
Why does monosodium glutamate tastes so good?
MSG Makes Good-Tasting Foods Taste Better
- First and foremost, MSG makes good-quality food taste better, but it will not improve the flavor of poor-quality food.
- A very small amount of MSG can increase the level of umami flavor by adding glutamate to a recipe.
- MSG can effectively enhance foods that are savory. ...
Is monosodium glutamate good or bad for You?
There is a ton of controversy surrounding MSG in the natural health community. It is claimed to cause asthma, headaches and even brain damage. On the other hand, most official sources like the FDA...
Is monosodium glutamate (MSG) actually that bad?
There’s a popular misconception that MSG is particularly bad for your health. MSG is generally regarded as safe in moderation by the FDA and other expert organizations. The claim that monosodium glutamate (MSG) is bad for you has been disproven by scientific research.
Does monosodium glutamate (MSG) harm the food in any way?
MSG is generally regarded as safe in moderation by the FDA and other expert organizations. The claim that monosodium glutamate (MSG) is bad for you has been disproven by scientific research. Still, the sentiment lingers, especially in American culture, where Chinese restaurants have gone so far as to ban the core ingredient from their kitchens.
See more

What is monosodium glutamate made from?
Today, instead of extracting and crystallizing MSG from seaweed broth, MSG is produced by the fermentation of starch, sugar beets, sugar cane or molasses. This fermentation process is similar to that used to make yogurt, vinegar and wine.
What is monosodium glutamate another name for?
MSG can go by these and many other synonymous names as well, including monosodium salt, monohydrate, monosodium glutamate, monosodium glutamate monohydrate, monosodium L-glutamate monohydrate, MSG monohydrate, sodium glutamate monohydrate, UNII-W81N5U6R6U, L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt, and monohydrate.
What is the full name of MSG?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is a flavor enhancer often added to restaurant foods, canned vegetables, soups, deli meats and other foods. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified MSG as a food ingredient that's generally recognized as safe. But its use is still debated.
Why is MSG used in food?
A popular seasoning and flavor enhancer, MSG, or monosodium glutamate, is the purest form of umami, the fifth taste. MSG (monosodium glutamate) is widely used to intensify and enhance umami flavors in sauces, broths, soups and many more foods.
Why is it called MSG?
Lee breaks down his reasoning: “MSG stands for monosodium glutamate. So sodium—everybody knows what that is—[is] the first ingredient in common table salt.” (Natural salt found in foods accounts for about 10 percent of a person's total daily intake, according to the Food and Drug Administration.)
Is MSG a salt?
Salt is sodium chloride while MSG is sodium + glutamic acid. Salt is salty while MSG has an “umami taste.” Salt could be bad for us while MSG is generally safe to use.
Does Maggi contain MSG?
Does MAGGI® contain MSG? At Nestlé, it is always our endeavour to provide consumers with complete information about the ingredients used in their favourite MAGGI® Noodles. Please be assured that MAGGI® Noodles and its Masala Tastemaker do not contain Monosodium Glutamate (MSG/E621).
Is MSG a pig?
The agency eventually declared that a monosodium glutamate-based taste enhancer contained enzymes grown on pork fat. The MSG seasoning had been made from a beef-based product until June, when the company switched to a pork enzyme. The reason for the switch was not clear.
What is the brand name for MSG?
Monosodium glutamate can be found simply labeled as MSG or under the brand name Ac'cent in the supermarket's spice aisle. The brand Ajinomoto is sold at Asian grocery stores and online.
What is the closest thing to MSG?
Beef Stock – The Most Common Substitute For MSG Beef stock has the most similar taste and is considered as the best substitute for MSG. It can add more flavor to your dish; however, it may slightly affect the taste. You can buy beef stock or beef stock cubes at the store or supermarket for convenient and instant usage.
What is MSG and why you should avoid it?
Some studies have shown that MSG may contribute to a variety of conditions, including obesity, central nervous system disorder, and reproductive malfunctions, though more research is needed in these areas. Symptoms that some have claimed occur after consuming MSG include: Nausea.
Is monosodium glutamate and baking soda same?
Sodium chloride and MSG are flavor enhancers, sodium nitrate is a preservative for meats, and sodium bicarbonate, or baking soda, is a leavening agent used in baked goods.
How is monosodium glutamate made?
MSG occurs naturally in a number of foods, including tomatoes and cheeses. Today MSG is created by the fermentation of starch, sugar beets, sugar c...
What is monosodium glutamate made of?
Monosodium glutamate was discovered by a Japanese chemist named Kikunae Ikeda more than 100 years ago, who obtained it from seaweed and found it ha...
What is monosodium glutamate used for?
Glutamic acid is naturally present in onions, raisins, cheeses, mushrooms and other foods. MSG is used as a flavour enhancer in the food industry w...
How does monosodium glutamate work?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is the glutamic acid sodium salt and is a non-essential amino acid. Interestingly, glutamic acid has no umami flavouring...
Why is MSG bad for your health?
There is a lot of debate within the natural health culture surrounding MSG. Asthma, headaches and even brain damage are reported. In comparison, mo...
How long does it take for glutamate to return to normal?
