What type of fermentation does bread use?
- Lactic acid fermentation. Yeast strains and bacteria convert starches or sugars into lactic acid, requiring no heat in preparation.
- Ethanol fermentation/alcohol fermentation.
- Acetic acid fermentation.
What are the steps in fermentation?
We will break down the 3 phases of fermentation/conditioning here:
- Primary fermentation
- Secondary fermentation (Optional)
- Bottle or keg conditioning and carbonation
What is the equation for the reaction of fermentation?
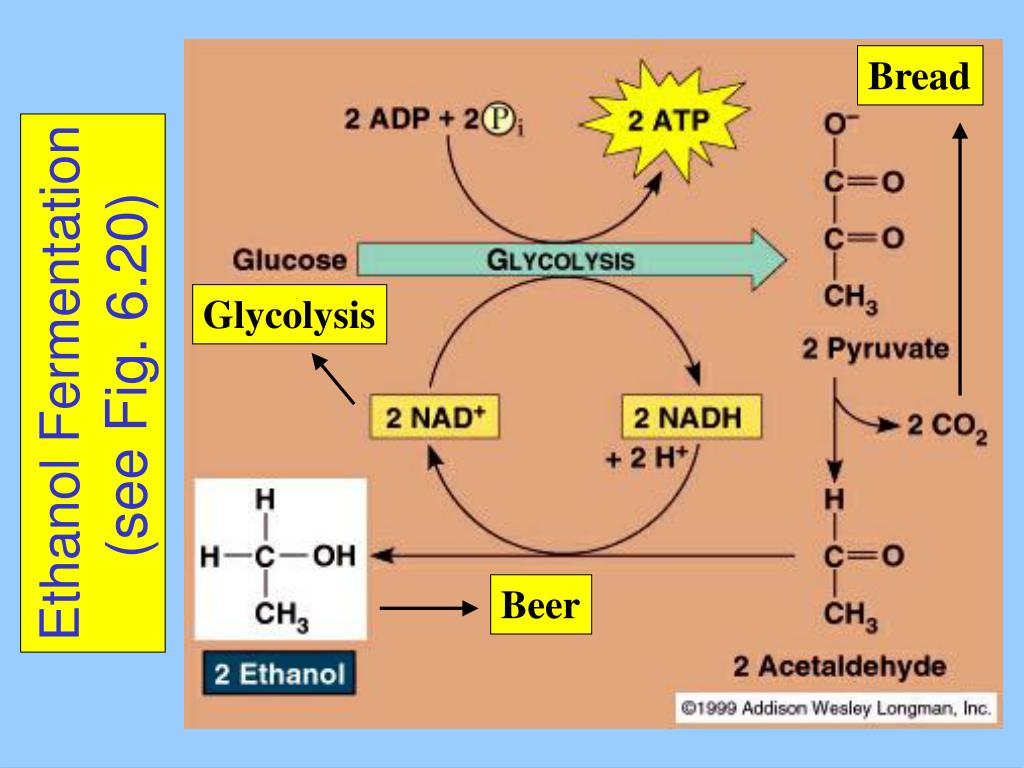
The chemical reaction for fermentation is expressed as the chemical equation: C6H12O6 ? 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2. Showing the alcoholic fermentation of glucose as chemical formula C6H12O6, this one glucose molecule is converted into two ethanol molecules expressed as 2C2H5OH and two carbon dioxide molecules expressed as 2CO2.
What is the chemical formula for fermentation?
What is the chemical equation for fermentation. The simple equation for lactic acid fermentation is glucose glycolysis 2 pyruvate fermentation 2 lactic acid. C 6 H 12 O 6 glucose 2 C 2 H 5 OH ethanol 2 CO 2 carbon dioxide. C6H12O6 2 C2H5OH 2 CO. The fermentation of carbohydrates produces alcohol.
How to make bread rise before baking?
What is the process of changing sugars and starches into carbon dioxide?
How to ferment bread?
How long does proofing bread last?
Why is fermentation important?
What is the process of yeast fermentation?
How long does bread fermentation last?
See 2 more

What is the fermentation process of bread?
In brief, fermentation refers to the chemical decomposition of complex organic compounds into simpler substances. With bread, this refers to the process where yeast converts sugar to carbon dioxide and alcohol in the absence of oxygen, causing dough to rise.
What is the reaction of fermentation?
