
What are the four parts of a brain?
Parts of the Brain: Structures and Their Functions
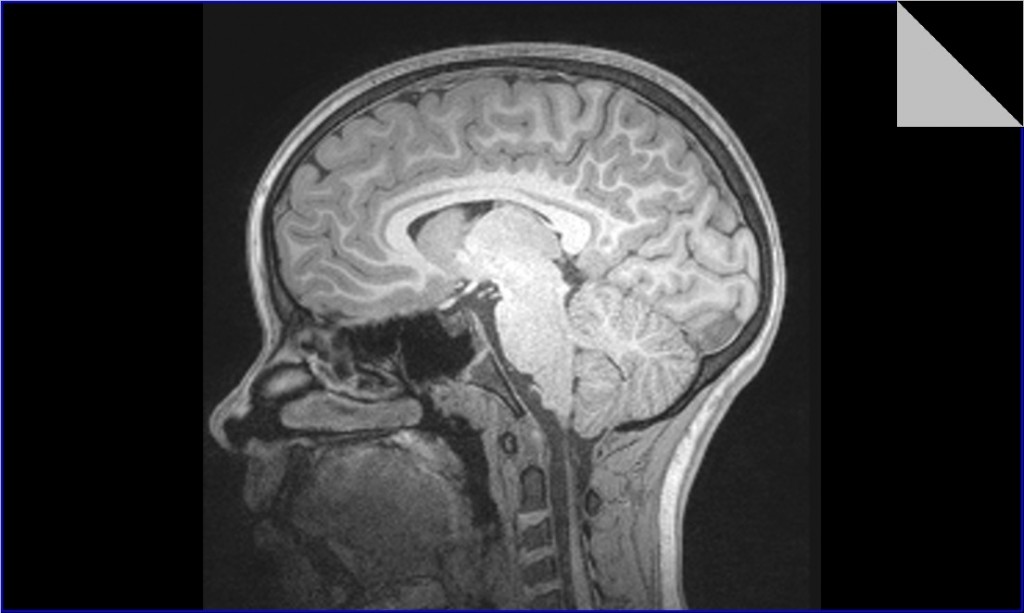
- Cerebrum. The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. ...
- Cerebellum. The cerebellum, also known as the little brain, is located in the back of the brain. ...
- Brainstem. The brain stem is the posterior part of the brain that connects the brain with the spinal cord. ...
- Limbic System. ...
- Skull. ...
When is the brain fully developed?
While no specific age has been identified as the age at which the human brain is fully mature, the Washington Post relates that many scientists agree that the brain does not reach maturity until at least the mid-20s. Some studies suggest that the brain continues to develop into the early 30s.
What is the Order of brain development?
These are the telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, and myelencephalon; the lateral ventricles, third ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, and upper and lower parts of the fourth ventricle in adulthood originated from these structures. The appearance of cortical folds first takes place during 24 and 32 weeks of gestation.
Which part of the brain controls all the vital functions?
Medulla: The medulla or medulla oblongata is an essential portion of the brain stem which maintains vital body functions such as the heart rate and breathing. Hope this guide on parts of the brain and their functions help you understand the issue more clearly.

When does the brain develop?
A few weeks after a baby is conceived, the brain begins to develop. For about eight weeks, the basic structures of the brain form. The neural tube is formed. This slowly becomes the brain and spinal cord. Around seven weeks after conception, the first neurons and synapses are developed in the spinal cord.
What are the structures that help the brain communicate?
Neurons and synapses are brain structures that help different parts of your brain communicate. They take chemical signals, transport them, and form new wiring within your brain. The work that neurons and synapses do lays the foundation for learning, memory, and other brain functions.
What are the grooves on the surface of the brain that surround the gyri?
Sulci are the grooves on the surface of the brain that surround the gyri. They help divide the brain into different sections, like lobes and hemispheres. Sulci also add more surface area to the brain. Together, gyri and sulci allow the brain to do more without making the brain too big to fit into the skull.
How long does it take for a baby to learn a language?
During this year, the parts of the brain that support language and speech abilities are greatly strengthened by surrounding language use. After a few months , a baby is able to tell the difference between their native language and a foreign language.
