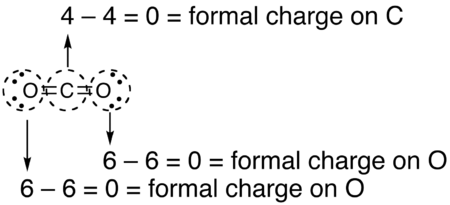
What is the formal charge of a carbon atom?
Carbon forms 4 bonds, which means it gets 4 electrons - 1 from each bond. Since carbon has 4 valence electrons, its formal charge will be zero.
What is a formal charge?
A formal charge ( F C) compares the number of electrons around a "neutral atom" (an atom not in a molecule) versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.
How do you determine the formal charge of an atom?
The easiest way to assign a formal charge on an atom is to compare the number of valence electrons that atom has with how many electrons it "gets" in a molecule - assuming bond electrons are shared equally at all times regardless of electronegativity. Let's start with the first Lewis structure.
What is the formal charge of an oxygen atom?
The same is true for both oxygen atoms. Both of them form 2 bonds, which means they get 2 electrons. In addition to these electrons, they both have 2 lone pairs; this brings the total number of electrons an oxygen atom gets to 6 (2 + 4). Since oxygen has 6 valence electrons, it will have a zero formal charge.
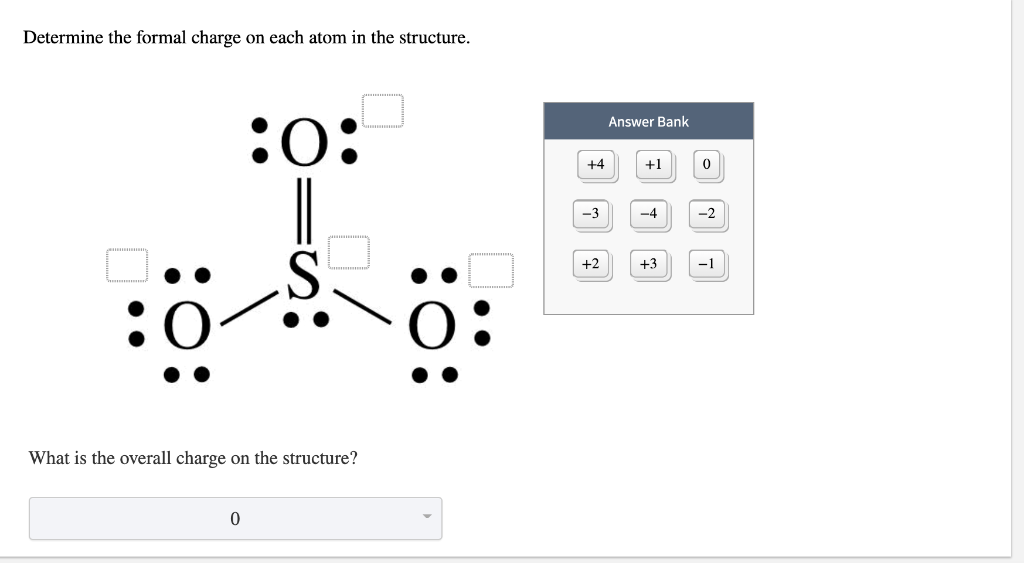
What are the formal charges on each atom in carbon monoxide CO?
- The oxygen formed a triple bond with carbon means oxygen has a positive charge on it. - Therefore the net formal charge on the carbon monoxide = - 1 + 1 = 0. - So the formal charge of carbon monoxide (CO) is zero. Note: We can count the formal charge of an individual atom and formal charge of a molecule also.
What is the charge of carbon in CO?
The oxidation state of carbon in carbon monoxide is +2 in each of these structures. It is calculated by counting all the bonding electrons as belonging to the more electronegative oxygen. Only the two non-bonding electrons on carbon are assigned to carbon.
How do you find the charge on CO?
0:461:33How to Calculate the Formal Charges for CO (Carbon Monoxide) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOne half of the bonded valence electrons which is two four six so six over two six minus two is fourMoreOne half of the bonded valence electrons which is two four six so six over two six minus two is four four minus three is plus one. So we'll put these formal charges up here for oxygen.
How do you find the formal charge of C in co2?
0:001:34Calculating Formal Charges for CO2 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThere are eight valence electrons that are involved in bonds with carbon we'll divide that by 2. SoMoreThere are eight valence electrons that are involved in bonds with carbon we'll divide that by 2. So 4 minus 0 minus 4 is 0. So the formal charge on carbon is 0.
What is the formal charge on the oxygen atom in CO?
0Answer: The formal charge of carbon monoxide can be determined for the Lewis structure given below. The formal charge of oxygen becomes +1. Hence, the formal charge of CO is 0.
