice President, correcting weaknesses in the earlier electoral system which were responsible for the controversial Presidential Election of 1800.
How is the number of Electoral College seats per state determined?
Every State is allocated a number of votes equal to the number of senators and representatives in its U.S. Congressional delegation—two votes for its senators in the U.S. Senate plus a number of votes equal to the number of its Congressional districts.
How many votes do you need to win the Electoral College?
On January 6, the votes are officially opened and counted in a joint session of Congress in the House of Representatives with the Vice President presiding. A candidate must receive 270 of the 538 electoral votes to become President or Vice President.
How we elect our President?
The President is elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the elected members of both the Houses of Parliament and the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of States and the Union Territories of Delhi and Pondicherry.
How many members are there in Electoral College?
Therefore, there were a total of 4796 electors in the list of Electoral College for this Presidential Election to participate in the election.
What Is the Electoral College?
The system calls for the creation, every four years, of a temporary group of electors equal to the total number of representatives in Congress. Technically, it is these electors, and not the American people, who vote for the president. In modern elections, the first candidate to get 270 of the 538 total electoral votes wins the White House.
Why was the electoral college created?
Not only was the creation of the Electoral College in part a political workaround for the persistence of slavery in the United States, but almost none of the Founding Fathers’ assumptions about the electoral system proved true.
How many electoral votes did the first candidate get?
In modern elections, the first candidate to get 270 of the 538 total electoral votes wins the White House. The Electoral College was never intended to be the “perfect” system for picking the president, says George Edwards III, emeritus political science professor at Texas A&M University. “It wasn’t like the Founders said, ‘Hey, what a great idea! ...
Which states have passed laws to give all of their electoral votes to the candidate who wins the state's popular vote count?
The assumption was that each elector’s vote would be counted. But over time, all but two states (Maine and Nebraska) passed laws to give all of their electoral votes to the candidate who wins the state’s popular vote count. Any semblance of elector independence has been fully wiped out.
Who decides the election?
The Founders also assumed that most elections would ultimately be decided by neither the people nor the electors, but by the House of Representatives. According to the Constitution, if no single candidate wins a majority of the electoral votes, the decision goes to the House, where each state gets one vote.
What did the 18th century voters think?
First, they thought 18th-century voters lacked the resources to be fully informed about the candidates, especially in rural outposts. Second, they feared a headstrong “democratic mob” steering the country astray. And third, a populist president appealing directly to the people could command dangerous amounts of power.
What is the Electoral College?
Contrary to what it may suggest, the Electoral College is not a group but rather a “process” that consists of the “selection of electors, the meeting of the electors where they vote for President and Vice President, and the counting of the electoral votes by Congress,” according to The National Archives and Records Administration.
Who is represented in the Electoral College and how does it work?
On Election Day, voters cast ballots as part of the popular vote — the term referring to the votes cast by the registered and qualified public. In the prior spring and summer seasons, state political parties nominate a slate of electors through various methods. Political parties tend to select people to be electors that are active in the party and individuals they want to honor, Berg said.
Why did the Founding Fathers adopt the electoral college?
They eventually adopted the Electoral College after concerns of placing the election in the hands of an uninformed public.
How many people deviated from voting in 2016?
Throughout the history of America, no faithless electors have altered the outcome of an election, but in the 2016 presidential election, 10 electors deviated from voting along party lines; the most since 1872.
What does it mean when a victor is declared?
Once the popular vote has been counted in each state, a victor is declared, indicating which slate of electors will cast their votes in favor of their party’s candidate. All but two states have a “winner-take-all system.”.
How many votes does the District of Columbia have?
Under the 23rd Amendment, the District of Columbia is also allocated three votes and treated like a state in the Electoral College.
Will faithless electors vote in 2020?
Although faithless electors have not swayed an election yet, states have been banding together to ensure there are no issues in 2020. Essentially, Pybas said the compact function to “bind” states to their electors to vote for the nationwide popular vote winner “irrespective of what happens in the state.”
