
The fluid mosaic model is one way of understanding biological membranes, consistent with most experimental observations. This model states that the components of a membrane such as proteins or glycolipids, form a mobile mosaic in the fluid-like environment created by a sea of phospholipids
Phospholipid
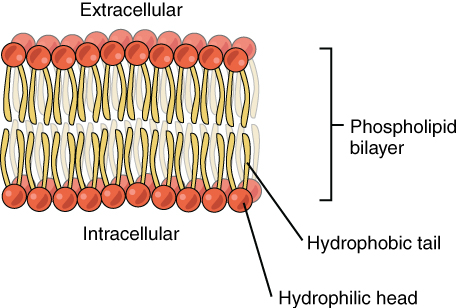
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. The structure of the phospholipid molecule generally consists of two hydrophobic fatty acid "tails" and a hydrophilic "head" consisti…
Why is the fluid mosaic model used?
- Some proteins in the membrane are called ‘intrinsic’. ...
- Some intrinsic proteins are ‘channel proteins’. ...
- Other transport proteins are ‘carrier proteins’. ...
- Carbohydrates are also a major component of plasma membranes. ...
- Along with peripheral proteins, carbohydrates form specialized sites on the cell’s surface that allow cells to recognize each other. ...
What is the structure of the fluid mosaic model?
What’s it made up of?
- Phospholipids There are two important parts of a phospholipid: the head and the two tails. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). ...
- Cholesterol Cholesterol is a type of steroid which is helpful in regulating molecules entering and exiting the cell. ...
- Proteins
What is the mosaic model of membrane structure?
These can travel across the cell membrane:
- Small, nonpolar molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can travel across the lipid bilayer and do so by squeezing through the phospholipid bilayers.
- Small, polar molecules such as water molecules cross without the help of proteins. ...
- Large, nonpolar molecules such as carbon rings also travel through but it is again a slow process.
What is the definition of fluid mosaic model?
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model? Fluid mosaic model definition: It describes the structure of cell membranes where a flexible lipid layer is spread with large protein molecules that act as channels through which other molecules enter and exit any cell.

What are the 3 parts of the fluid mosaic model?
According to the fluid mosaic model, the plasma membrane is a mosaic of components—primarily, phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins—that move freely and fluidly in the plane of the membrane.
Why are membranes described as fluid mosaic?
Cell membranes are represented according to a fluid-mosaic model, due to the fact that they are: Fluid – the phospholipid bilayer is viscous and individual phospholipids can move position. Mosaic – the phospholipid bilayer is embedded with proteins, resulting in a mosaic of components.
Why are cell membranes described as fluid?
It is fluid because it is flexible due to different quantities of cholesterol within the membrane. The mosaic structure refers to the varied composition of the molecules that includes phospholipids as well an array of different structural and functional proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
Which sentence best describes the fluid mosaic model?
D is correct. The Fluid Mosaic Model describes the liquid-like movement of the lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that make up the plasma membrane. These components travel freely across its surface.
What is the fluid mosaic model and what does it tell us?
The fluid mosaic model is a model of the cell membrane that explains how the components are able to move freely, laterally in the bilayer, and that...
Who proposed fluid mosaic model of cell membrane?
S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane in 1972 to describe its molecular structure.
Why is it called the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model describes the main characteristics of the plasma membrane. First, the membrane is fluid with the molecules moving and the me...
1. What are the Factors Affecting the Fluidity of the Plasma Membrane?
Three main factors influence cell membrane fluidity:Temperature: The temperature affects phospholipids. When it’s cold the phospholipid molecules a...
2. Who Proposed the Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane?
Plasma membrane is the cell membrane that separates the interior and exterior components of the cell from the surroundings. The cell wall is on the...
3. What are the Molecules That can go Through the Cell Membrane?
There are 5 major categories of molecules found in the cellular environment. These can travel across the cell membrane:Small, nonpolar molecules su...
4. Explain the Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane.
The Fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972. As stated in this model, the quasi-fluid nature of lipids allows lateral moveme...
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition
The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane describes how the membrane is fluid, flexible and made of many different components or macromolecules. This structure allows for the membrane to move with the cell and perform various functions, including maintaining homeostasis, facilitating cellular movement, communication and more.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are lipids that have two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol molecule, which is attached to a phosphate group. The fatty acid chains are considered the tail of the phospholipid and are hydrophobic. The phosphate group is negatively charged, called the "head," and is hydrophilic.
