Who formulated the five factors of soil formation?
scientist Hans Jenny2The five factors of soil formation. Dokuchaev's ideas set the scene for others: Swiss scientist Hans Jenny2, in particular, who developed the most influential model of soil formation in the 1940's.
What is the acronym for soil forming factors?
CLORPT stands for Climate, Organisms, Parent Material, Time and Topography. These five soil factors affect all of the soils on the planet and describe the physical characteristics that have contributed to the development of soils over time.
What are the 4 types of soil formation?
Loamy Soil.Sandy Soil. The first type of soil is sand. ... Silt Soil. Silt, which is known to have much smaller particles compared to sandy soil and is made up of rock and other mineral particles, which are smaller than sand and larger than clay. ... Clay Soil. Clay is the smallest particle among the other two types of soil.
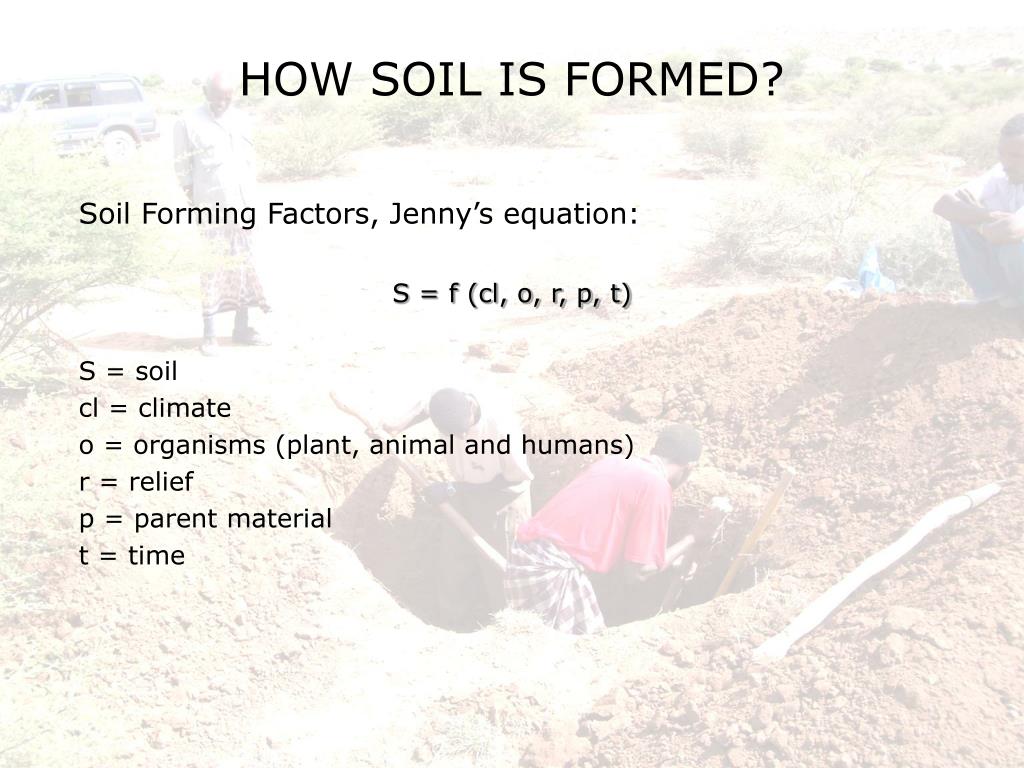
What is Jenny's equation?
His intensive education helped him formulate the Jenny Equation, which is S = f(cl, o, r, p, t, …). In this equation the “S” represents soil formation, "cl" is climate, "o" is organisms in the soil, "r" is relief such as the topography, “p” is the parent material, “t” is the time that takes place.
What is the Clorpt equation?
The standard conceptual model for pedology, soil geomorphology, and soil geography is often called the “clorpt” model, for the way it was portrayed in Hans Jenny's famous 1941 book The Factors of Soil Formation: S = f(cl, o, r, p, t) . . . .
What is the 2 types of soil formation?
As mentioned above, the soils can be formed by physical or chemical weathering processes.
What is the process of soil formation?
They are produced from rocks (parent material) through the processes of weathering and natural erosion. Water, wind, temperature change, gravity, chemical interaction, living organisms and pressure differences all help break down parent material.