What is electoral college?
The Electoral College is an election topic that inspires confusion, controversy and conflict. Many people know that the Electoral College is part of the Presidential election process but may be unsure about its importance and how it works.
Why is the electoral college important?
Another common theory about the justification for the Electoral College is that it prevented Presidential candidates from ignoring the smaller, less populated states while running for election. If the outcome was just based on the popular vote, candidates could focus primarily on high-population states and urban centers and mostly ignore smaller states and more rural areas of the country.
How many electoral votes do presidential candidates get?
Based on the Electoral College, Presidential campaigns prioritize victories in states that will total more than 270 electoral votes, rather than trying to win the most actual direct votes nationwide. The key reason for this strategy is that in every state, except Nebraska and Maine, the candidate who wins the most votes in a state also wins all ...
How many electoral votes does a state need to win?
There is a total of 538 electoral votes and the candidate must win the majority of the electoral votes to win the election. Therefore, the candidate who gets more than half (270 electoral votes) ...
Why did the South lose every presidential election if there was no electoral college?
One theory is that its roots are in slavery. If there had been no Electoral College, the South would have lost every Presidential election because a large percentage of the Southern population were enslaved people who could not vote.
What was the compromise for the election of the President?
Some suggested that Congress should choose the President. Others argued that it should be a democratic vote by the people. The compromise was the Electoral College , which has been in effect ever since.
What is the role of states in the election?
Individual states have the responsibility of overseeing federal elections and make decisions about their state’s election and voting laws and policies. Each state has the power to adopt and implement critical policies that expand or restrict voting.
How many electors are there in the electoral college?
The Electoral College is made up of 538 electors who cast votes to decide the President and Vice-President of the United States. When voters go to the polls on Tuesday, they will be choosing which candidate receives their state’s electors.
What is electoral vote?
In all but two states, the candidate who wins the majority of votes in a state wins that state’s electoral votes. In Nebraska and Maine, electoral votes are assigned by proportional representation, meaning that the top vote-getter in those states wins two electoral votes (for the two Senators) while the remaining electoral votes are allocated ...
What happens if no one gets a majority of the electoral college?
What happens if no one gets a majority of Electoral College votes? If no one gets a majority of electoral votes, the election is thrown to the U.S. House of Representatives. The top three contenders face off with each state casting one vote. Whoever wins a majority of states wins the election.
How do political parties nominate electors?
Usually, political parties nominate electors at their state conventions. Sometimes that process occurs by a vote of the party’s central committee. The electors are usually state-elected officials, party leaders, or people with a strong affiliation with the Presidential candidates.
Do you have to vote for your party's candidate?
Neither the Constitution nor Federal election laws compel electors to vote for their party's candidate. That said, twenty-seven states have laws on the books that require electors to vote for their party's candidate if that candidate gets a majority of the state's popular vote. In 24 states, no such laws apply, but common practice is for electors to vote for their party's nominee.
How does voting for the Electoral College work?
The Electoral College is widely known as a "winner take all" system because the winner of the popular vote in each state gets all of the state’s electoral votes.
What is the issue with the electoral college?
A key issue to understand about Electoral College is "it proportionately favors smaller states over larger states, " says Erwin Chemerinsky, dean of the law school a U.C. Berkley.
How many delegates are there in the electoral college?
The Electoral College is made up of 538 delegates: people who cast the votes that formally elect the president.
Why are big states forced to live with the electoral system?
So big states are forced to live with the system because there are too many smaller states that would fight off a constitutional amendment to abolish the Electoral College.
How many electoral votes do you need to win the presidential election?
It takes 270 or more electoral votes to win a presidential election.
