During aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid which is formed during glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO + H. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and N…
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitami…
What liberates an electron from chlorophyll?
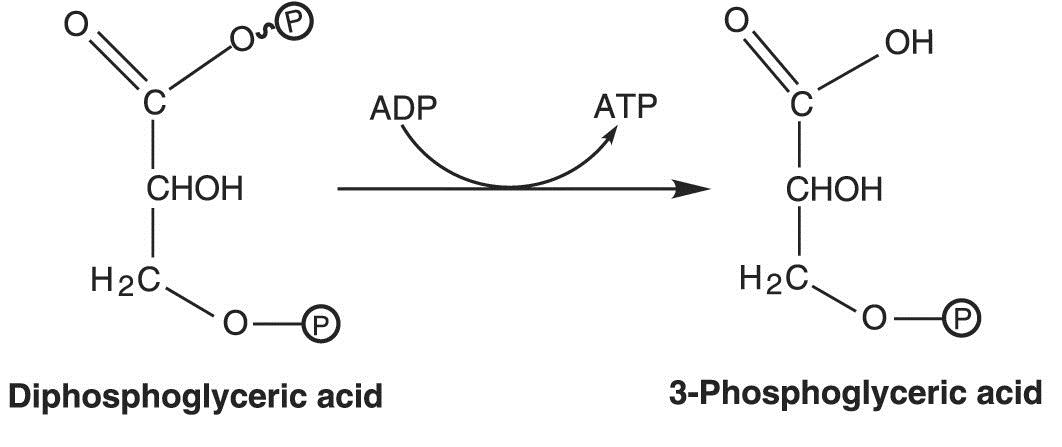
Which is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP?
About this website
What happens to pyruvic acid in aerobic respiration?
Pyruvic acid supplies energy to living cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle ) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration); it ferments to produce lactic acid when oxygen is lacking ( fermentation ).
What is the fate of pyruvate in aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Note: In the aerobic respiration, the acetyl CoA which was produced enters the Krebs cycle and in the anaerobic respiration, pyruvate which is aldose form convert to keto form and it is finally converted to lactate in the presence of enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
Why is ATP 38 or 36?
During citric acid cycle, 36 ATP molecules are produced. So, all together there are 38 molecules of ATP produced in aerobic respiration and 2 ATP are formed outside the mitochondria. Thus, option A is correct.
What are the 2 fates of pyruvate?
Next, show that in aerobic conditions (the presence of oxygen), pyruvate has two possible fates: - The first is cellular respiration, which occurs in fed conditions – when glucose is abundant. - The second is gluconeogenesis, which occurs in fasting conditions – when glucose is in demand.
What are the 3 fates of pyruvate?
The Three Fates of Pyruvate Lactate formation. Ethanol formation. Acetyl CoA formation.
How many ATP is released in aerobic respiration?
Theoretically, 38 ATP molecules can be produced by the complete oxidation of one glucose molecule in aerobic respiration.
How many ATP is produced in glycolysis?
2 ATPDuring glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; a total of 2 ATP is derived in the process (Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi --> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O).
How many ATP are made during aerobic respiration?
36 ATPAerobic vs anaerobic respirationAerobicProductsATP, water, CO 2LocationCytoplasm (glycolysis) and mitochondriaStagesGlycolysis (anaerobic), Krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylationATP producedLarge amount (36 ATP)1 more row
What is the fate of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen?
Solution : In the absence of oxygen pyruvate will be converted to lactic acid releasing small amount of energy .
What are the fates of pyruvate Class 10?
Pyruvate is found at the intersection of various metabolic pathways. When oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle after decarboxylation and formation of acetyl CoA. When oxygen is absent, pyruvate undergoes fermentation, i.e. alcoholic or lactic acid fermentation.
What are the possible fates of pyruvate after glycolysis?
Glycolysis produces two molecules of 'pyruvate' from a single glucose molecule. These pyruvates can enter into different metabolic reactions and produces energy through different pathways. Based on the pathway they enter, pyruvate may be converted to ethanol, lactic acid, acetyl CoA, or oxaloacetate.
What happens to pyruvate after glycolysis?
In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are the sites of cellular respiration. There, pyruvate will be transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A (CoA).
What liberates an electron from chlorophyll?
A) Light liberates an electron from chlorophyll.
Which is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP?
C) ATP is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP.
What liberates an electron from chlorophyll?
A) Light liberates an electron from chlorophyll.
Which is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP?
C) ATP is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP.