What is the oxidation state of CO?
The most common oxidation states of cobalt are +2 and +3. [Co(H2O)6]2+ and [Co(H2O)6]3+ are both known but the latter is a strong oxidizing agent and in aqueous solution, unless it is acidic, it decomposes rapidly as the CoIII oxidizes the water with evolution of oxygen.
Does CO ligand have a charge?
They occur as neutral complexes, as positively-charged metal carbonyl cations or as negatively charged metal carbonylates. The carbon monoxide ligand may be bound terminally to a single metal atom or bridging to two or more metal atoms.
What charge does cobalt have?
In its compounds cobalt nearly always exhibits a +2 or +3 oxidation state, although states of +4, +1, 0, and −1 are known.
What is the formal charge of oxygen atom in CO of co3 2 ion?
The carbon, in the carbonate ion, has 4 x 1 = 4 electrons assigned to it (one from each of its four bonds), therefore it has a formal charge of zero (neutral). The top oxygen has two lone pairs and two bonding pairs giving a total of 4 + 2 = 6 electrons. Thus the formal charge on this oxygen is also zero.
What is the formal charge of con?
The formal charge of carbon is 0. Oxygen (O) is in group 16, so that means it has 6 valence electrons. There are 4 dots around oxygen, so that means it has 4 nonbonding electrons.
What is the oxidation number of C in co2?
+4As a result, carbon in CO2 has an oxidation number of +4.
Does CO ligand have a charge?
They occur as neutral complexes, as positively-charged metal carbonyl cations or as negatively charged metal carbonylates. The carbon monoxide ligand may be bound terminally to a single metal atom or bridging to two or more metal atoms.
Why oxidation number of CO is zero?
We can also confirm that the given compound is chargeless or neutral because there is no charge mentioned in its molecular formula. Thus, the total oxidation state of the compound is 0.
What charge does cobalt have?
In its compounds cobalt nearly always exhibits a +2 or +3 oxidation state, although states of +4, +1, 0, and −1 are known.
Is cobalt positive or negative?
Because this species has no charge, it is an atom in its elemental form. This is cobalt. In this case, there is a 2+ charge on the atom, so it is a cation.
What is formal charge?
The formal charge over an atom of a polyatomic molecule or ion is the difference between the valence electron of that atom in the elemental state and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in Lewis structure.
How many valency does oxygen have?
Oxygen should have 6 as valency, but has 5 attached, Formal charge = 6-5 =+1. Net Formal Charge. +1 and -1 cancel for a net formal charge of zero.
How many valence electrons does carbon dioxide have?
The carbon dioxide molecule has a total of 16 valence electrons - 4 from the carbon atom and 6 from each of the two oxygen atoms, all of which being accounted for in the three Lewis structures above.
How many bonds does carbon have?
Moving on to the second Lewis structure. Carbon is in the same position it was earlier - it forms 4 bonds → zero formal charge. However, things have changed for the oxygen atoms. Notice the oxygen on the left now forms 3 bonds with the carbon and has 1 lone pair instead of 2.
How many resonance structures does CO2 have?
In order to determine formal charges for the atoms in the carbon dioxide molecule you need to take into account the fact that CO2 has three resonance structures that look like this: SIDE NOTE: the actual structure of the carbon dioxide molecule is a hybrid between these three structures, but I'll just show you each of them separate ...
How many electrons does oxygen have?
The oxygen on the right forms 1 bond with the carbon and has 3 lone pairs, for a total of 7 electrons; since it has one more electron than it needs, it will automatically have a (-1) formal charge.
What is the sum of formal charges?
In this case, the sum of the formal charges is 0 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 1+ , which is the same as the overall charge of the ammonium polyatomic ion.
What is the charge of a carbon radical?
Two other possibilities are carbon radicals and carbenes, both of which have a formal charge of zero. A carbon radical has three bonds and a single, unpaired electron. Carbon radicals have 4 valence electrons and a formal charge of zero. Carbenes are a highly reactive species, in which a carbon atom has two bonds and one lone pair of electrons, giving it a formal charge of zero. Though carbenes are rare, you will encounter them in section 8.10 Addition of Carbenes to Alkenes.
What is the bonding pattern of hydrogen?