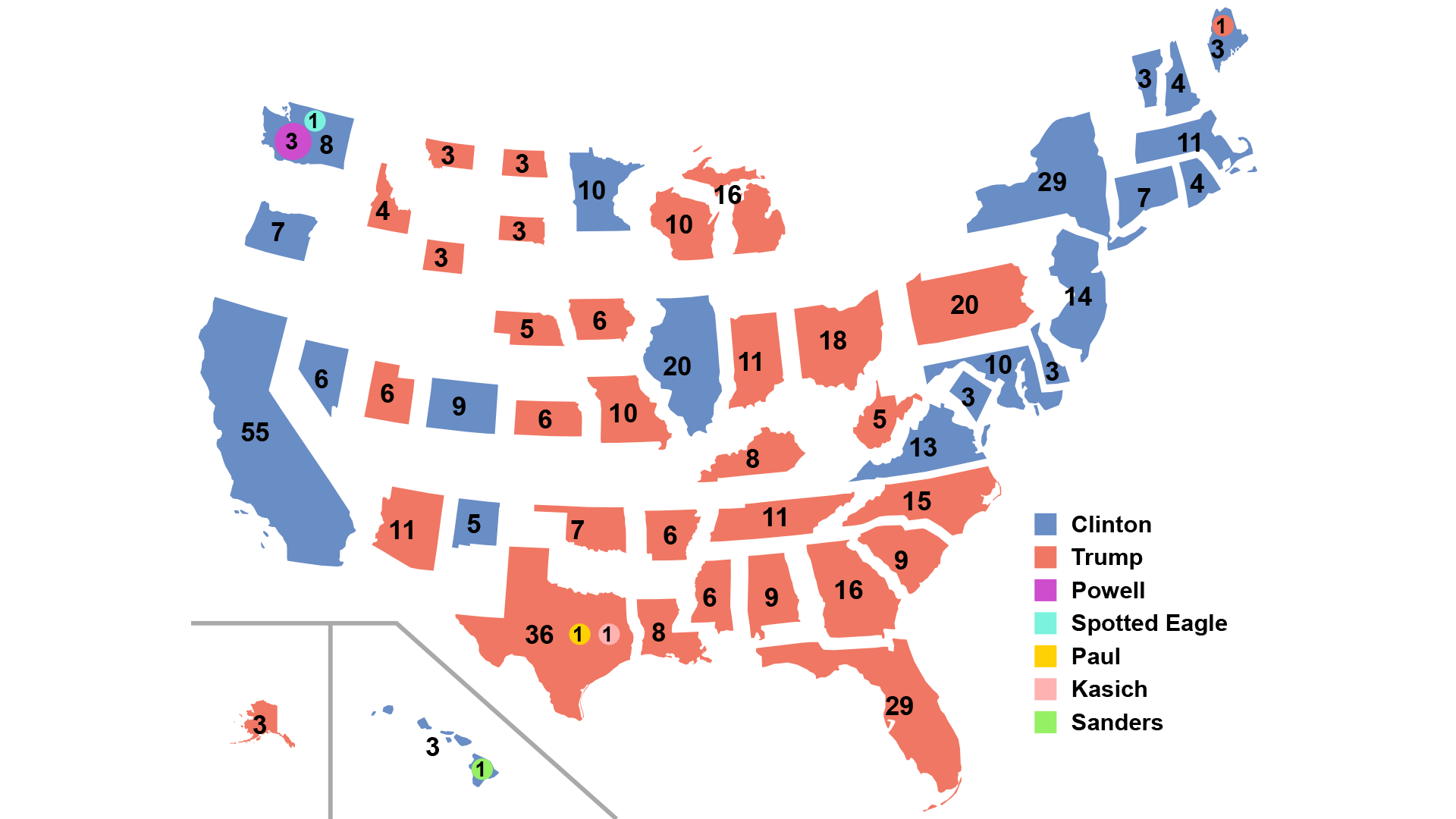
What system made Donald Trump president?
EXPLAINED. The Electoral College is the system that made Donald Trump president even though Hillary Clinton won the popular vote handily. Here's a quick refresher on what it is and how it works.
What is the Electoral College and how does it work?
The Electoral College is a group of intermediaries designated by the Constitution to select the president and vice president of the United States. Each of the 50 states is allocated presidential electors equal to the number of its representatives and senators. The ratification of the 23rd Amendment in 1961 allowed citizens in the District of Columbia to participate in presidential elections as well; they have consistently had three electors.