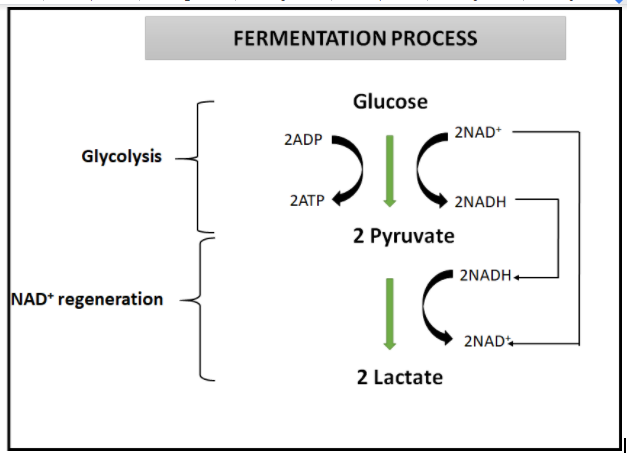
Fermentation reacts NADH with an endogenous, organic electron acceptor. Usually this is pyruvate formed from sugar through glycolysis. The reaction produces NAD+ and an organic product, typical examples being ethanol, lactic acid, and hydrogen gas (H2), and often also carbon dioxide.
What type of reaction is bread making?
Specifically, it participates in the Maillard reaction, a series of reactions between sugars and amino acids that occur rapidly above 140˚C. These reactions produce a whole range of products, which can add flavour to the bread, and also help to form the brown crust of the bread.
What is the reaction for fermentation in yeast?
During fermentation, yeast cells convert cereal-derived sugars into ethanol and CO 2 . At the same time, hundreds of secondary metabolites that influence the aroma and taste of beer are produced.
What are the two reactions of fermentation?
There are two types of fermentation, alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
What reaction is taking place in the yeast cells during bread making?
fermentationOne such chemical reaction is the fermentation of sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide by yeast. This process is the fundamental step to making bread dough. Before most bread doughs get baked, they require time to rise. This is also the time when fermentation takes place.
What is the reaction that turns bread into toast?
When does bread become toast? The browning process we call toasting is an example of the Maillard reaction, in which amino acids and sugars interact to produce the characteristic brown color, texture, and flavor we know as toast.
What type of reaction is baking?
As you bake a cake, you are producing an endothermic chemical reaction that changes ooey-gooey batter into a fluffy, delicious treat!
Is baking bread a reaction or process?
Answer and Explanation: Baking bread is an endothermic process. An endothermic reaction is one that must absorb energy, in this case heat, in order to make the reaction occur.
Is baking bread a synthesis reaction?
Synthesis is a chemical reaction where two or more substances combine to form one substance. Proteins in flour combine through a synthesis reaction to form gluten. Gluten is an important ingredient which forms to give baked goods their signature structure.
What are the reactions involved in baking dough?
The chemical reactions in bread making include changes in the starch present in the dough, producing a process known as gelatinization, where the starch absorbs water, disintegrating the granules in which it is found, these reactions are noticed in the thickness of the dough, where they produce deformation and changes ...
What are three chemical reactions that occur in bread making?
Enzymes catalyze three main reactions in bread-making: breaking starch into maltose, a complex sugar; breaking complex sugars into simple sugars; and breaking protein chains.
What is the perfect fermentation temperature for artisan bread?
Artisan bakers typically operate the first rise at 25-28C (75-82F), but the second rise can vary. A 32C (90F) final proof is possible, whereas cool...
Is bench rest fermentation?
Fermentation does not pause whilst the dough is bench rested between preshaping and final shaping. Though the bench rests role is to allow the doug...
Why does bread stop rising in the oven?
The yeast gets too hot and diesThe crust hardens preventing the loaf from risingThe yeast runs out of simple sugars
Is yeast fermentation the same as dough fermentation?
Yeast is the strain that initiates fermentation in the dough with carbohydrates. The dough does not ferment, the yeast does. Both phrases are used...
Where does yeast consume the sugars?
In aerobic respiration the consumption of sugars into carbon dioxide, water and HTP occurs inside the yeast cell. Anaerobic respiration can take pl...
What is the difference between yeast fermentation vs respiration?
Yeast has to respire before it can ferment. It can do this with or without oxygen. In the case of aerobic respiration, there is no fermentation. Wh...
Are organic acids good for bread dough?
They help in the production of the bread as its machinability improves, has a bigger rise, a bigger oven spring, lighter crumb, tastes, smells and...
Is zymase used in dough fermentation?
