What is the El Niño ENSO?
"ENSO" refers to the El Niño/Southern Oscillation, the interaction between the atmosphere and ocean in the tropical Pacific that results in a somewhat periodic variation between between below-normal and above-normal sea surface temperatures and dry and wet conditions over the course of a few years.
What does ENSO stand for?
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) The Southern Oscillation refers to changes in sea level air pressure patterns in the Southern Pacific Ocean between Tahiti and Darwin, Australia. During El Niño conditions, the average air pressure is higher in Darwin than in Tahiti. Therefore, the change in air pressures in the South Pacific...
What is the ENSO warm phase?
Often the term ENSO Warm Phase is used to describe El Niño and ENSO Cold Phase to describe La Niña. During ENSO neutral conditions, surface trade winds blow westward across the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Blowing against the ocean’s surface, these winds result in a westward current.
How does ENSO affect weather patterns around the world?
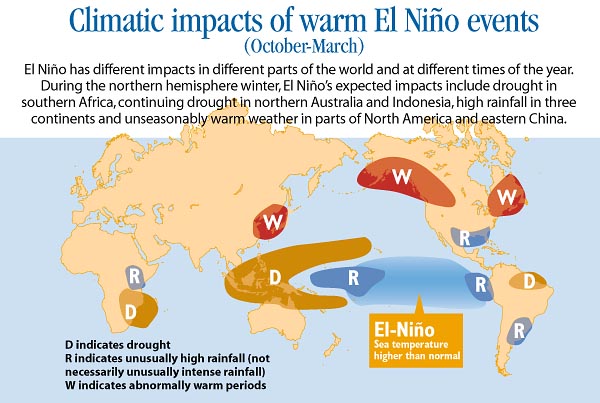
These warmer or cooler than normal ocean temperatures can affect weather patterns around the world by influencing high and low pressure systems, winds, and precipitation. ENSO may bring much needed moisture to a region while causing extremes of too much or too little water in others.

What causes the ENSO phenomenon?
An El Niño condition occurs when surface water in the equatorial Pacific becomes warmer than average and east winds blow weaker than normal. The opposite condition is called La Niña. During this phase of ENSO, the water is cooler than normal and the east winds are stronger.
What do you understand by the phenomenon of ENSO Class 9?
"ENSO" refers to the El Niño/Southern Oscillation, the interaction between the atmosphere and ocean in the tropical Pacific that results in a somewhat periodic variation between between below-normal and above-normal sea surface temperatures and dry and wet conditions over the course of a few years.
Is ENSO a climate phenomenon?
Though ENSO is a single climate phenomenon, it has three states, or phases, it can be in. The two opposite phases, “El Niño” and “La Niña,” require certain changes in both the ocean and the atmosphere because ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon.
What are the 3 stages of ENSO?
We can use surface-water temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific to designate conditions as one of three phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) system — neutral (or “normal”), warm (El Nino), and cold (La Nina).
What is El Nino explain any two features of it Class 9?
el nino means christian name called baby christ. (i) The presence of the EL-Nino leads to an increase in sea-surface temperatures. (ii) It weakens the trade winds in the regions and causes heavy rainfall, floods or droughts in different regions of the world. hope it helps you.
What is monsoon Class 9?
A monsoon is a seasonal wind which lasts for several months. The word was first used in English for the seasonal rains in the Indian subcontinent. These rains blow in from the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area.
What are 3 effects of El Niño?
Severe drought and associated food insecurity, flooding, rains, and temperature rises due to El Niño are causing a wide range of health problems, including disease outbreaks, malnutrition, heat stress and respiratory diseases.
How does ENSO affect rainfall?
El Niño occurs when warm water builds up along the equator in the eastern Pacific. The warm ocean surface warms the atmosphere, which allows moisture-rich air to rise and develop into rainstorms.
How often does ENSO occur?
every 3-7 yearsEl Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of a natural climate pattern across the tropical Pacific Ocean that swings back and forth every 3-7 years on average. Together, they are called ENSO (pronounced “en-so”), which is short for El Niño-Southern Oscillation.
What is ENSO and how does it affect climate?
El Niño and La Niña are the warm and cool phases of a recurring climate pattern across the tropical Pacific—the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO” for short. The pattern shifts back and forth irregularly every two to seven years, and each phase triggers predictable disruptions of temperature, precipitation.
How does ENSO cycle work?
During ENSO events the changes in sea surface temperature cause (and are influenced by) changes in atmospheric circulation (i.e. wind and pressure patterns) and in temperature and rainfall. Through atmospheric dynamics, these atmospheric changes extend well beyond the tropical Pacific region.
What phase of ENSO are we currently in?
La Niña Advisory is currently in effect. La Niña conditions are present. La Niña is slightly favored to continue through the end of 2022 (50-60% chance)....El Nino & La Nina Information.Winter (Nov-Mar) TemperatureSummer (May-Sept) TemperatureWinter (Nov-Mar) PrecipitationSummer (May-Sept) Precipitation3 more rows
What do you understand by the phenomenon of ENSO 5m?
A feature connected with the SO is the El Nino, a warm ocean current that flows past the Peruvian coast, in place of the cold Peruvian current every 2 to 5 years. The changes in pressure conditions are connected to the El Nino. Hence, the phenomenon is referred to as ENSO (El Nino Southern Oscillations).
How is the El Nino phenomenon connected with the Southern Oscillation Class 9?
