
The external environment, also known as the macro environment, is out of the control of an individual business. Factors like competition, market, economic, demographic, and environmental factors all play a role in the external environment of an organisation.
What are the six elements of the external environment?
Elements of the external environment include the economy, changes in technology, regulation, competition, socio-economic factors, and others. Several areas within the organization influence HR activities, including top management, organizational strategy and culture, technology, structure, and size.
What do you mean by external environment?
External Environment. The external environment constitutes factors and forces which are external to the business and on which the marketer has little or no control. The external environment is of two types: Micro marketing environment; Macro marketing environment; Micro Environment. The micro-component of the external environment is also known as the task environment.
What are some external environmental factors?
Environmental factors include weather, climate, and climate change, which may especially affect industries such as tourism, farming, and insurance.Furthermore, growing awareness to climate change is affecting how companies operate and the products they offer--it is both creating new markets and diminishing or destroying existing ones.
What is meant by the internal environment?
Internal Environment is that part of the business environment which is concerned with the different factors present within the organization. It comprises of conditions, forces, members and events which has the capability to influence the company’s decisions and operations.
What is the meaning external environment?
Definition. The environment outside of the organism, which pertains to the physical, chemical, biological and social conditions surrounding the organism. Supplement. The external environment is used in contrast to the internal environment of the organism.
What is an example of an external environment?
The external environment of a business are the external factors in the environment that affects the business. Example of external environment are Institutions, organizations, forces operating outside the company.
What is the external environment of organizations?
The big picture of an organization's external environment, also referred to as the general environment, is an inclusive concept that involves all outside factors and influences that impact the operation of a business that an organization must respond or react to in order to maintain its flow of operations.
What are the 6 external environments?
In particular, PESTEL reflects the names of the six segments of the general environment: (1) political, (2) economic, (3) social, (4) technological, (5) environmental, and (6) legal.
What is the external environment and why is it important?
External environment factors are elements that exist outside of a company's internal environment that can affect a company's operations. These outside forces can help the business or present challenges to its current processes.
What are 5 external environments?
We explain below all these factors determining external macro-environment:Economic Environment: ... Social and Cultural Environment: ... Political and Legal Environment: ... Technological Environment: ... Demographic Environment:
What is external environment in management?
The external environment refers to factors, forces, situations, and events outside the organization that affects its performance. It includes economic, demographic, political/legal, sociocultural, technological, and global components.
What is internal and external environment?
Meaning. Internal Environment refers to all the inlying forces and conditions present within the company, which can affect the company's working. External Environment is a set of all the exogenous forces that have the potential to affect the organization's performance, profitability, and functionality. Nature.
What is the internal environment of a business?
An organization's internal environment is composed of the elements within the organization, including current employees, management, and especially corporate culture, which defines employee behavior. Although some elements affect the organization as a whole, others affect only the manager.
What are the 7 factors of the external environment?
Customers, competition, economy, technology, political and social conditions, and resources are common external factors that influence the organization. Even if the external environment occurs outside an organization, it can have a significant influence on its current operations, growth and long-term sustainability.
What are the two types of external environment?
The external environment can be broken down into two types: the micro environment and the macro environment.
What are the 5 environments of business?
5 Major Components of Business Environment | Business Studies(i) Economical Environment:(ii) Social Environment:(iii) Political Environment:(iv) Legal Environment:(v) Technological Environment:
What are the two types of external environment?
The external environment is divided into two parts:Directly interactive: This environment has an immediate and firsthand impact upon the organization. ... Indirectly interactive: This environment has a secondary and more distant effect upon the organization.More items...
What are the examples of internal environment?
There are 14 types of internal environment factors:Plans & Policies.Value Proposition.Human Resource.Financial and Marketing Resources.Corporate Image and brand equity.Plant/Machinery/Equipments (or you can say Physical assets)Labour Management.Inter-personal Relationship with employees.More items...•
What is external and internal environment?
Meaning. Internal Environment refers to all the inlying forces and conditions present within the company, which can affect the company's working. External Environment is a set of all the exogenous forces that have the potential to affect the organization's performance, profitability, and functionality. Nature.