What are the soil forming factors PDF?
The major factors affecting the formation of soil are relief, parent material, climate, vegetation and other life-forms and time. Besides these, human activities also influence it to a large extent. The parent material of soil may be deposited by streams or derived from in-situ weathering.
What is CV in soils?
The coefficient of consolidation is the parameter used to describe the rate at which saturated clay or other soil undergoes consolidation, or compaction, when subjected to an increase in pressure. It is measure in square centimeters per second or square inches per minute.
What does ESP stand for in soil?
Exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) is, accordingly, the amount of adsorbed sodium on the soil exchange complex expressed in percent of the cation exchange capacity in milliequivalents per 100 g of soil.
What does SSD stand for in soil?
SSD stands for saturated surface-dry and it describes a condition that a concrete surface must be brought to when a cement product is to be applied to it. The surface is SSD when the substrate is saturated with water, filling the voids in the substrate's aggregate, but the outer surface is devoid of free water.
What is FoS soil?
Factor of Safety (FoS) is a measure used in engineering design to represent how much greater the resisting capacity of a structure or component is relative to an assumed load. With respect to slope stability, FoS is the ratio of shear resistance to driving force along a potential failure plane.
What are recurring patterns of topography?
Recurring patterns of topography result in toposequences or soil catenas. These patterns emerge from topographic differences in erosion, deposition, fertility, soil moisture, plant cover, other soil biology, fire-history, and exposure to the elements.
What is the topography of a terrain?
Topography. The topography, or relief, is characterized by the inclination ( slope ), elevation, and orientation of the terrain. Topography determines the rate of precipitation or runoff and rate of formation or erosion of the surface soil profile.
What is the parent material of soil?
Parent material. The mineral material from which a soil forms is called parent material. Rock, whether its origin is igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic, is the source of all soil mineral materials and the origin of all plant nutrients with the exceptions of nitrogen, hydrogen and carbon.
What are the factors that influence soil formation?
They are: parent material, climate, topography (relief), organisms, and time. When reordered to climate, relief, organisms, parent material, and time, they form the acronym CROPT.
How do soils form?
Soils develop from parent material by various weathering processes. Organic matter accumulation, decomposition, and humification are as critically important to soil formation as weathering. The zone of humification and weathering is termed the solum.
What is the study of pedogenesis?
Other branches of pedology are the study of soil morphology, and soil classification. The study of pedogenesis is important to understanding soil distribution patterns in current ( soil geography) and past ( paleopedology) geologic periods.
How do termites and ants affect soil?
Termites and ants may also retard soil profile development by denuding large areas of soil around their nests, leading to increased loss of soil by erosion. Large animals such as gophers, moles, and prairie dogs bore into the lower soil horizons, bringing materials to the surface.
How does climate affect soil?
Climate - Soils vary, depending on the climate. Temperature and moisture amounts cause different patterns of weathering and leaching. Wind redistributes sand and other particles, especially in arid regions. The amount, intensity, timing, and kind of precipitation influence soil formation. Seasonal and daily changes in temperature affect moisture effectiveness, biological activity, rates of chemical reactions, and kinds of vegetation.
How many factors do soil scientists use to explain how soils form?
Soils and their horizons differ from one another, depending on how and when they formed. Soil scientists use five soil factors to explain how soils form and to help them predict where different soils may occur.
How are soils named?
Soils are named and classified on the basis of physical and chemical properties in their horizons (layers). “Soil Taxonomy” uses color, texture, structure, and other properties of the top two meters of soil to key the soil into a classification system to help people use soil information.
What are the factors that contribute to soil formation?
Factors Contributing to Soil Formation. Parent material - Few soils weather directly from the underlying rocks. These residual soils have the same general chemistry as the original rocks. More commonly, soils form in materials that have moved in from elsewhere. Materials may have moved many miles or only a few feet.
What are the biological factors that affect soil formation?
Biological factors - Plants, animals, microorganisms, and humans affect soil formation. Animals and microorganisms mix soils and form burrows and pores. Plant roots open channels in the soils. Different types of roots have different effects on soils.
What is a soil survey?