The Southern Oscillation is a change in air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean. When coastal waters become warmer in the eastern tropical Pacific (El Niño), the atmospheric pressure above the ocean decreases. Climatologists define these linked phenomena as El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
What Is ENSO
El Niño and La Niña are the warm and cool phases of a recurring climate pattern across the tropical Pacific—the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO” for short. The pattern shifts back and forth irregularly every two to seven years, and each phase triggers predictable disruptions of temperature, precipitation.
U.S. Impacts
El Niño is anchored in the tropical Pacific, but it affects climate "downstream" in the United States. In the summer, El Niño's primary influence on U.S. climate is on the hurricane season in both the eastern Pacific and the Atlantic. In winter, it influences the jet stream and the path of storms that move from the Pacific over the United States.
Global Impacts
El Niño and La Niña have their strongest influence on global climate during the Northern Hemisphere winter. During La Niña winters, the southern tier of the United States is often drier than normal. Northern Australia, Indonesia, and the Philippines are often wetter than normal.
Understanding the ENSO Alert System
On the second Thursday of each month, scientists with NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center in collaboration with forecasters at the International Research Institute for Climate and Society (IRI) release an official update on the status of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Here is a description of the categories and criteria they use.
Why are ENSO events different?
Because ENSO events differ in their strength, coverage, and seasonality, there isn't unanimous agreement on what constitutes and ENSO event. But, there are broad agreements and you can find some of the lists researchers have used along with how they chose those years. The list in the right column represents ENSO years based on PSL's Extended Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI.ext).
Why use single time series in ENSO?
While ENSO is a process that varies both in space and time, it can be convenient to use single time series to represent in monitoring and analysis. Some of these time series are SST averages in a specific region of the tropical Pacific while others use more than 1 variable to attempt to capture more of the dynamical processes that occur in ENSO.
What is the contour interval for SST anomalies?
SST data used in these forecasts have been provided by NCEP, courtesy of R. W. Reynolds. Contour interval is 0.3 degrees C.
What are the two types of forecasts?
There are two types of forecasts: those obtained from various ocean–atmosphere models and those obtained from statistical models. These models vary in their skill and sometimes can even do better during certain phases of ENSO than others. Forecasters try to take all this in account when making predictions.
Does ENSO cause moisture?
ENSO may bring much needed moisture to a region while causing extremes of too much or too little water in others. Understanding the processes driving these types of interactions is a key component in improving forecasts and warnings.
Does ENSO affect weather?
As ENSO impacts weather and climate in general, researchers need to potentially look at all atmospheric and ocean variables. PSL maintains an extensive collection of gridded datasets including our 20th Century Reanalysis (1851-2014). Other dataset can be found from links on PSL's data information webpage. Some other NOAA sites also link to ENSO related datasets: for example, NOAA/CPC has an ENSO data/info list .
What is SOI in weather?
The SOI is a mathematical way of smoothing the daily fluctuations in air pressure between Tahiti and Darwin and standardizing the information. The added bonus in using the SOI is weather records are more than 100 years long which gives us over a century of ENSO history. Location of El Niño monitoring zones.
When were nio 1 and nio 2 created?
These regions were created in the early 1980s. Since then, continued research has led to modifications of these original regions. The original Niño 1 and Niño 2 are now combined and is called Niño 1+2.
How does ENSO affect weather?
This is because the low-pressure system in the Pacific draws up warm air into Canada , some of which filters into the northern United States. Another low-pressure system draws cold moist air into the southern United States, bringing lower than normal temperatures. The same low-pressure system in the southern United States is also responsible for increases in precipitation during an El Niño, especially in those areas close to the Gulf of Mexico.
How many copies of each student's briefings and logs are there?
Briefings and Logs (one copy of each per student)
Can you play Enso as a group?
Part 5. The ENSO game may be played as individuals or in small groups . Direct students to proceed with the game as it is presented in Briefing 2: The ENSO game. After deciding whether the data point to an El Niño or La Niña, students can use the table in the ENSO Game Log to record their investment decisions. Tell them to leave blank the two columns marked “Multiplier” and “Outcome” because you will supply them with the multiplier information at the end of the game.
What is the cool phase of ENSO?
La Nina, the “cool phase” of ENSO, is a pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the region’s surface waters. El Niño and La Niña are considered the ocean part of ENSO, while the Southern Oscillation is its atmospheric changes.
How do buoys help scientists?
These buoys transmit data daily to researchers and forecast ers around the world. Using data from the buoys, along with visual imagery they receive from satellite imagery, scientists are able to more accurately predict El Niño and visualize its development and impact around the globe.
What is the term for the oceanic nino index?
Today, most scientists use the terms El Niño and ENSO interchangeably. Scientists use the Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) to measure deviations from normal sea surface temperatures. El Niño events are indicated by sea surface temperature increases of more than 0.9° Fahrenheit for at least five successive three-month seasons.
What is the name of the ocean that describes the unusual cooling of the region's surface waters?
Vocabulary. El Niño is a climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. El Nino is the “warm phase” of a larger phenomenon called the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). La Nina, the “cool phase” of ENSO, is a pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the region’s surface waters.
What is the Southern Oscillation?
The Southern Oscillation is a change in air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean. When coastal waters become warmer in the eastern tropical Pacific (El Niño), the atmospheric pressure above the ocean decreases. Climatologists define these linked phenomena as El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
What is a floating object anchored to the bottom of a body of water?
floating object anchored to the bottom of a body of water. Buoys are often equipped with signals.