What are the 5 external environmental factors that affect marketing?
To get a better idea of how they affect a firm's marketing activities, let's look at each of the five areas of the external environment.The Political and Regulatory Environment. ... The Economic Environment. ... The Competitive Environment. ... The Technological Environment. ... The Social and Cultural Environment. ... Consumer Behavior.More items...
Name a model used to analyse the external environment.
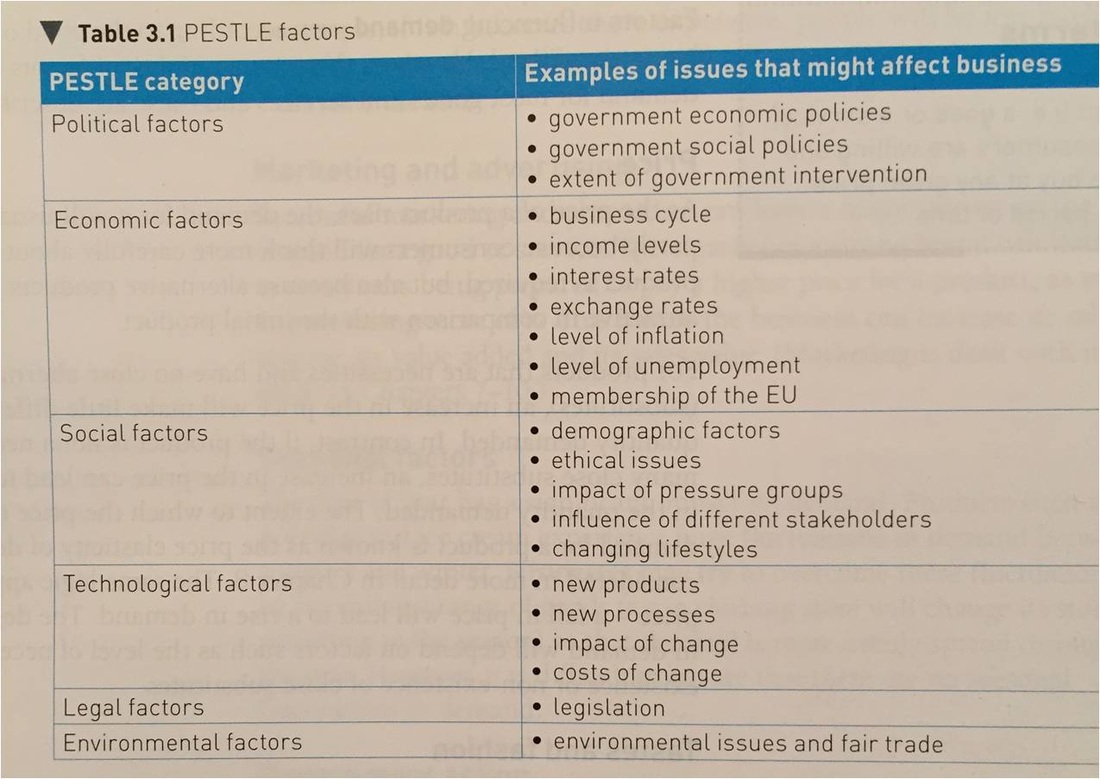
PESTLE analysis can be used to conduct external environment or macro analysis. PESTLE takes a look at six different external factors that could inf...
List the different components of the PESTLE analysis with an example of each.
PESTLE evaluates political, economic, social, technological, legal, environmental and ethical factors. Examples: Political stability Inflation rat...
Name some of the social factors that are attributed to the external environment.
Demographics Lifestyles and lifestyle changes Education levels Attitudes Level of consumerism (how important consumption of goods and services is...
Name some of the technological factors that are attributed to the external environment.
Levels of government and industrial R&D investment Disruptive technologies New production processes Big Data & AI Speed of technology transfer...
How would you define the concept of a business's external environment?
The external environment of a business includes a group of factors that are outside the direct control of the business but can still have a large i...
