
What are the steps of electron transport?
The three main steps in the electron transport chain are:
- Generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. Proton accumulation occurs in the intermembrane space of mitochondria.
- Reduction of molecular oxygen and formation of water.
- ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis.
What product is made by the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
What is the process of electron transport chain?
Things to Remember
- In eukaryotes, mitochondria is the site for aerobic respiration. ...
- The electron transport chain consists of 5 complexes present in a sequence that carry out the transfer of electrons and coupled ATP production.
- Electrons in the electron transport chain are transferred from molecules of lower redox potential to that of higher redox potential.
What happens in the electron transport chain?
- The iron-sulfur (FeS) proteins exist in the oxidized (Fe 3+ ) or reduced (Fe 2+)
- These are non-heme iron-sulfur proteins.
- The simplest iron-sulfur protein is FeS in which iron is tetrahedrally coordinated by four cysteines.
- About half a dozen FeS proteins connected with respiratory chain have been identified which participates in electron transport.
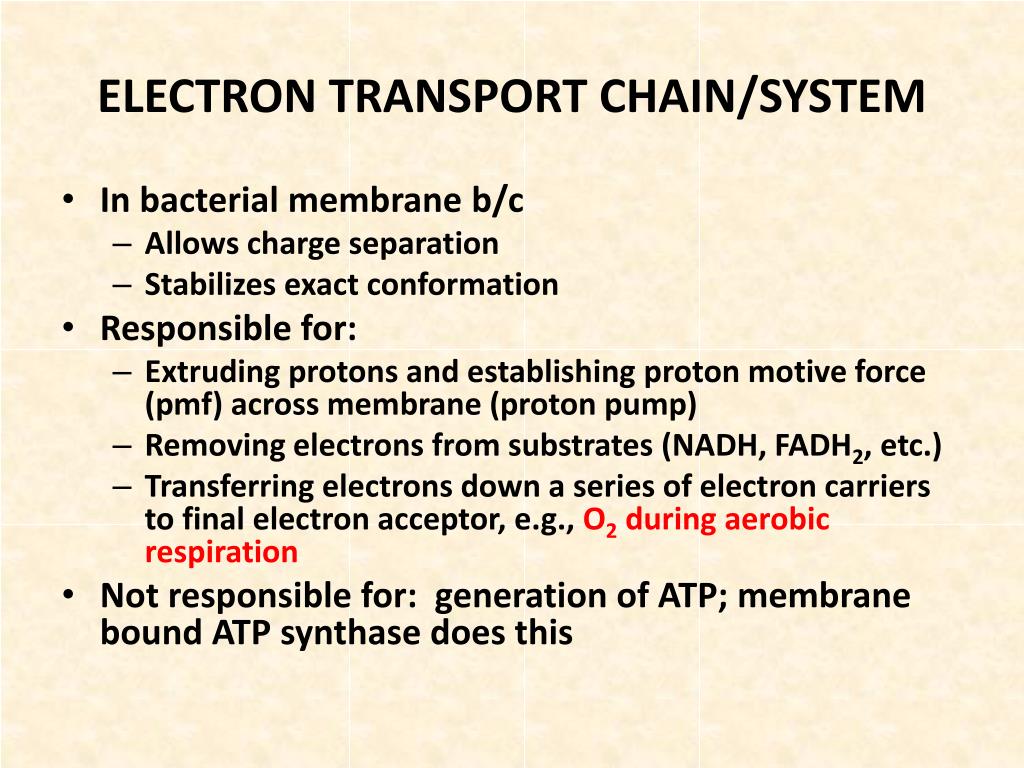
What is the final electron acceptor?
A final electron acceptor is the last substance to obtain an electron in an electron transport chain, including the oxygen in aerobic cellular respiration, or the terminal cofactor to receive an electron in photosynthesis reaction center electron transfer domain. The final electron acceptor during fermentation is the derivatives of pyruvate molecules. In anaerobic respiration, nitrate, sulfate, or sulfur act as the terminal electron acceptor.
Why is the potential of these electron acceptor molecules less efficient?
The potential of these electron acceptor molecules is less efficient because minimum energy is released by the oxidation of a molecule.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
The electron transport chain is the last mechanism that occurs in the cellular respiration process. It has several membrane linked protein molecule complexes and linked mobile accessory carriers of the electron. The electron transport chain is a multistep process that involves various enzymes and cofactors. Anaerobic respiration is respiration that yields energy during the nonexistence of oxygen. It utilizes the electron acceptors rather than the molecular oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is used, when oxygen is absent for respiration. Anaerobic organisms carry out the anaerobic respiration process by consuming inorganic chemicals rather than oxygen, as the final electron acceptor.
What is the role of NADH and FADH2 in ATP?
NADH and FADH2 are involved in a set of redox reactions that transfer electrons in oxidative phosphorylation to produce an increased amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
How many complexes are there in ATP synthase?
From one to four complexes along with the two molecules, the electrons get shuffled from one complex to the other. The ATP synthase pumps the proton gradient to generate ATP. In complex IV, the formation of water takes place. Cyt b is encountered in complex III and cyt C carries the electrons from complex III to complex IV.
Which organisms are most likely to be able to perform aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is common in prokaryotic organisms (bacteria and archaea) that survive in anaerobic environments. The method of producing chemical energy without investing any oxygen molecule or electron transport chain is referred to as fermentation.
Where does lactic acid fermentation take place?
The lactic acid fermentation takes place in the animal cells, such as muscle cells and bacteria. It is a biochemical process, in which the conversion of sugar into lactic acid takes place and cellular energy is released.
Answer
The electron transport chain is the final step of the cellular respiration. This is an aerobic process (requires oxygen) that from glucose it generates energy in the form of ATP molecules.
New questions in Biology
What kind of tree was the first Christmas tree? Merry Christmas Everyone!!!!!!!!
Which chain accepts high energy electrons?
The electron transport chain accepts high-energy electrons from:
What happens to electrons as they move along a series of carriers?
In the electron transport chain, as electrons move along a series of carriers, they release energy that is used to:
What happens to electrons when they star out at high energy?
A. Electrons star out at very high energy and lose energy at each transfer step
What chapter is PCB3134?
Start studying PCB3134 chapter 14. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Which membrane is permeable to all small molecules, including small proteins?
The outer membrane of a mitochondrion is permeable to all small molecules, including small proteins.
Do electrons lose energy at each transfer step?
A. Electrons start out at very high energy and lose energy at each transfer step.
