What are the equations for aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
- C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 6O2 (Oxygen)6CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) + 6H2O (Water)+ energy (as ATP)
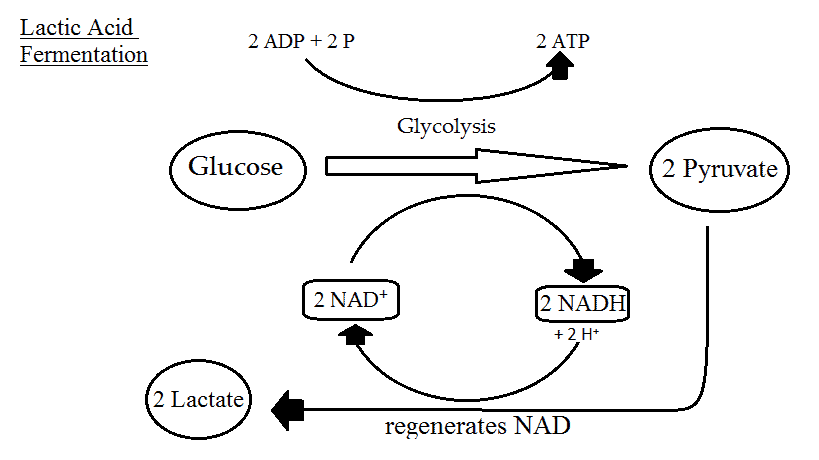
- C6H12O6 (glucose)2C3H6O3 (Lactic Acid) + Energy.
- Question 1: State one difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in terms of energy?
What is the correct equation for cellular respiration?
· What is the equation for aerobic cellular respiration? Aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria and requires oxygen and glucose, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The chemical equation is C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O (glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water).
What is the overall summary equation for cellular respiration?
The chemical equation for aerobic respiration is glucose + oxygen gives carbon dioxide + water + energy whereas the equation for anaerobic respiration is glucose, giving lactic acid + energy Mitochondria in aerobic respiration cytoplasm occurs while anaerobic respiration only …
What is the overall chemical equation for aerobic respiration?
The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below- Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen 6 (O2) → Carbon-dioxide 6 (CO2) + Water 6 (H2O) + Energy (ATP) According to the above-given chemical equation, energy is released by splitting the glucose molecules with the help of …
What are the four steps in aerobic respiration?
· Biochemically, aerobic cellular respiration is defined as the process of metabolizing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from a series of redox …

What are the equation for aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of nutrients to carbon dioxide, water, and energy, and involves an electron transport system in which molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor. The overall reaction is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 yields 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (as ATP).
What is the equation for aerobic cellular respiration quizlet?
The correct equation for aerobic respiration in humans is: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
What is the formula for aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy Anaerobic respiration produces a relatively lesser amount of energy as compared to aerobic respiration, as glucose is not completely broken down in the absence of oxygen.
What is the equation for cellular respiration in?
Notice that the equation for cellular respiration is the direct opposite of photosynthesis: Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O.
What is the general equation for anaerobic respiration?
The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol / lactic acid. Though it does not produce as much energy as aerobic respiration, it gets the job done.
How is the aerobic respiration equation oversimplified?
How is the overall equation for respiration (C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6H₂O + 6CO₂) an oversimplification? Glucose does not react directly with oxygen. Many separate reaction and stages involved in respiration. Glucose is not the only respiratory substrate.
What is the product of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration breaks down glucose and combines the broken down products with oxygen, making water and carbon dioxide.
What is the end product of aerobic respiration?
During aerobic respiration, the respiratory substrate is fully oxidised to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy in a series of enzymatic reactions.
What are the products of aerobic cellular respiration?
The correct answer: The products of aerobic cellular respiration are d) water, carbon dioxide, and ATP. Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration .
What is aerobic respiration in biology?
Listen to pronunciation. (ayr-OH-bik RES-pih-RAY-shun) A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars). Also called aerobic metabolism, cell respiration, and oxidative metabolism.
What is the equation for cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
The products of one process are the reactants of the other. Notice that the equation for cellular respiration is the direct opposite of photosynthesis: Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O. Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6+ 6O.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Cellular respiration that proceeds in the absence of oxygen is anaerobic respiration. Cellular respiration that proceeds in the presence of oxygen is aerobic respiration.
What is aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form...
2. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
Answer:Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of free oxygen and anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
3. How many ATP are produced in aerobic respiration?
Answer: 38 ATP molecules are produced during aerobic respiration.