Why is the external environment important?
The external environment of a business, also known as the macro environment, includes all factors outside the reach of the business, that can impac...
External Environment - Key takeaways
All businesses are impacted by their external environment. Sometimes a business has to act upon and react to what happens outside of the scope of its operations.
External business environment
All businesses are impacted by their external environment. Sometimes a business has to act upon and react to what happens outside of the scope of its operations. These external influences are known as external factors. Multiple different factors can influence a business's external environment.
External environmental factors
Four main components make up the external environment of businesses. These are the main external factors you have to consider when operating a business.
External environment analysis
A useful tool for analysing the external environment of an organisation is 'PESTLE'. PESTLE analysis takes a look at six different external factors that could have an impact on your business and rates the intensity and importance of each. PESTLE stands for political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental/ethical factors.
Frequently Asked Questions about External Environment
The external environment of a business, also known as the macro environment, includes all factors outside the reach of the business, that can impact the operations of the business.
What is external environment?
The External Environment. All outside factors that may affect an organization make up the external environment. The external environment is divided into two parts: Directly interactive: This environment has an immediate and firsthand impact upon the organization. A new competitor entering the market is an example.
What are the political dimensions of the external environment?
The political and legal dimensions of the external environment include regulatory parameters within which an organization must operate. Political parties create or influence laws, and business owners must abide by these laws.
What are some examples of favorable economic conditions?
A favorable economic climate generally represents opportunities for growth in many industries, such as sales of clothing, jewelry, and new cars. But some businesses traditionally benefit in poor economic conditions. The alcoholic beverage industry, for example, traditionally fares well during times of economic downturn.
What is global dimension?
The global dimension of the environment refers to factors in other countries that affect U.S. organizations. Although the basic management functions of planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling are the same whether a company operates domestically or internationally, managers encounter difficulties and risks on an international scale. Whether it be unfamiliarity with language or customs or a problem within the country itself (think mad cow disease), managers encounter global risks that they probably wouldn't have encountered if they had stayed on their own shores.
Why are external environment factors important?
External environment factors are important because they can cause direct and indirect effects on business operations, personnel and revenue. The external environment of a company changes constantly in ways beyond the company's control, but executives and managers can track these changes and minimize their consequences. Choosing to monitor the dynamic nature of external environment factors allows businesses to protect themselves against predictable events and mitigate the effects of unexpected changes.
How many types of external environment factors affect businesses?
Here are the nine types of external environment factors that affect businesses:
Why is it important to monitor external environmental factors?
It's also important to monitor any external environmental factors that can affect how the business functions as well as develop methods for overcoming these challenges. In this article, we discuss what external environment factors are, their importance and nine of these factors that affect businesses.
How does environmental awareness affect business?
As environmental awareness continues to grow, more consumers have realized the effects of business processes on the planet. Some consumers have used their purchases to support companies that develop ecologically friendly practices, such as using compostable packaging and solar energy. By paying attention to these external concerns and changing their operations, businesses can make changes that help them protect the environment, retain customers and increase revenue.
Why do executives have a duty to keep track of both domestic and global issues?
Executives have a duty to keep track of both domestic and global issues, especially if they conduct business internationally. By learning about social issues that affect those in other countries and their cultural norms, consumer trends and economic status, company leaders can provide their teams with relevant training. This enables them to develop products or offer services that meet the needs of international customers by providing solutions to challenges they face as consumers.
What is task environment?
The task environment consists of stakeholders with whom organizations interacton a fairly regular basis. These stakeholders include domestic and internationalcustomers, suppliers, competitors, government agencies and administrators, localcommunities, activist groups, unions, and financial intermediaries. MichaelPorter, an economist at Harvard University, assimilated years of economic re-search into a simple model that helps determine the influence of the first three ofthese stakeholders—suppliers, customers, and competitors—on competition inan industry. His model will be presented in the next section.11
How do firms influence the broad environment?
