What is the formula for effusion? Often, it is used to compare the effusion rates of two gases. This is represented by the formula: $frac { ext {rate of effusion A}} { ext {rate of effusion B}} = sqrt {frac {M_ {B}} {M_ {A}}}$ where $M$ refers to molar mass. Click to see full answer.
How do you calculate effusion?
What to order for lights criteria?
- Effusion protein/serum protein ratio greater than 0.5.
- Effusion lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)/serum LDH ratio greater than 0.6.
- Effusion LDH level greater than two-thirds the upper limit of the laboratory’s reference range of serum LDH.
What is ratio of effusion?
The ratio of the rates of effusion of two gases is equal to the square root of the inverse ratio of their molar masses or densities. The effusion rate of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Do lighter gases diffuse faster? On average, lighter gases travel faster than heavier gases at the same temperature.
What is the formula for diffusion?
Diffusion Formula. Diffusion was quantitatively measured by Adolf Fick in 1880’s determining the rate of diffusion to be the difference in the concentration gradient. The law formulated from Fick’s derivation is the “Fick’s first law” from the given equation. Js = -Ds ΔCs / Δ x. Js is the density of the diffusion at a unit area per ...
What is the rate of effusion?
The rate of effusion is determined by the number of molecules that diffuse through the hole in a unit of time, and therefore by the average molecular velocity of the gas molecules. What is effusion give an example? Effusion is defined as a loss of material across a boundary.
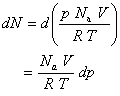
How do you solve effusion problems?
1:4913:37Graham's Law of Effusion Practice Problems, Examples, and FormulaYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd that's the main idea behind it now the equation that you need graham's law of effusion. It's uhMoreAnd that's the main idea behind it now the equation that you need graham's law of effusion. It's uh r2 over r1 is equal to the square root of the second molar mass divided by the first.
How do you find the effusion ratio?
The ratio of the rates of effusion of two gases is equal to the square root of the inverse ratio of their molar masses or densities. The effusion rate of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass.
What is effusion rate?
The rate of effusion of a gaseous substance is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Graham's law is an empirical relationship that states that the ratio of the rates of diffusion or effusion of two gases is the square root of the inverse ratio of their molar masses.
What is the law of effusion?
Graham's law of diffusion was formulated by Scottish physical chemist Thomas Graham in 1848. Graham found experimentally that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of its particles.
What is effusion example?
Effusion is defined as a loss of material across a boundary. A common example of effusion is the loss of gas inside of a balloon over time. The rate at which gases will effuse from a balloon is affected by a number of factors.
What is effusion of gas?
Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is, the average distance traveled between collisions. Effectively, this means that only one particle passes through at a time.
What is the formula for diffusion?
Diffusion coefficient is the proportionality factor D in Fick's law (see Diffusion) by which the mass of a substance dM diffusing in time dt through the surface dF normal to the diffusion direction is proportional to the concentration gradient grad c of this substance: dM = −D grad c dF dt.
What is the effusion rate of o2?
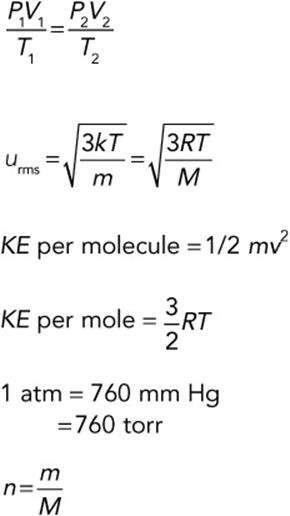
From Graham's law, we can use the molar mass of each gas: rate of effusion of hydrogenrate of effusion of oxygen=√32g mol−1 √2g mol−1 =√16√1=41 rate of effusion of hydrogen rate of effusion of oxygen = 32 g mol − 1 2 g mol − 1 = 16 1 = 4 1 Hydrogen effuses four times as rapidly as oxygen.
What is the formula of rms velocity?
v rms = v 2 – = 3 k B T m . The rms speed is not the average or the most likely speed of molecules, as we will see in Distribution of Molecular Speeds, but it provides an easily calculated estimate of the molecules' speed that is related to their kinetic energy.