It was thought that the enzyme, zymase kick starts yeast fermentation. It occurs from yeast and turns the monosaccharides, glucose and fructose, in...
The Basics of Bread Fermentation | Wild + Whole - MeatEater
A sourdough starter is built on this same concept; it is essentially a jar of dough that is continually fed and cultured to kick-start the fermentation of each new loaf. Much like the SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast) or "mother" that turns sugar and tea into bubbling kombucha, a sourdough starter turns flour, water, and salt into a fluffy loaf of bread.
What Is Fermented Bread? (with pictures) - Delighted Cooking
Fermented bread is bread made from dough that has been allowed to rise slowly using a starter of naturally occurring bacteria and yeast carried in the air. Unlike quick-rising breads that use a single strain of specially cultured yeast, usually sold in packets and called fast-rising or instant yeast, fermented bread contains a variety of yeasts and bacteria that help to convert the important ...
Bread: Preparation, Types and Its Fermentation - Biology Discussion
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the preparation, types and abnormal fermentation of bread. Preparation of Bread: Flours and meals for the preparation of bread are usually made from wheat or rye, occasionally from maize or barley. They are all high in starch, and the first two contain a considerable proportion of protein, […]
Yeast Fermentation: How Does Yeast Fermentation Work?
Find out how yeast fermentation works. Yeast is the most commonly used leavener in bread baking and the secret to great bread making lies in its fermentation, or the metabolic action of yeast.
What is yeast?
Yeast is a single cell organism of the fungus species. Although modern yeast production has been around since the early 1800s, the use of wild yeasts has been around for tens of thousands of years. Sourdough, the original levain used to ferment bread has been traced back to ancient Egyptians and beyond.
How to end yeast fermentation?
Like other fungi and bacteria, once they get too hot they become permanently inactive. When the oven temperature reaches 68C (155F) the yeast cells die, bringing yeast fermentation to an end. This is the Yeast Kill Point.
Is yeast fermentation the same as dough fermentation?
Yeast is the strain that initiates fermentation in the dough with carbohydrates. Dough does not ferment, the yeast does. Both phrases are used interchangeably in bread baking.
Where does yeast consume the sugars?
In aerobic respiration the consumption of sugars into carbon dioxide, water and HTP occurs inside the yeast cell. Anaerobic respiration can take place inside or outside the cell walls.
What is the difference between yeast fermentation vs respiration?
Yeast has to respire before it can ferment. It can do this with or without oxygen. In the case of aerobic respiration , there is no fermentation. When yeast respires anaerobically, both alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation occur.
What is fermentation?
Fermentation comes from the Latin word “Fermentare”, meaning “to leaven.” It is an important stage in many popular food products such as cheese, yoghurt, alcohol, pickled foods and bread. For fermentation to occur, a base and a strain are required. A base will be a form of carbohydrate, and the strain is a type of bacteria or fungus.
Is ethanol needed in bread dough?
Ethanol produced during fermentation is not a by-product of the process. It is absolutely necessary to mature the dough. In bread, ethanol improves odour, flavour and keeping quality. During baking, much of the ethanol evaporates, but traces can remain. If your bread smells too much like alcohol, it’s probably over-proofed.
What is fermentation in bread?
Fermentation is a process that converts the sugar into carbon dioxide along with other substances like alcohol or lactic acid. The release of an abundant amount of carbon dioxide is actually responsible for the rise of the bread.
What happens to bread when it is kneaded?
During kneading, the gluten is stretched into a network of stretches that later trap the carbon dioxide released by the yeast during fermentation and hence rise the bread. Due to this property of gluten, the bread with zero gluten mostly has a very dense and chewy texture.
Why does bread expand during baking?
Baking. In the final stage, the bread is expanding during baking due to the carbon dioxide released during fermentation by the yeast and also from steam generation. Bread Fermentation Reviewed by Dr. Hashmi on February 11, 2020 Rating: 5.
Why is the smoothness of bread important?
The smoothness of the dough increases its ability to hold more amount of carbon dioxide thus improves the quality of the bread. 2. Quantity of yeast. The lower amount of yeast will prolong the fermentation time to complete the process required to make a mature bread.
How long does it take to make bread with zero gluten?
Due to this property of gluten, the bread with zero gluten mostly has a very dense and chewy texture. Due to entrapped air within the gluten stretches, the volume of the bread increases to double during this stage. This process can take up to 8 hours; however, for a 'no-time dough' the time can be 0-15 minutes long. 2.