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a steroid lipid that is small and ring shaped. It fits in between the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids and helps regulate fluidity in the membrane. The membrane must be flexible and able to bend with the cell. Animal cells must move, grow, divide, and perform functions in the body which require them to change their shape.
Proteins
Proteins are a type of macromolecule in the cell that is used for many functions, including structure, support, metabolism, communication, and more.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
In this, the phospholipid bilayer was said to be punctuated by various proteins that formed a mosaic-like pattern in the lipid membrane. These proteins could traverse the entire membrane, or interact with one of the two lipid layers. Some proteins could even be attached to the membrane only through a short lipid chain.
How is the fluid nature of the lipid matrix forming the membrane illustrated?
The fluid nature of the lipid matrix forming the membrane was first illustrated by an experiment where membranes with different compositions were artificially fused. The proteins of both cells redistributed themselves across the entire fused membrane in less than an hour.
Why is cholesterol inserted in the middle of the phospholipid layer?
It appears to be inserted in the middle of phospholipids Cholesterol prevents the compaction of the hydrophobic tails at low temperatures as well as the expansion of the membrane under heat. This way, small molecules like carbon dioxide and oxygen can always move freely across the membrane, while the cell retains its selective permeability for larger molecules.
What is fluid mosaic?
The fluid mosaic model is one way of understanding biological membranes, consistent with most experimental observations. This model states that the components of a membrane such as proteins or glycolipids, form a mobile mosaic in the fluid-like environment created by a sea of phospholipids. There are restrictions to lateral movements, and subdomains within the membrane have specific functions.
What are the three types of proteins in the membrane?
In addition, the membrane has three types of proteins. Integral membrane proteins span the entire membrane, usually with alpha-helices forming the transmembrane region. These proteins form channels and pores that allow the movement of large or polar molecules across the hydrophobic segment of membrane.
When were cell membranes first visualized?
More than 25 years after the lipid bilayer model was proposed, cell membranes were first visualized in the 1950s. The initial observations seemed to suggest that the lipid membrane was coated on either side by thin sheets of proteins. However, in 1972, two scientists, Singer and Nicolson, refined this to create the fluid mosaic model.
What are the components of a biological membrane?
Biological membranes, especially cell membranes are made of phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins.
What is the function of the fluid mosaic model?
Fluid Mosaic Model Function. The cell membranes cause compartmentalisation, they separate the cells from their external environment. As organelle coverings, they allow the cell organelles to maintain their identity, internal environment and functional individuality. The plasma membrane protects the cell from any injury.
What is the mosaic model of membrane structure?
The mosaic model of membrane structure describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, cholesterol, and proteins that gives the membrane a fluid character. Plasma membranes range from 5 -10 nm in thickness. The proportions of proteins, lipids, ...
Why is fluidity important?
It is due to the hydrophobic interactions of lipids and proteins. The fluidity is important for a number of membrane functions. Phospholipids and many intrinsic proteins are amphipathic that is they possess both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups.
How thick is the plasma membrane?
Plasma membranes range from 5 -10 nm in thickness. The proportions of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in the plasma membrane are different from cell types. For example, myelin constitutes 18% of protein and 76% of lipid. The mitochondrial inner membrane has 76% of protein and 24% of lipid.
What is fluid mosaic?
Fluid mosaic model definition: It describes the structure of cell membranes where a flexible lipid layer is spread with large protein molecules that act as channels through which other molecules enter and exit any cell.
What molecules can travel across the cell membrane?
These can travel across the cell membrane: Small, nonpolar molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can travel across the lipid bilayer and do so by squeezing through the phospholipid bilayers.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane which is also called the plasma membrane is a thin membrane that surrounds every living cell. It delimits the cell from the environment around it. Within the cell are its components, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and substances that are involved in cellular ...
What are the restrictions to the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by the
There are restrictions to the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by the formation of subdomains within the lipid bilayer.
What are membrane domains?
Another way to define membrane domains is the association of the lipid membrane with the cytoskeleton filaments and the extracellular matrix through membrane proteins. The current model describes important features relevant to many cellular processes, including: cell-cell signaling, apoptosis, cell division, membrane budding, and cell fusion. ...