What is Graham Law of effusion?
Graham's law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely propertional to the square root of the density of the gas.
What is the formula of Graham's law of diffusion?
Graham's law states that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. See this law in equation form below. r ∝ 1/(M)½ or. r(M)½ = constant.
What is the formula for partial pressure?
As has been mentioned in the lesson, partial pressure can be calculated as follows: P(gas 1) = x(gas 1) * P(Total); where x(gas 1) = no of moles(gas 1)/ no of moles(total).
What is the inverse of the rate of effusion of a gas?
Scottish chemist Thomas Graham (1805–1869) found experimentally that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles. In other words, the ratio of the rates of effusion of two gases at the same temperature and pressure is given by the inverse ratio of the square roots of the masses of the gas particles.
How does the Knudsen effusion cell work?
The Knudsen effusion cell is used to measure the vapor pressures of a solid with very low vapor pressure. Such a solid forms a vapor at low pressure by sublimation. The vapor slowly effuses through a pinhole, and the loss of mass is proportional to the vapor pressure and can be used to determine this pressure. The heat of sublimation can also be determined by measuring the vapor pressure as a function of temperature, using the Clausius–Clapeyron relation.
What is the process of gas escape?
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Such a hole is often described as a pinhole and the escape of the gas is due to the pressure difference between the container and the exterior.
Is the effusion rate proportional to the square root of the molecular weight?
At constant pressure and temperature, the root-mean-square speed and therefore the effusion rate are inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight. Gases with a lower molecular weight effuse more rapidly than gases with a higher molecular weight, so that the number of lighter molecules passing through the hole per unit time is greater.
Which law states that atoms with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than atoms with higher mo
According to Graham’s Law, at constant pressure and temperature, molecules or atoms with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than the higher molecular mass molecules or atoms. Thomas even found out the rate at which they escape through diffusion.
What is diffusion in science?
Diffusion is a phenomenon where there is a movement of one material move from area of high concentration to the area of low concentration. This means particles or molecules spread through medium. For example, if you spray at the one end of the room you would be able to smell at the other end. This is because of diffusion phenomenon.
What is the formula for comparing the rates of two different gases at equal pressures and temperatures?
Formula can be written as. M 1 is the molar mass of gas 1. M 2 is the molar mass of gas 2. Rate 1 is the rate of effusion of the first gas. Rate 2 is the rate of effusion for the second gas. It states that rate of diffusion ...
Pleural effusion volume calculator for ultrasound
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for clinical judgment. Radcalculators.org makes no claims of the accuracy of the information contained herein.
Notes
As reflected by this calculator too, there are several different published methods and equations that aid in estimating the approximate volume of the pleural effusion.
Overview
Effect of molecular weight
At constant pressure and temperature, the root-mean-square speed and therefore the effusion rate are inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight. Gases with a lower molecular weight effuse more rapidly than gases with a higher molecular weight, so that the number of lighter molecules passing through the hole per unit time is greater.
Scottish chemist Thomas Graham (1805–1869) found experimentally that the rate of effusion of …
Etymology
The word effusion derives from the Latin word, effundo, which means "shed, pour forth, pour out, utter, lavish, waste."
Measures of flow rate
According to the kinetic theory of gases, the kinetic energy for a gas at a temperature is
where is the mass of one molecule, is the root-mean-square speed of the molecules, and is the Boltzmann constant. The average molecular speed can be calculated from the Maxwell speed distribution as (or, equivalently, ). The rate at which a gas of molar mass effuses (typically expressed as the number of molecules passing through the hole per second) is then
Knudsen effusion cell
The Knudsen effusion cell is used to measure the vapor pressures of a solid with very low vapor pressure. Such a solid forms a vapor at low pressure by sublimation. The vapor slowly effuses through a pinhole, and the loss of mass is proportional to the vapor pressure and can be used to determine this pressure. The heat of sublimation can also be determined by measuring the vapor pressure as a function of temperature, using the Clausius–Clapeyron relation.