What are the stages of child development?
The five stages of child development include the newborn, infant, toddler, preschool and school-age stages.
When do kids have synapses?
Before a child turns three, they’ll have almost double the number of synapses that they’ll have later on as adults. Synapses are created at such a high rate during early childhood that your brain will end up making more than you actually need. Synapses are strengthened as you use skills or are exposed to things repeatedly.
When does a baby's synapse peak?
Synapse creation will peak during a baby's third year. Various areas of the brain are strengthened and brain ability greatly improves. During this year, a child will develop a more clear understanding of past and present events and cause and effect.
What is the first step in brain development?
The neural tube is the first step of brain development. Special stem cells, known as neural progenitor cells, are created within the neural tube . Neural progenitor cells continuously divide, forming two new progenitor cells with each division.
Where do new neurons migrate?
As new neurons are created, they migrate from the neural tube to new destinations to form parts of the brain and spinal cord. Complex chemical signals determine where new neurons will migrate, and which brain structures they ultimately contribute to.
How did something so complex originate from only one cell?
In a fascinatingly complex series of events during early pregnancy, one fertilized cell divides into a small mass of identical cells known as stem cells. Stem cells are special in that they can turn into almost any type of cell in the body; hair, skin, bone, nerve cells. As these cells continue to multiply, specific genes within the cells are turned on and begin giving instructions via chemical signals to aid in development
What makes the neural tube?
As cells divide, they separate into three germ layers known as the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm.
How is the number of neurons regulated?
Not only are connections between neurons regulated, but the actual number of neurons is also regulated by something known as programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Embryonic development gives rise to an overproduction of neurons. Although still not completely understood, apoptosis during this time occurs in response to both environmental and genetic factors.
How do new connections between neurons work?
New connections between neurons, on the other hand, are constantly being formed, removed, and replaced. New connections are made when you learn skills and make memories. Connections can be lost when you fail to use or strengthen them. New research suggests that certain parts of your brain, especially areas involved in planning and working memory—also known as short-term memory—continue to develop and mature their connections well into your twenties.
Which glial cells are responsible for the climb through the brain?
For example, glial cells known as Bergmann glia act as a branch on which two cerebellar neurons, Purkinje and granule cells, will climb through the brain to their ultimate destination of the cerebellum.
Why is early brain development important?
One of the main reasons is how fast the brain grows starting before birth and continuing into early childhood. Although the brain continues to develop and change into adulthood, the first 8 years can build a foundation ...
Why is the brain growing in infants?
Because children’s brains are still growing, they are especially vulnerable to traumatic head injuries, infections, or toxins, such as lead. Childhood vaccines, such as the measles vaccine, can protect children from dangerous complications like swelling ...
How can a baby learn and grow?
To learn and grow appropriately, a baby’s brain has to be healthy and protected from diseases and other risks. Promoting the development of a healthy brain can start even before pregnancy. For example, a healthy diet and the right nutrients like sufficient folic acid will promote a healthy pregnancy and a healthy nervous system in the growing baby. Vaccinations can protect pregnant women from infections that can harm the brain of the unborn baby.
Why is it important to nurture the mind?
Nurturing care for the mind is critical for brain growth. Children grow and learn best in a safe environment where they are protected from neglect and from extreme or chronic stress. external icon. with plenty of opportunities to play and explore.
How does stress affect the brain?
Exposure to stress and trauma can have long-term negative consequences for the child’s brain, whereas talking, reading, and playing can stimulate brain growth. Ensuring that parents, caregivers, and early childhood care providers have the resources and skills to provide safe, stable, nurturing, and stimulating care is an important public health ...
Why is early childhood important?
The importance of early childhood experiences for brain development . Children are born ready to learn, and have many skills to learn over many years. They depend on parents, family members, and other caregivers as their first teachers to develop the right skills to become independent and lead healthy and successful lives.
When does the brain grow?
Brain volume continues growing in the second year (an estimated 15 percent). Developmental peaks in childhood: The brain grows more gradually, with brain size peaking around age 10 for girls and age 14 for boys. The density of synapses in the brain reaches its height and begins to decrease.