4. Name the first product formed in the Krebs cycle.
Answer: The first product formed in the Krebs cycle is citric acid, hence it is also called the citric acid cycle.
5. What is the role of oxygen in aerobic respiration?
Answer: Oxygen is responsible for accepting electrons in the electron transport chain.
6. Name the pathway that is common between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: Glycolysis or EMP pathway is the common pathway between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
7. Which step of aerobic respiration produces maximum ATP?
Answer: Oxidative phosphorylation produces maximum ATP, i.e. 34 ATP molecules are formed in this step.
What do you understand by aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What are the different stages of aerobic respiration?
The different stages of aerobic respiration are: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Citric acid cycle Electron Transport Chain
What are the end products of aerobic respiration?
The end products of aerobic respiration include 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water and 30 molecules of ATP.
Where does aerobic and anaerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytop...
What is the importance of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is impo...
What are the different types of aerobes?
The different types of aerobes include: Obligate aerobes that strictly need oxygen to grow. Facultative aerobes can grow in the presence as well as...
What are the two types of cellular respiration?
The cellular respiration is of two types, i.e. aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
What is the end product of aerobic respiration?
In aerobic respiration, free oxygen is used in the complete breakdown of glucose with the formation of carbon dioxide and water as end-products. The equation of aerobic respiration is given below:
What is the process of ATP production?
Definition: Oxidative phosphorylation is the process of ATP production with the help of energy released during the oxidation of coenzymes. It is the last step in aerobic respiration. Phosphorylation is defined as the process of formation of ATP during a process.
What is the first product of the tricarboxylic acid cycle?
Citric acid is the first product of this cycle. Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle).
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
What is the process of breakdown of primary metabolites in the cell with the release of energy in the form of
The process of breakdown of primary metabolites (like glucose, protein, fatty acids, etc.) in the cell with the release of energy in the form of ATP is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP. Cellular respiration can take place in the presence or absence of molecular oxygen. Aerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration is a type ...
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below-. According to the above-given chemical equation, energy is released by splitting the glucose molecules with the help of oxygen gas.
What is the third step of aerobic respiration?
The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle , which is also called the Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a series of reactions and produces 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, ...
Where does oxygen enter the plant cells?
During the respiration process in plants, the oxygen gas enters the plant cells through the stomata, which is found in the epidermis of leaves and stem of a plant. With the help of the photosynthesis process, all green plants synthesize their food and thus releases energy. Also refer : Respiration.
How is energy released in a chemical reaction?
According to the above-given chemical equation, energy is released by splitting the glucose molecules with the help of oxygen gas. At the end of the chemical reaction, energy, water molecules, and carbon dioxide gas are released as the by-products or end products of the reactions.
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is important.
What is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP?
Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP. The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What are the stages of cellular respiration?
Stages of Cellular Respiration. 1. Glycolysis. The first metabolic pathway during cellular respiration is glycolysis. Coming from the Greek word “ glyk ” which means “ sweet ” and “ lysis ” which means “ dissolution “, glycolysis is the breakdown of one molecule of glucose (sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate.
Which type of cellular respiration requires the presence of oxygen?
Aerobic respiration is the type of cellular respiration that requires the presence of oxygen. Among all the types of cellular respiration it is the most efficient.
What happens when oxygen levels are depleted?
When oxygen levels are depleted, electrons will be simply dispersed and the electron transport chain will discontinue.
Where is oxygen found in cellular respiration?
But where does it exactly fit in the picture? Basically, oxygen can be found at the end of the ETC (during aerobic respiration) where it accepts electrons while picking up protons in order to produce water molecules.
Where does the final pathway of cellular respiration occur?
The final pathway in the cellular respiration ( PDF) is comprised of the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation which both occur in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What is the goal of the Krebs cycle?
Note that the goal of the Krebs cycle is to generate high energy electrons from carbon sources. Also notice that the process itself does not generate huge amounts of ATP and does not use oxygen as a precursor molecule. Instead it uses the electrons from acetyl coA to form NADH and FADH 2. 3.
How many steps are involved in the Krebs cycle?
Also called as the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle, or simply the Citric Acid cycle, the Krebs cycle (identified by Hans Adolf Krebs) is an 8-step process that involves 18 different enzymes.
How much ATP does aerobic respiration produce?
The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. In fact, each molecule of sugar digested by a plant or animal cell yields 36 molecules of ATP! By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP.
How does aerobic respiration work?
Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. This chain of proteins within the mitochondrial membrane uses the energy from these electrons to pump protons to one side of the membrane. This creates an electromotive force, which is utilized by the protein complex ATP synthase phosphorylate a large number of ATD molecules, creating ATP.
Which organelle brings together all the reactants needed for cellular respiration in a small, membrane-bound space
The specialized anatomy of the mitochondria – which bring together all the necessary reactants for cellular respiration in a small, membrane-bound space within the cell – also contributes to the high efficiency of aerobic respiration.
Why is aerobic respiration so efficient?
Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. Oxygen “loves” electrons – and its love of electrons “pulls” them through the electron transport chain of the mitochondria.
Which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration?
Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria – organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. Mitochondria are often called “the powerhouse of the cell” because they are able to produce so much ATP!
Which molecules are the final acceptors of electrons used in cellular respiration?
While ATP and carbon dioxide are regularly produced by all forms of cellular respiration, different types of respiration rely on different molecules to be the final acceptors of the electrons used in the process.
What is carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration. Typically, carbon dioxide is considered a waste product and must be removed. In an aqueous solution, carbon dioxide creates acidic ions. This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. To avoid this, cells must actively expel carbon dioxide.
What is the cellular respiration equation?
The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules.
How does the equation of cellular respiration help in calculating the release of energy?
The equation of cellular respiration helps in calculating the release of energy by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen in a cell. If you are searching for information on the formula of cellular respiration equation, the following BiologyWise article will prove to be useful.
What is the reaction that reduces oxygen to water?
The reduction of oxygen to water with the passage of electron to oxygen is the reduction reaction . The NAD + (nictotinadenine dinucleotide) is a co-enzyme that is reduced to NADH, when it picks up two electrons and one hydrogen ion, making it an energy carrier molecule.
How many ATPs are produced in the last step of the ATP cycle?
This step yields the maximum number of ATPs, that is 32 ATP molecules, which makes the total energy produced to 36 ATPs.
What is the first step in glycolysis?
Steps Involved. The first step involves glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cell’s cytoplasm and is an anaerobic process, that does not require oxygen. Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate in a 10-step process yielding 2 ATPs.
What is the name of the reaction in which a molecule gains energy?
This reaction in which a molecule gains energy is known as endergonic reaction . The molecule from which the phosphate is removed tends to lose energy and give off heat. Such a reaction is known as exergonic reaction and the energy level of the molecule decreases.
What is the free energy that is used by cells?
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is the free energy that is used by cells. It is basically an organic molecule that contains high-energy phosphate bonds. When a phosphate is passed from one ATP to another molecule, that molecule tends to gain energy. This reaction in which a molecule gains energy is known as endergonic reaction.
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is one of two types of cellular respiration used by organisms to break down organic compounds into usable cellular energy. When oxygen is not present, cells can undergo a process called anaerobic respiration, but this process releases less usable energy for cells.
How many molecules of glucose are in the aerobic respiration process?
As shown in the equation, six molecules of glucose enter the process with six molecules of diatomic oxygen. These reactants are then combined with two molecules of ATP, which is a catalyst, to cycle through the steps of aerobic respiration. As glucose is broken down and rearranged into ATP, waste products of six water molecules and six carbon dioxide molecules are released by the cells.
How many molecules are created from each glucose molecule?
This step creates the largest amount of ATP, with 28 molecules being created from each original glucose molecule.
What is the process of releasing energy in the mitochondria?
The Krebs cycle, or the citric acid cycle, continues the process in the mitochondria, releasing energy as acetyl-CoA, NADH, and oxygen molecules enter the pathway. Here acetyl-CoA is rearranged into carbon chains, allowing more electrons to be oxidized and sent to the final step in the process. The electrons, in the form of NADH, H+ ions, and FADH2, will be needed to create the largest amount of ATP.
What is the end product of pyruvate?
Pyruvate is broken down by a specialized enzyme that oxidizes the pyruvate molecules to create an end product called acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA. During this step, a CO2 molecule is released as a waste product while the three-carbon pyruvate molecules are turned into two-carbon molecules with an attached sulfur group. This is the acetyl-CoA molecule needed to enter the next step of aerobic respiration.
Why do pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria?
The two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria to be able to further release the chemical energy stored. This occurs in the mitochondria due to the needed reactant - oxygen. Without oxygen present, the process could not continue.
What happens to the product of aerobic respiration?
As outlined above, each product of this first step of aerobic respiration either continues through the process to release more ATP or exits the cell as waste.