What is the first stage of fermentation?
It is an optional stage during which, dough, flour, and water is fermented for a longer period of time. This gives a specific taste and aroma to the bread. 2. First Fermentation. In this step, preferment is added in the rest of the dough. The first stage of fermentation starts after the bread is kneaded.
What is the best pH for yeast?
Yeast performs best at the slightly acidic conditions. The pH ranges between 4.5-6.5 is considered best for bread fermentation . 7. Water content. 50% of water is considered optimal for the bread fermentation. Uncontrolled yeast reproduction can be observed when an excessive amount of water is present. 8.
What is the basic chemical equation for respiration?
The basic chemical equation for respiration is: Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration). The basic chemical equation of fermentation is: Kneading enables more respiration to occur because air is added, and thus more oxygen, resulting in a faster rise but less flavour.
What does fermentation produce?
Fermentation produces ethanol which increases flavour. Some microorganisms, in anaerobic conditions, produce lactic acid, resulting in a different flavour.
What is the process of making bread?
The bread-making process known as "fermentation" is responsible for the holes and the flavour of bread. In actual fact the holes are bubbles of carbon dioxide produced through the process of respiration. Flavour is from the alcohol and other compounds produced through fermentation . Respiration occurs when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration).
What is the first sign of fermentation?
Those bubbles are carbon dioxide, and the first sign that fermentation is happening inside the floury slush. This is basic sourdough fermentation — the bread equivalent of making natural wine. Ambient yeast that live in the air are finding food and a new home in the flour mixture and starting to eat the sugar molecules inside the flour — a.k.a. fermenting — the dough. By slowly digesting the sugar, these yeast fundamentally change the flour, developing the tangy funk that makes sourdough unique.
Why does native yeast bread taste weird?
If the temperature drops, the process happens at a painfully slow pace. If it gets too hot, the flavors don’t develop well. Sometimes these breads and native ferments taste just plain weird. Because native fermentations depend on wild yeast, which varies from place to place, no two sourdough cultures are exactly alike. As a result, you’ll see loaf-to-loaf variation, just like the bottle variation that’s inherent in natural wines.
How to make bread with water and flour?
You don’t need heavy equipment or any training to make bread. You just need flour and water. To see the miracle of fermentation in action, mix equal parts flour and water — start with a cup of each — in a large bowl, and cover it. Leave it alone in a warm place, and over the course of 24 hours you’ll start to see bubbles in the mixture, like the bubbles in pancake batter. Every day over the course of a week, add more flour and more water. Gradually, the bubbles will multiply and even become frothy.
How to mimic wine making?
Put a pack of instant or rapid-rise yeast into a cup of warm water and watch. The bubbles that took a full day to develop on the counter will be active in as little as 15 minutes. Add flour, and rising takes no time at all.
How long does it take for a pancake batter to bubble?
Leave it alone in a warm place, and over the course of 24 hours you’ll start to see bubbles in the mixture, like the bubbles in pancake batter. Every day over the course of a week, add more flour and more water. Gradually, the bubbles will multiply and even become frothy.
Is sourdough bread the same as a loaf?
Because native fermentations depend on wild yeast, which varies from place to place, no two sourdough cultures are exactly alike. As a result, you’ll see loaf-to- loaf variation, just like the bottle variation that’s inherent in natural wines.
Is bread an alcoholic?
Bread isn’t alcoholic, but the same process that gives wine its delightful alcoholic kick is what gives bread its airy texture and signature rise. The process is almost identical to alcoholic fermentation: Yeast eats sugar and releases carbon dioxide. With beverages, that CO2 is released into the air, but in bread, gluten proteins trap the gas inside the dough, causing it to rise.
What is Fermentation?
Fermentation is an anaerobic biological process that converts sugars and starches into simpler substances. In baking, it causes yeast and bacteria to convert sugars into carbon dioxide, among other things. This is what causes the dough to rise.
Why is extended dough fermentation important?
Extended dough fermentation has been used effectively for improving dough development and enhancing bread shelf life. In this context, this process is considered an effective alternative to traditional dough conditioners. So this provides bakers with the means to produce clean label bakery products. 2
What do LAB and yeast feed on?
Carbon source: LAB and yeast feed on monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Why are bread loafs expanded?
Baking: Loaves are expanded due to yeast and steam generation.
What is the salt level of yeast?
Salt level: up to 2.5%. Higher levels exert considerable osmotic stress on yeast cells.
When does yeast/lab start to work?
It continues through early stages of baking where the yeast/LAB is inactivated by heat. The fastest rate occurs during proofing and oven spring stages.
Why does bread dough have carbon dioxide?
In bread making (or special yeasted cakes), the yeast organisms expel carbon dioxide as they feed off of sugars. As the dough rises and proofs, carbon dioxide is formed; this is why the dough volume increases. The carbon dioxide expands and moves as the bread dough warms and bakes in the oven. The bread rises and sets.
What temperature does yeast stop producing carbon dioxide?
However, the yeast stops creating carbon dioxide when the temperature reaches 26 degrees celsius (78.8 degrees fahrenheit) This is the temperature in which the yeast would stopped its activity.
What happens when yeast is fermented?
Fermentation produces air bubbles as well as yeast. When the dough is mixed, you leave the dough to rise. During the time it is rising, fermentation is going on producing air bubbles. VOCAB WORDS USED IN THIS TAB. Chemical Reaction: a process in which one or more subtances turn into a whole another subtance.
What is the main ingredient in bread?
Yeast. Yeast is an essential part of the making of bread. Yeast is what makes bread rise! The yeast eat simple sugars and produce carbon dioxide, which make the bread light and fluffy. The gas from the carbon cause there to be tiny air pockets .
What is the reaction that causes bread to rise?
Bread rises from an acid-base reaction that produces carbon dioxide, which is called neutralization. Also, when yeast releases carbon dioxide, the biochemical of it would probably be the water and the carbon dioxide. Heat also plays a role in making bread.
What temperature does yeast go to make bread?
Heat also plays a role in making bread. It has to go all the way into 140°F in which the yeast would have been completely killed. Also, the point in the graph below it had a different point of temp. with the activity. The graph above shows the activity of yeast. When the temperature goes up, the yeast will produce more carbon dioxide.
What is fermentation in food?
Fermentation is a chemical change. Fermentation is when microbes converting into starches and sugars to gas. In fact, the warmer the gas is the bigger the air pockets will be. Fermentation happens in many foods such as cocoa, buttermilk, cod liver oil, pickles, sour cream, soy sauce, yogurt, etc. This takes place when the bread is mixed ...
How to make bread rise before baking?
All you’re doing is removing some of the gas bubbles that developed while the dough was rising. Push the dough down in the middle then fold the sides into the center to make a deflated bowl of dough. Proofing is the next step in the bread fermentation process. This is where the final rise happens before baking.
What is the process of changing sugars and starches into carbon dioxide?
Fermentation. Bread fermentation is the anaerobic biological method that changes sugars and starches into a different form. When this process is used in baking bread and the creation of dough, the fermentation facilitates the yeast and bacteria changing sugars and starches into carbon dioxide.
How to ferment bread?
Steps in Bread Fermentation 1 Preferment: This is an optional step but one that can enhance the fermentation process. It allows the yeast to be activated, giving the flour a longer time to break down. This creates a better bread structure. Unique bread flavors are created with this process and it can extend shelf life. 2 Initial fermentation is mixing preferments with the rest of the ingredients that make the dough. This step can be a lengthy one and may last up to 8 hours if you are making artisan bread. 3 Second fermentation happens after the dough is punched the first time. Punching the dough is not as harsh as it sounds. All you’re doing is removing some of the gas bubbles that developed while the dough was rising. Push the dough down in the middle then fold the sides into the center to make a deflated bowl of dough. 4 Proofing is the next step in the bread fermentation process. This is where the final rise happens before baking. This can last from one hour up to a day depending on the recipe and mode of cooking. It is often also called a “rest period” for the dough. 5 The final step happens when the bread is baking. The loaves expand from the yeast and steam generated in the hot oven.
How long does proofing bread last?
This is where the final rise happens before baking. This can last from one hour up to a day depending on the recipe and mode of cooking . It is often also called a “rest period” for the dough. The final step happens when the bread is baking.
Why is fermentation important?
Knowing what affects the process allows you to adjust elements to improve the process for better looking and tasting products. It also allows you to experiment with recipes to change or improve outcomes.
What is the process of yeast fermentation?
These yeast microorganisms start the fermentation process by eating the simple sugars produced by amylase found in all types of flour. The whole process makes carbon dioxide and other composites that create the individual taste and consistency of the bread.
How long does bread fermentation last?
Initial fermentation is mixing preferments with the rest of the ingredients that make the dough. This step can be a lengthy one and may last up to 8 hours if you are making artisan bread.