Why is the electoral college important?
The Electoral College, Explained. A national popular vote would help ensure that every vote counts equally, making American democracy more representative. In the United States, the presidency is decided not by the national popular vote but by the Electoral College — an outdated and convoluted system that sometimes yields results contrary to ...
How did slavery shape the Electoral College?
At the time of the Constitutional Convention, the northern states and southern states had roughly equal populations. However, nonvoting enslaved people made up about one-third of the southern states’ population. As a result, delegates from the South objected to a direct popular vote in presidential elections, which would have given their states less electoral representation.
What are faithless electors?
However, the Constitution does not require them to do so, which allows for scenarios in which “faithless electors” have voted against the popular vote winner in their states. As of 2016, there have been 90 faithless electoral votes cast out of 23,507 in total across all presidential elections. The 2016 election saw a record-breaking seven faithless electors, including three who voted for former Secretary of State Colin Powell, who was not a presidential candidate at the time.
What happens if no candidate wins a majority of Electoral College votes?
If no ticket wins a majority of Electoral College votes, the presidential election is sent to the House of Representatives for a runoff. Unlike typical House practice, however, each state only gets one vote, decided by the party that controls the state’s House delegation. Meanwhile, the vice-presidential race is decided in the Senate, where each member has one vote. This scenario has not transpired since 1836, when the Senate was tasked with selecting the vice president after no candidate received a majority of electoral votes.
What did the 2020 election reveal about the Electoral College?
Additionally, during the certification process for the election, some members of Congress also objected to the Electoral College results, attempting to throw out electors from certain states. While these efforts ultimately failed, they revealed yet another vulnerability of the election system that stems from the Electoral College.
Why does the electoral college dilute the power of black voters?
Today, Codrington argues, the Electoral College continues to dilute the political power of Black voters: “Because the concentration of black people is highest in the South, their preferred presidential candidate is virtually assured to lose their home states’ electoral votes.
What is the electoral college?
The Founding Fathers established the Electoral College in the Constitution, in part, as a compromise between the election of the President by a vote in Congress and election of the President by a popular vote of qualified citizens. However, the term “electoral college” does not appear in the Constitution. Article II of the Constitution and the 12th ...
How many proposals have been made to reform the electoral college?
Reference sources indicate that over the past 200 years more than 700 proposals have been introduced in Congress to reform or eliminate the Electoral College. There have been more proposals for Constitutional amendments on changing the Electoral College than on any other subject.
Which amendments do not refer to electoral colleges?
Article II of the Constitution and the 12th Amendment refer to “electors,” but not to the “electoral college.”. Since the Electoral College process is part of the original design of the U.S. Constitution it would be necessary to pass a Constitutional amendment to change this system.
Is the electoral college part of the original design of the Constitution?
Constitution it would be necessary to pass a Constitutional amendment to change this system.
What is the good, bad, and ugly about the electoral college?
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly about The Electoral College. A history professor shares his insights on the governmental institution that has increasingly become the deciding factor in American presidential races. The 2020 presidential election is fast approaching, which means it’s the perfect time for a refresher on the governmental institution ...
How many electoral votes does each state get?
Every state gets a minimum of three electoral votes. However, each state’s total allotment is based on its representation in the Senate (always two people) and the House (varies by population). “So take Washington, D.C., as an example,” says DeRosa.
What is a faithless elector?
An elector who defies that assignment is called a faithless elector, and the state has the choice whether to tolerate them. “You don’t get them very often because they’re chosen as party loyalists, and we’ve never had faithless electors swing an election,” says DeRosa.
How many votes did the original plan call for?
The original plan called for each elector to cast two votes for president. Whoever received a majority of votes from electors became president; the runner-up became vice president. States can do what they want with their electoral votes, says DeRosa. Most give them to the candidate who wins a state majority.
What are the advantages of electing a president?