The National Cooperative So il Survey identifies and maps over 20,000 different kinds of soil in the United States. Most soils are given a name, which generally comes from the locale where the soil was first mapped. Named soils are referred to as soil series. Soil survey reports include the soil survey maps and the names and descriptions of the soils in a report area. These soil survey reports are published by the National Cooperative Soil Survey and are available to everyone.
What are the factors that determine the native vegetation?
The native vegetation depends on climate, topography, and biological factors, plus many soil factors such as soil density , depth, chemistry, temperature, and moisture. Leaves from plants fall to the surface and decompose on the soil. Organisms decompose these leaves and mix them with the upper part of the soil.
Why do microorganisms play a role in soil formation?
Microorganisms play an even greater role in soil formation because of how they guide the soil nitrogen process, which is essential for the balance of minerals and chemical reactions in the soil. Without the soil nitrogen process, the ocean and other bodies of water would become inhabitable for sea life.
What are the three stages of soil formation?
Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt . But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation.
Why is classification important?
Classification is necessary because of the sheer number of soil types there are. All soils can break down into three types – clay, sand, and silt – which combine to form the different variations of soils. Many elements also contribute to soil formation.
What is the definition of soil formation?
Encyclopedia Britannica defines soil formation as “The evolution of soils and their properties.”
Why is it important to classify soil types?
Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields, or gardeners when they wish to plant only the best species of plants that will thrive in the soil.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Soil formation happens over hundreds, sometimes thousands, of years, but you can still see evidence of that formation today. You can see the soft, dark topsoil layer and every layer underneath, all the way down to the impenetrable bedrock. These layers are called soil horizons.
What are the horizons of soil?
Deeper horizons usually remain unmoving until someone digs into the ground. The soil horizons are O, A, E, B, C, and R. Many factors go into soil formation, and how the soil turns out in appearance and feel depends entirely upon them.
Abstract
All working ecologists with interests in vegetation find themselves at some stage in their careers drawn into close contact with the earth sciences of pedology, geomorphology and geochemisty.
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
What is another process that may be operative in soils?
Another process that may be operative in soils is pedoturbation. It is the process of mixing of the soil.
What is the process of differentiation of soil in different horizons along the depth of the soil body?
The differentiation is due to the fundamental processes, humification, eluviation and illuviation.
Why is precipitation important?
Precipitation is the most important among the climatic factors. As it percolates and moves from one part of the parent material to another. It carries with it substances in solution as well as in suspension. The substances so carried are re deposited in another part or completely removed from the material through percolation when the soil moisture at the surface evaporates causing an upward movement of water. The soluble substances move with it and are translocated to the upper layer. Thus rainfall brings about a redistribution of substances both soluble as well as in suspension in soil body.
What are passive soil forming factors?
The passive soil forming factors are those which represent the source of soil forming mass and conditions affecting it. These provide a base on which the active soil forming factors work or act for the development of soil.
Why is soil on steep slopes shallow?
It is due to accelerated erosion, which removes surface material before it has the time to develop. Reduced percolation of water through soil is because of surface runoff, and lack of water for the growth of plants, which are responsible for checking of erosion and promote soil formation.
Which process is slower, pedogenic or geological?
The pedogenic processes, although slow in terms of human life, yet work faster than the geological processes in changing lifeless parent material into true soil full of life.
Is podzolization a negative process?
It is a process of soil formation resulting in the formation of Podzols and Podzolic soils. In many respects, podzolization is the negative of calcification. The calcification process tends to concentrate calcium in the lower part of the B horizon, whereas podzolization leaches the entire solum of calcium carbonates.
Origins
The Jenny Equation was created by Hans Jenny, one of the Founders of Soil Concepts to explain the soil formation process. It was first internationally recognized when Hans Jenny published his book “Factors of Soil Formation” in 1941.
Hans Jenny
Hans Jenny was born in Switzerland in 1899. His college career started with the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (Zurich) where he received a bachelor in agriculture in 1922. He later received degrees in chemistry and ion exchange reactions by 1927, also from Zurich.
Uses of Jenny Equation
The Jenny Equation helps determine the physical properties of soil based on several independent factors. These factors are from the pedogenesis processes, which in this equation are climate, organisms, topography, parent material, time, and any other factors that may apply.