When does the brain mature?
While the brain typically reaches a mature state of development in early adulthood, the internal processes that make and remake the brain—the birth of new neurons and death of old ones, the creation and dissipation of neural connections, and more—persist across the lifespan. At most any age, the brain retains the capacity to change.
How does brain volume change in the first year?
The first years: Brain volume doubles in the first year of life as connections between neurons grow and other developmental processes unfold—including myelination, which boost s signaling speed between neurons . White matter pathways between spaced-apart regions of the cortex develop. Brain volume continues growing in the second year (an estimated 15 percent).
What is the transition period in the brain?
Brain areas beneath the cortex (such as those in the limbic system) exhibit relatively little change. A transition period during adolescence: In teen brains, gray matter in the cortex thins considerably. The number of synapses between neurons in the cortex is scaled back.
How much of the brain is expanded by age 3?
By age 3, it will have expanded to about 80 percent of adult size. While most of the brain’s neurons are thought to be created before birth, an explosion in neural connections, the myelination of axons, and other developments boost its total volume.
What are the environmental factors that affect brain development?
There are also many known environmental factors that can affect a brain’s development. Starting in the womb, adequate nutrition can help ensure healthy brain development, while exposure to certain infections or toxins (such as alcohol) can lead to abnormalities in brain development.
How do genes affect the brain?
An individual’s genes are a key factor affecting how the brain develops throughout early life. Genes contribute to normal individual variation in brain development , and relatively rare genetic alterations can lead to neurodevelopmental conditions such as Down syndrome due to their impact on the brain.
What is the history of brain development?
Early history of brain development. Main article: Evolution of nervous systems. One approach to understanding overall brain evolution is to use a paleoarchaeological timeline to trace the necessity for ever increasing complexity in structures that allow for chemical and electrical signaling.
When was the brain first discovered?
Fossilization of brain, or other soft tissue, is possible however, and scientists can infer that the first brain structure appeared at least 13 years ago, with fossil brain tissue present in sites of exceptional preservation.
How do genes control the brain?
The study began with the researchers assessing 214 genes that are involved in brain development. These genes were obtained from humans, macaques, rats and mice. Lahn and the other researchers noted points in the DNA sequences that caused protein alterations. These DNA changes were then scaled to the evolutionary time that it took for those changes to occur. The data showed the genes in the human brain evolved much faster than those of the other species. Once this genomic evidence was acquired, Lahn and his team decided to find the specific gene or genes that allowed for or even controlled this rapid evolution. Two genes were found to control the size of the human brain as it develops. These genes are Microcephalin (MCPH1) and Abnormal Spindle-like Microcephaly (ASPM). The researchers at the University of Chicago were able to determine that under the pressures of selection, both of these genes showed significant DNA sequence changes. Lahn's earlier studies displayed that Microcephalin experienced rapid evolution along the primate lineage which eventually led to the emergence of Homo sapiens. After the emergence of humans, Microcephalin seems to have shown a slower evolution rate. On the contrary, ASPM showed its most rapid evolution in the later years of human evolution once the divergence between chimpanzees and humans had already occurred.
How did DNA sequences change?
Each of the gene sequences went through specific changes that led to the evolution of humans from ancestral relatives. In order to determine these alterations, Lahn and his colleagues used DNA sequences from multiple primates then compared and contrasted the sequences with those of humans. Following this step, the researchers statistically analyzed the key differences between the primate and human DNA to come to the conclusion, that the differences were due to natural selection. The changes in DNA sequences of these genes accumulated to bring about a competitive advantage and higher fitness that humans possess in relation to other primates. This comparative advantage is coupled with a larger brain size which ultimately allows the human mind to have a higher cognitive awareness.
How does the brain structure evolve?
The principles that govern the evolution of brain structure are not well understood. Brain to body size scales allometrically. Small bodied mammals have relatively large brains compared to their bodies whereas large mammals (such as whales) have smaller brain to body ratios. If brain weight is plotted against body weight for primates, the regression line of the sample points can indicate the brain power of a primate species. Lemurs for example fall below this line which means that for a primate of equivalent size, we would expect a larger brain size. Humans lie well above the line indicating that humans are more encephalized than lemurs. In fact, humans are more encephalized than all other primates.
Why do animal groups have small brains?
Some scientists argue that this difference is due to vertebrate and cephalopod neurons having evolved ways of communicating that overcome the scalability problem of neural networks while most animal groups have not. They argue that the reason why traditional neural networks fail to improve their function when they scale up is because filtering based on previously known probabilities cause self-fulfilling prophecy -like biases that create false statistical evidence giving a completely false worldview and that randomized access can overcome this problem and allow brains to be scaled up to more discriminating conditioned reflexes at larger brains that lead to new worldview forming abilities at certain thresholds. This is explained by randomization allowing the entire brain to eventually get access to all information over the course of many shifts even though instant privileged access is physically impossible. They cite that vertebrate neurons transmit virus-like capsules containing RNA that are sometimes read in the neuron to which it is transmitted and sometimes passed further on unread which creates randomized access, and that cephalopod neurons make different proteins from the same gene which suggests another mechanism for randomization of concentrated information in neurons, both making it evolutionarily worth scaling up brains.
Which part of the brain is the most advanced?
The neocortex is the most advanced and most evolutionarily young part of the human brain. It is six layers thick and is only present in mammals. It is especially prominent in humans and is the location of most higher level functioning and cognitive ability.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
How many nerves are in the cranium?
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
What organ controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger, and every other process?
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
Which part of the brain controls movement?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex.
What is the brain development in early childhood?
Neurological and brain development in the early years of a child's life occurs very quickly. The brain is creating and pruning connections rapidly. It’s not all happening simultaneously though. Brain development stages differ depending on the age of a child.
Which part of the brain is responsible for making new neurons?
The cerebellum and prefrontal cortex continue making new neurons. Synaptic density is reduced to half by age 2. Myelination continues and proceeds from the back to the front of the brain and from the center to the sides. The brain reaches 50% of adult size at age 1.
What is the neural connection?
About those synapses - the neural connections are like interstates carrying the knowledge to and from different areas of the brain. Over time, the brain sheds the neural connections that it isn’t using.
What happens to neural connections as a child ages?
As mentioned, a child’s neural connections are rapidly developing. If a parent is kind and happy for the most part, their toddler is growing "kind-and-happy" connections. As the child ages, those synapses get stronger and healthier. Those connections will follow them to adulthood and they'll know how to build strong, healthy relationships.
How does vitamin deficiency affect the brain?
Vitamin deficiency could have a profound and lasting negative impact on a brain. According to Harvard Health, the first 1,000 days of a child's life are particularly important. The brain is busy creating its neural connections between the billions of neurons floating around in there.
How many neural connections do babies have?
For example, when a parent picks up their baby a connection is formed. When a baby enters the world, they have 50 trillion neural connections, also known as synapses. By the time they reach adulthood they’ll have around 500 trillion. As a child grows, their brains are rapidly developing new neural connections.
How many neurons are in a baby's brain?
A baby’s brain contains 100 billion neurons when they are born.
How Did Something So Complex Originate from only One cell?
What Makes The Neural Tube?
- As cells divide, they separate into three germ layers known as the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. At approximately the third week of gestation, or development, the neural tube begins to form within the ectoderm layer. The neural tube is the first step of brain development. Special stem cells, known as neural progenitor cells, are created within ...
Where Do The Neurons Go?
- As new neurons are created, they migrate from the neural tube to new destinations to form parts of the brain and spinal cord. Complex chemical signals determine where new neurons will migrate, and which brain structures they ultimately contribute to. These chemical signals provide directions, much like a map, to each neuron. Once neurons reach the end of their journey, it’s ti…
What Changes After birth?
- The developing brain engages in an intricate dance with its outside environment and is a sponge for information. During early development, 700 to 1,000 new neural connections are formed every second. These early connections are the fundamental groundwork and precursors for more sophisticated connections later on. Although it is very important for new neurons to form long-las…