What is the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. According to this biological model, there is a lipid bilayer (two molecules thick layer consisting primarily of amphipathic phospholipids) in which protein molecules are embedded. The lipid bilayer gives fluidity and elasticity to the membrane.
What are the building blocks of lipid rafts?
Lipid rafts are membrane nanometric platforms with a particular lipid and protein composition that laterally diffuse, navigating on the liquid bilipid layer. Sphingolipids and cholesterol are important building blocks of the lipid rafts.
What did the Frye-Edidin experiment show?
The Frye-Edidin experiment showed that when two cells are fused the proteins of both diffuse around the membrane and mingle rather than being locked to their area of the membrane. An important experiment that provided evidence supporting fluid and dynamic biological was performed by Frye and Edidin.
When are non-bilayer lipids useful?
These membrane structures may be useful when the cell needs to propagate a non bilayer form, which occurs during cell division and the formation of a gap junction.
What is asymmetric membrane?
Membrane asymmetry. Additionally, the two leaflets of biological membranes are asymmetric and divided into subdomains composed of specific proteins or lipids, allowing spatial segregation of biological processes associated with membranes.
What are the proteins in the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane has three types of proteins: 1 Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane. 2 Peripheral Proteins: These are found embedded in a single leaflet of the membrane. They carry signals from one segment of the membrane and relay it to the another. 3 Glycoproteins: They stabilize the membrane and are responsible for intercellular communication.
Why is the plasma membrane important?
It helps the plasma membrane to retain the fluidity. It is present between the phospholipids and prevents the compaction of hydrophilic tails at low temperatures and their expansion at high temperatures.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acid chains have a single bond between the carbon atoms whereas, unsaturated fatty acid chains have double bonds between the carbon atoms. Double bonds make it harder for the chain to pack tightly by creating kinks. These kinks increase the fluidity of the membrane.
Where are carbohydrates found in a fluid mosaic?
Carbohydrates are found on the external surface of the membrane where they are bound to proteins or lipids. For more information on fluid mosaic model, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.
Which protein is found in the hydrophobic layer of the membrane?
Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane. Peripheral Proteins: These are found embedded in a single leaflet of the membrane. They carry signals from one segment of the membrane and relay it to the another.
Where are lipid rafts located?
Lipid Rafts. These are the lipid domains found on the external leaflet of the plasma membrane. Cholesterol, glycosphingolipids, glycosylphosphatidylinositol are the building blocks of lipid rafts.
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition
Development of The Fluid Mosaic Model
- This model was developed over many years, through painstaking work of scientists across the world. It began with the hypothesis that the membrane was made of a lipid bilayer, where membrane phospholipid self-assembled into a dual layer, with the non-polar, hydrophobic tails facing each other. The hydrophilic ‘head’ regions face the cytosol and the extracellular region. Th…
Functions and Components of Biological Membranes
- The main function of cell membranes is to demarcate the inner and outer regions of the cell. Within the cell, membranes of organelles perform the same function for subcellular structures. This function comes along with a caveat – the cell needs to actively communicate with the external environment, exchange materials, while also retaining important nutrients and keeping …
Other Models For Membrane Structure
- The fluid mosaic model was refined in the early 1980s, by two scientists called Mouritsen and Bloom to create the ‘mattress model’ for membrane structure. They demonstrated the fact that while earlier experiments had suggested that the entire membrane is fluid and allows free diffusionof proteins, there are in fact, subdomains within each membrane. For instance, when a t…
Related Biology Terms
- Amphipathic Molecules– Molecules containing polar hydrophilic regions and non-polar hydrophobic regions.
- Antigen– Any molecule capable of producing an immune response.
- Signal Transduction– Transmission of information, in the form of electrical or chemical signals, from the exterior of the cell to the interior.
- Amphipathic Molecules– Molecules containing polar hydrophilic regions and non-polar hydrophobic regions.
- Antigen– Any molecule capable of producing an immune response.
- Signal Transduction– Transmission of information, in the form of electrical or chemical signals, from the exterior of the cell to the interior.
- Sphingolipids– Fatty acid derivatives of a molecule called sphingosine. Often seen in membrane lipid rafts.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these statements about the structure of membranes is true? A. Made primarily of cholesterol molecules B. Glycoproteins on the cell surface are necessary for immune recognition C. Lipid rafts were predicted by early models of cell membrane structure D.All of the above 2. Which of these are features of the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes? A. Lipid bilayer forme…