Climate
Two of the most influential factors of climate are temperature and moisture. Temperature has a direct effect on the rate that chemical reactions can occur in the soil. The higher the temperature, the quicker the reactions will happen within the soil. Moisture also affects the rates of chemical reactions that can happen in the soil.
Organisms
The organisms in the soil also influence the soils processes and functions. The vegetation and animals have a significant role. Plants roots help to break up the soil by creating more surface area for water to seep into. This allows chemical reactions to occur here as plants excrete chemicals that help these chemical reactions to take place.
Topography
The next factor in the equation is topography. Topography is the slope of the land, whether there is a hill, valley, flat plain, or other meaningful change in elevation. The topography of the land is a significant factor for the moisture content of the soil.
Parent Material
The parent material of the soil is determined from what type of rock it is derived from. Igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary rock break down and create different types of soil, whether it is sandy, silt or clay dominated soil.
Summary
History of research
Russian geologist Vasily Dokuchaev, commonly regarded as the father of pedology, determined in 1883 that soil formation occurs over time under the influence of climate, vegetation, topography, and parent material. He demonstrated this in 1898 using the soil forming equation:
soil = f(cl, o, p) tr
Russian geologist Vasily Dokuchaev, commonly regarded as the father of pedology, determined in 1883 that soil formation occurs over time under the influence of climate, vegetation, topography, and parent material. He demonstrated this in 1898 using the soil forming equation:
soil = f(cl, o, p) tr
Overview
Soil develops through a series of changes. The starting point is weathering of freshly accumulated parent material. A variety of soil microbes (bacteria, archaea, fungi) feed on simple compounds (nutrients) released by weathering, and produce organic acids and specialized proteins which contribute in turn to mineral weathering. They also leave behind organic residues which contribute to humus formation. Plant roots with their symbiotic mycorrhizal fungi are also able to extract nutr…
Factors of soil formation
Soil formation is influenced by at least five classic factors that are intertwined in the evolution of a soil. They are: parent material, climate, topography (relief), organisms, and time. When reordered to climate, organisms, relief, parent material, and time, they form the acronym CLORPT.
The mineral material from which a soil forms is called parent material. Rock, w…
Soil forming processes
Soils develop from parent material by various weathering processes. Organic matter accumulation, decomposition, and humification are as critically important to soil formation as weathering. The zone of humification and weathering where pedogenic processes are dominant and where biota play an important role is termed the solum.
Soil acidification resulting from soil respiration supports chemical weathering. Plants contribute t…
What Is Soil Formation?
Soil Formation Steps
- Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt. But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation. 1. Erode – Elements of weather cause the rocks, soil, and plant matter in an area to erode and become sediment that contains various minerals and nutrients that were in the previous materia…
Factors Affecting Soil Formation
- There are many factors in nature that influence soil formation. These factors determine what type of soil forms (sandy, loam, red clay…etc.) and its location in the world after formation. The first and most important factor affecting soil formation is the parent material. After that, various things can change the formation process, but each factor can have an impact on the final product.
Types of Soil Formation
- Clay, sand, and silt are the three textures of soil that mix to form all the different soil types. Although the soil formation process is relatively the same for all three, some variations are important to recognize.
Soil Taxonomy
- Soil taxonomy refers to the classification of soil types. Classification is necessary because of the sheer number of soil types there are. All soils can break down into three types – clay, sand, and silt – which combine to form the different variations of soils. Many elements also contribute to soil formation. Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields…
Soil Maps
- Soil maps are created from soil surveys. Soil scientists (pedologists) and farmers are the most common people who might need a soil survey map. Soil maps can identify the limitations and qualities of the soil in a large area of land. Landscapers can also utilize a soil survey map for aeration purposes. A soil survey mapshows the results of a soil survey mapped out on a scaled-…
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does it take for soil to form?
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), it can take at least 500 years for one inch of topsoil to form. Although, many soil scientists say it takes even longer. To form all the horizons in soil, it can take thousands, if not millions, of years. - Can soil be created?
Yes. Many gardeners use compost, moisture, much, and decomposing plants to create nutrient-rich topsoil, though making a soil from scratch without a parent material may prove to be difficult.