However, the concentration typically returns to normal within two hours. In general, foods providing metabolizable carbohydrate significantly attenuate peak plasma glutamate levels at doses up to 150 mg/kg body weight.
What is the MSG number?
The label must have the food-additive class name (e.g. "flavour enhancer"), followed by the name of the additive ("MSG") or its International Numbering System (INS) number, 621.
What is MSG in food?
Monosodium glutamate ( MSG ), also known as sodium glutamate, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.
How is MSG made?
MSG has been produced by three methods: hydrolysis of vegetable proteins with hydrochloric acid to disrupt peptide bonds (1909–1962); direct chemical synthesis with acrylonitrile (1962–1973), and bacterial fermentation (the current method). Wheat gluten was originally used for hydrolysis because it contains more than 30 g of glutamate and glutamine in 100 g of protein. As demand for MSG increased, chemical synthesis and fermentation were studied. The polyacrylic fiber industry began in Japan during the mid-1950s, and acrylonitrile was adopted as a base material to synthesize MSG.
How long has MSG been used?
MSG has been used for more than 100 years to season food. Consumption and manufacture of high-salt and high-glutamate foods, which contain both sodium and glutamate, stretch back far longer, with evidence of cheese manufacture as early as 5,500 BCE.
What is the name of the food additive that is used in ribonucleotide?
The ribonucleotide food additives disodium inos inate (E631) and disodium guanylate (E627), as well as conventional salt are usually used with monosodium glutamate-containing ingredients as they seem to have a synergistic effect. "Super salt" is a mixture of 9 parts salt, to one part MSG and 0.1 parts disodium inosinate and disodium guanylate.
Which is the most soluble MSG?
Of them, sodium glutamate was the most soluble, most palatable, and easiest to crystallize. Ikeda called his product "monosodium glutamate", and submitted a patent to produce MSG; the Suzuki brothers began commercial production of MSG in 1909 as Ajinomoto ("essence of taste").
What is Monosodium Glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate, often abbreviated to MSG, is a sodium salt of glutamic acid. The chemical formula of MSG is C5H8NO4Na and its IUPAC name is sodium 2-aminopentanedioate. Since it is known to intensify meaty flavours in food, monosodium glutamate is widely used as a flavour enhancer in the food industry.
What are the three methods of producing monosodium glutamate?
The three most common methods of producing monosodium glutamate are listed below. Hydrolysis of some vegetable proteins in the presence of hydrochloric acid. Chemical synthesis with the help of acrylonitrile (CH 2 CHCN). A bacterial fermentation process involving starch or molasses.
What is MSG crystal?
This compound was first produced by the Japanese chemist Kikunae Ikeda in the year 1908. At room temperature, MSG exists as a crystalline solid which is white in colour. It does not have any distinct odour. Crystals of Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) Among the sodium, magnesium, potassium, and calcium salts of glutamic acid, ...
Why is MSG added to ramen noodles?
MSG is often added to tobacco in order to enhance its taste. It also finds use in the treatment of hepatic coma. MSG is an important component of several instant ramen noodle products. Monosodium glutamate has been associated with several symptoms such as headaches, tingling sensations, and burning sensations.
What is glutamic acid?
Glutamic acid is naturally present in onions, raisins, cheeses, mushrooms and other foods. MSG is used as a flavour enhancer in the food industry with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavour of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in products like stews and meat soups.
How is MSG made?
Today MSG is created by the fermentation of starch, sugar beets, sugar cane or molasses instead of extracting and crystallizing MSG from seaweed broth. The process of fermentation resembles that used to produce yoghurt, vinegar and wine.
What is the bond between Na + and C 5 H 8 NO 4–?
MSG molecules feature an ionic bond between Na + and C 5 H 8 NO 4–. The structure of a monosodium glutamate molecule is illustrated below.
What is monosodium glutamate?
Monosodium Glutamate is a white or off-white colour crystalline compound with a slight odour like peptone. Monosodium Glutamate imparts a meat-like flavour and hence is used in the food industry as a flavour enhancer. Monosodium Glutamate is found in vegetables like grapes, cheese, tomatoes, and mushrooms. Let us learn the chemical properties of Monosodium Glutamate.
Is monosodium glutamate stable?
The structural representation of Monosodium Glutamate is as shown in the figure below. Monosodium Glutamate is highly stable to high temperatures and hence can be used in industrial food-processing conditions.
What is the pH of monosodium glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate appears as white or off-white crystalline powder with a slight peptone-like odor. pH (0.2% solution)7.0. (NTP, 1992)
How many people are exposed to monosodium glutamate?
NIOSH (NOES Survey 1981-1983) has statistically estimated that 60,341 workers (22,829 of these are female) are potentially exposed to monosodium glutamate in the US (1). Occupational exposure to monosodium glutamate may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where monosodium glutamate is produced or used (SRC). The general population is exposed to monosodium glutamate primarily via ingestion of food products containing this additive (SRC).
How does monosodium glutamate release into the atmosphere?
If released to air, monosodium glutamate will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere since it is a salt. Particulate-phase monosodium glutamate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Monosodium glutamate does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, monosodium glutamate is expected to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 4. