What are the first three phases of the cell cycle?
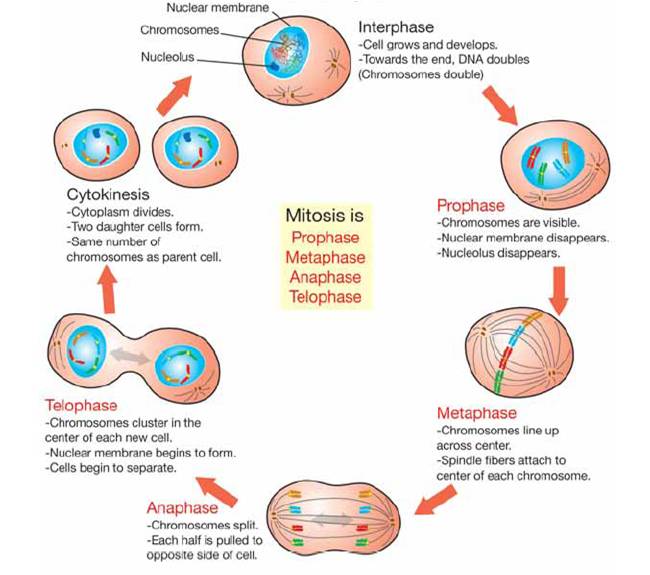
- Interphase. very active period, cell grows, maintains routine functions,
- prophase. chromosomes form; nuclear envelope disappears.
- metaphase.
- anaphase.
- telophase.
What are the five steps of the cell cycle?
- Interphase : The cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. ...
- Prophase : The chromosomes start to condense and the nucleolus disappears. ...
- Metaphase : Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate which is the centre of the cell.
- Anaphase : Chromatids of each chromosome are separated and start migrating towards opposite poles of the cell.
Which phase of the cell cycle occurs first?
What are the six stages of cell cycle?
- Interphase. The cell grows to its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares to divide into two cells. …
- Prophase. Chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. …
- Metaphase. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. …
- Anaphase. The centromeres split. …
- Telophase. …
- Cytokinesis.
What is the second step in the cell cycle?
Step 2: Induction. Transduction is the second step of cell signaling and involves the binding of signaling molecules to the receptor which in turn initiates a series of events in the transduction pathway. Apart from some of the ligands (e.g. ions) that actually enter the cell through the cell membrane, most ligands do not enter the cell because ...

What is Stage 1 of the cell cycle?
The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then replication of DNA . The single strand of DNA that makes up each chromosome produces an exact copy of itself. All of the organelles inside the cell are also copied. These processes happen in a stage of the cell cycle called interphase .
What are the 4 stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
What are the stages of the cell cycle in order?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the 3 stages of cell cycle?
The cell cycle is composed of 3 main stages - interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis. During the interphase stage of the cell cycle, the cell grows and organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes double.
What is G1 and G2 phase?
G1 phase is the first phase of the interphase of the cell cycle in which cell shows a growth by synthesizing proteins and other molecules. G2 phase is the third phase of interphase of the cell cycle in which cell prepares for nuclear division by making necessary proteins and other components.
What happens in G1 of the cell cycle?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What are the 5 cell cycles?
The phases in the reproduction and growth of a cell is known as the cell cycle. The five stages of cell cycle are – interphase, which is in turn classified into G1, S and G2 phase, Mitosis, also called as the M phase, which is further divided into 4 parts (prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase) and Cytokinesis.
What is the second stage of the cell cycle?
Interphase is the second phase of the cell cycle.
What are the 3 stages of the cell cycle quizlet?
The three stages of the cell cycle is interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
What is the life cycle of a cell?
Other organisms, from humans to plants to bacteria, also have a life cycle: a series of developmental steps that an individual goes through from the time it is born until the time it reproduces. The cell cycle can be thought of as the life cycle of a cell.
How many stages of mitosis are there?
Mitosis takes place in four stages: prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells.
What is the M phase?
M phase involves two distinct division-related processes: mitosis and cytokinesis. In mitosis, the nuclear DNA of the cell condenses into visible chromosomes and is pulled apart by the mitotic spindle, a specialized structure made out of microtubules.
How many steps does mitosis go through?
The cell goes through 4 steps (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.) The cells at the end of the process also have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end, 2 cells are produced. Mitosis is used to make body cells, and occurs in the body.
Where does cytokinesis take place?
Importantly, cytokinesis takes place differently in animal and plant cells. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells. In an animal cell, a contractile ring of cytoskeletal fibers forms at the middle of the cell and contracts inward, producing an indentation called the cleavage furrow. Eventually, the contractile ring pinches the mother cell in two, ...
How long does it take for a cell to divide?
A typical human cell might take about 24 hours to divide, but fast-cycling mammalian cells, like the ones that line the intestine, can complete a cycle every 9-10 hours when they're grown in culture. Different types of cells also split their time between cell cycle phases in different ways.
How do plant cells divide?
Because of this, plant cells divide in two by building a new structure down the middle of the cell. This structure, known as the cell plate, is made up of plasma membrane and cell wall components delivered in vesicles, and it partitions the cell in two.
What are the two major phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase ( Figure 1 ). During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. During the mitotic phase, the replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides.
What is the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase is divided into G 1, S, and G 2 phases.
What is the function of the centrosome during mitosis?
The two centrosomes will give rise to the mitotic spindle, the apparatus that orchestrates the movement of chromosomes during mitosis. The centrosome consists of a pair of rod-like centrioles at right angles to each other. Centrioles help organize cell division.
How many stages of mitosis are there in animal cells?
Figure 2. Animal cell mitosis is divided into five stages—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase —visualized here by light microscopy with fluorescence. Mitosis is usually accompanied by cytokinesis, shown here by a transmission electron microscope. (credit “diagrams”: modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal; credit “mitosis micrographs”: modification of work by Roy van Heesbeen; credit “cytokinesis micrograph”: modification of work by the Wadsworth Center, NY State Department of Health; donated to the Wikimedia foundation; scale-bar data from Matt Russell)
Which stage of the cell cycle is the stage of chromosomes being lined up at the metaphase plate?
the stage of mitosis during which chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate. mitosis. the period of the cell cycle at which the duplicated chromosomes are separated into identical nuclei; includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. mitotic phase.
What are the stages of interphase?
For a cell to move from interphase to the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. The three stages of interphase are called G 1, S, and G 2.
How do you make two daughter cells?
To make two daughter cells, the contents of the nucleus and the cytoplasm must be divided. The mitotic phase is a multistep process during which the duplicated chromosomes are aligned, separated, and moved to opposite poles of the cell, and then the cell is divided into two new identical daughter cells.
What is the most important stage of the cell cycle?
Interphase is the most important stage of cell cycle. The cell stays in the interphase for maximum periods. During this phase the cell prepares itself for division. The cell undergoes cell growth and replication during this phase.
What are the phases of the cell cycle?
The different phases of a cell cycle include: Interphase – This phase includes the G1 phase, S phase and the G2 phase. M phase – This is the mitotic phase and is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis – In this phase the cytoplasm of the cell divides.
What is the interphase of a cell?
G1 phase (Gap 1) – G1 phase is the phase of the cell between mitosis and initiation of replication of the genetic material of the cell. During this phase, the cell is metabolically active and continues to grow without replicating its DNA.
What is the cell cycle?
“Cell cycle refers to the series of events that take place in a cell, resulting in the duplication of DNA and division of cytoplasm and organelles to produce two daughter cells.”
What is the mitotic phase?
This is the mitotic phase or the phase of the equational division as the cell undergoes a complete reorganization to give birth to a progeny that has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What is the process of cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis. In this phase, the cytoplasm of the cell divides. It begins as soon as the mitosis ends. Plant cells are much tougher than animal cells, as they have a rigid cell wall and high internal pressure. Thus, cytokinesis occurs in plant and animal cells differently.
What phase does centriole divide?
The centriole also divides into two centriole pairs in the cells which contain centriole. G2 phase (Gap 2) –During this phase, the RNA, proteins, other macromolecules required for multiplication of cell organelles, spindle formation, and cell growth are produced as the cell prepares to go into the mitotic phase.