Forces in the broad environment can have a tremendous impact on a firm and its task environment; however, individual firms typically have only a marginal abil- ity to influence these forces. In rare cases, individual firms can influence trends in the broad environment, as when innovations at Intel influence technological trends in the microprocessor, microcomputer, and software industries. In general, however, it is virtually impossible for one independent firm to dramatically in- fluence societal views on abortion, policies on free trade with China, migration to the Sun Belt, the number of school-age children, or even the desirability of par- ticular clothing styles. Consequently, although firms may be able to influence the broad environment to some degree, the emphasis in this book generally will be on analyzing and responding to this segment of the environment. The most im- portant elements in the broad environment, as it relates to a business organization and its task environment, are global socio-cultural, economic, technological, and political/legal forces.
What are the barriers to entry in an industry?
2. Large capital requirements, also known as start-up costs, can prevent a small competitor from entering an industry. 3. High levels of product differentiation, which means that some firms enjoy a loyal customer base, making it harder for a new firm to draw away customers. 4. High switching costs, which apply not only to suppliers , can also serve as an entry barrier protecting established firms in an industry. 5. Limited access to distribution channels, which may prevent new compa- nies from getting their products to market. 6. Government policies and regulations that limit entry into an industry, ef- fectively preventing new competition. 7. Existing firm possession of resources that are difficult to duplicate in the short term, such as patents, favorable locations, proprietary product tech- nology, government subsidies, or access to scarce raw materials. 8. A past history of aggressive retaliation by industry competitors toward new entrants. Taken together, these forces can result in high, medium, or low barriers. In in- dustries with high entry barriers, few new firms enter the industry, which reduces the competitive intensity and stabilizes profits for industry incumbents. When entry barriers are low, new firms can freely enter the industry, which increases ri- valry and depletes profits. Examples of industries that are traditionally associated with high barriers to entry are aircraft manufacturing (due to technology, capital costs, and reputation) and automobiles manufacturing (due to capital costs, dis- tribution, and brand names). Medium-high barriers are associated with industries such as household appliances, cosmetics, and books. Low entry barriers are found in industries such as apparel manufacturing and most forms of retailing. One of the most powerful effects of the Internet has been the ability to circumvent traditional barriers to entry. For many Americans, Amazon.com is as synonymous with book retailing as Barnes and Noble. Amazon, however, never had to face the extraordinary expense of leasing or buying land, building large bookstores in pre- mium retail locations, stocking and maintaining inventories in remote locations, and hiring and training a workforce experienced in the nuances of book retailing. They circumvented those barriers to entry by going straight to consumers with an exclusive Internet strategy.
How does economics affect organizational performance?
Economic forces can have a profound influence on organizational behavior and performance. Economic growth, interest rates, the availability of credit, inflation rates, foreign exchange rates, and foreign trade balances are among the most crit- ical economic factors. Economic growth can also have a large impact on consumer demand for products and services. Consequently, organizations should consider forecasts of economic growth in determining when to make critical resource allo- cation decisions such as plant expansions. Inflation and the availability of credit, among other factors, influence interest rates that organizations have to pay. High interest payments can constrain the strategic flexibility of firms by making new ventures and capacity expansions prohibitively expensive. Low interest rates, such as those experienced in the U.S. in the late 1990s, coupled with fears that the Federal Reserve would raise rates, have led to volatile reactions in the stock market. Foreign exchange rates are another major source of uncertainty. For global or- ganizations, profit earned in a foreign country may turn into a loss due to unfa- vorable exchange rates. Finally, foreign trade balances are highly relevant to both domestic and global organizations because they are an indication of the nature of trade legislation that might be expected in the future. For example, the United States has a large trade surplus with the European Union (EU). As a result, American manufacturers who export to the EU are concerned about new protec- tionist legislation, such as high tariffs, that may be enacted to reduce the trade imbalance.7
How does socio-cultural change affect economics?
The socio-cultural forces discussed in the last section often interact with the economic forces. In the United States, birthrates (a socio-cultural force) are low and, because of improved health care and lifestyles (another socio-cultural force), more people are living longer. This demographic shift toward an older population is influencing the economic forces in society. For example, the older