If presidents were elected purely by popular vote, a candidate could win the presidency with less than 50% of the vote. “If you had more than two parties contending for the presidency, you might have somebody winning with 30% of the votes, and that’s a ticket to an extremist candidate.”
What is the deciding factor in the 2020 presidential election?
The 2020 presidential election is fast approaching, which means it’s the perfect time for a refresher on the governmental institution that has increasingly become the deciding factor in American presidential races: the Electoral College.
Is the electoral college here to stay?
Love it or hate it, the Electoral College is here to stay because changing it would require “constitutional surgery,” says DeRosa. “You would need three-fourths of the states to ratify any change, and too many states that are intent on suppressing votes benefit from the Electoral College.” The downside? “If you never have to appeal to the electorate because you’re successfully suppressing some large part of it, then you have a broken system.”
Which states are underrepresented in the electoral college?
In particular, the two most populous states — California and Texas — are underrepresented by fewer votes when looking at representation among the voting-eligible population instead of the total resident population. These large states have higher proportions of non-citizen adults and a lower median age than many other states, so their shares of the voting-eligible population are smaller than their shares of the total US population. For example, California makes up 12.1% of the total US population but 11% of the citizen voting-age population; so by total population share, the state is about 10 votes underrepresented in the Electoral College, but by its share of eligible voters, the difference is closer to four votes.
Why is the electoral process not a popular vote?
This is because of the winner-take-all rule for choosing state electors, currently used by 48 states and Washington, DC. According to this rule, all electoral votes go toward the candidate that earns the most votes in the state’s general election; therefore, votes cast for any other candidate do not earn any of the state’s electoral votes.
How many electoral votes will be in 2020?
The 2020 election will be the last of the decade before electoral votes are reallocated based on Census results. See how the current distribution of the nation’s 538 electoral votes compares to the number of people living in all 50 states and Washington, DC.
How does total population affect electoral votes?
Total population helps determine how electoral votes are allocated, but eligible voters determine how the votes are cast. These examples demonstrate electoral representation based on each state’s share of the national population, and that’s because states receive representation in both the House of Representatives and the Electoral College ...
How many votes are underrepresented in California?
For example, California makes up 12.1% of the total US population but 11% of the citizen voting-age population; so by total population share, the state is about 10 votes underrepresented in the Electoral College, but by its share of eligible voters, the difference is closer to four votes.
What does it mean when you cast your vote for the president?
So, when voters cast ballots for president and vice president on Election Day, they’re actually voting for a slate of electors who have pledged to vote for their favored candidates. Most states (with the exceptions of Maine and Nebraska) use a “winner-take-all” system of choosing electors, meaning that — assuming electors vote according to their pledges — all of the state’s electoral votes are cast for the candidate that wins the majority of the state’s popular vote.
How many votes do you need to win a race?
A candidate needs a majority of 270 electoral votes to win each race. In this system, known as the Electoral College, each state gets the same number of electors as it has members of Congress — one for each member in the House of Representatives and one for each of the state’s two senators.
How The Electoral College Works
Rationale For The Electoral College
- Many believe that the origins of the Electoral College are more complex. One theory is that its roots are in slavery. If there had been no Electoral College, the South would have lost every Presidential election because a large percentage of the Southern population were enslaved people who could not vote. Instead, eight of the first nine Presidential races were won by a Virginian ba…
What Critics Say
- Critics of the Electoral College believe that it compromises the “one person, one vote” principle and it is less democratic than a popular vote. Not only can someone win the presidency without winning the popular vote, another consequence is that it influences how and where candidates campaign. Under the current system, if it seems clear that one candidate is likely to win a partic…
States’ Election and Voting Policies
Public Opinion About The Electoral College
- In a 2020 Pew Research study, more than half of U.S. adults (58%) expressed the opinion that the Constitution should be amended so that the Presidential candidate who wins the popular vote (i.e., receives the most votes nationwide) should win the election. Women and young adults are more likely to support amending the Constitution to end the Electoral College. There are also diff…