The common bonding pattern for hydrogen is easy: hydrogen atoms in organic molecules typically have only one bond, no unpaired electrons and a formal charge of zero. The exceptions to this rule are the proton, H +, the hydride ion, H -, and the hydrogen radical, H.. The proton is a hydrogen with no bonds and no lone pairs and a formal charge of 1+. The hydride ion is a is a hydrogen with no bonds, a pair of electrons, and a formal charge of 1−. The hydrogen radical is a hydrogen atom with no bonds, a single unpaired electron and a formal charge of 0. Because this book concentrates on organic chemistry as applied to living things, however, we will not be seeing ‘naked’ protons and hydrides as such, because they are too reactive to be present in that form in aqueous solution. Nonetheless, the idea of a proton will be very important when we discuss acid-base chemistry, and the idea of a hydride ion will become very important much later in the book when we discuss organic oxidation and reduction reactions. As a rule, though, all hydrogen atoms in organic molecules have one bond, and no formal charge.
How many valence electrons does nitrogen have?
A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons (it is in group 15). From the Lewis structure, the nitrogen atom in ammonia has one lone pair and three bonds with hydrogen atoms. Substituting into Equation 2.3.1, we obtain
How many electrons are in each atom of a bond?
Bonding electrons are divided equally between the two bonded atoms, so one electron from each bond goes to each atom.
How many bonds does each hydrogen atom have?
Each hydrogen atom in has one bond and zero non-bonding electrons. The formal charge on each hydrogen atom is therefore
Which arrangement of oxygen has a formal charge of zero?
The common arrangement of oxygen that has a formal charge of zero is when the oxygen atom has 2 bonds and 2 lone pairs. Other arrangements are oxygen with 1 bond and 3 lone pairs, that has a 1− formal charge, and oxygen with 3 bonds and 1 lone pair that has a formal charge of 1+. All three patterns of oxygen fulfill the octet rule.
How to calculate formal charge of an atom?
The formal charge of any atom in a molecule can be calculated by the following equation: where V is the number of valence electrons of the neutral atom in isolation (in its ground state); N is the number of non-bonding valence electrons on this atom in the molecule; and B is the total number of electrons shared in bonds with other atoms in ...
What is formal charge?
A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. When determining the best Lewis structure (or predominant resonance structure) for a molecule, the structure is chosen such that the formal charge on each ...
What is formal charge compared to oxidation state?
Formal charge compared to oxidation state. Formal charge is a tool for estimating the distribution of electric charge within a molecule. The concept of oxidation states constitutes a competing method to assess the distribution of electrons in molecules. If the formal charges and oxidation states of the atoms in carbon dioxide are compared, ...
How many electrons are in a covalent bond?
Count up the number of electrons in the atom's "circle." Since the circle cuts the covalent bond "in half," each covalent bond counts as one electron instead of two.
Why is the covalent bonding aspect overemphasized?
The covalent (sharing) aspect of the bonding is overemphasized in the use of formal charges, since in reality there is a higher electron density around the oxygen atoms due to their higher electronegativity compared to the carbon atom. This can be most effectively visualized in an electrostatic potential map.
This problem has been solved!
What is the formal charge on the carbon atom in CO? Part B What is the formal charge on the oxygen atom in CO? My answer was +1, +2 and this was incorrect. Could you shed some light on the error of my thinking?
Best Answer
Step 1) A formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule. The formal charge of any atom in a molecule can be calculated by the following equation: Formal charge = V - N - (B / 2) Where V is the number of valence electrons of t … View the full answer
What does formal charge mean in chemistry?
Finally, the formal charge can give an indication as to how a molecule will behave during a reaction. If an atom has a negative formal charge, it is more likely to be the source of electrons in a reaction (a nucleophile). Conversely, if it has a positive one, then it is more likely to be accept electrons (an electrophile), and that atom specifically is most likely to be the site of the reaction.
What is the sum of all the formal charges of the atoms in a molecule?
It is also worth noting that the sum of all the formal charges of the atoms in a molecule must equal the overall charge on the molecule/ion. That is, they should sum up to zero if its an neutral molecule, and should sum up to the ion’s charge if it is not.
What is Formal Charge?
Formal Charge is a charge assigned to an atom under the assumption that all electrons in bonds are shared equally. This is a hypothetical measure, not a real representation of the actual charge on an atom, which looks at the ways electrons are actually shared between atoms in a bond. But more on that later!
How many valence electrons does hydrogen have?
Hydrogen has one valence electron, two bonded electrons, and zero unbonded electrons. This makes its formal charge: (1) – (½) (2) – (0) = 0.
What is the most stable state for an atom to be in?
Ideally, an atom in a molecule wants to have a formal charge of zero: this is the lowest energy, and thus the most stable state for it to be in. This clues us into the structure of a molecule if there are multiple options: the one with the least/lowest formal charges is the preferred structure. There are even specific guidelines to help you figure this out:
What is an ion?
Ion: an atom or molecule with a net ionic charge, due to the presence or lack of electrons.
What is the charge of a formal ion?
As we can see, the formal charges add up to 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + (-1) = -1. This sum does equal the overall charge on the ion, which is -1.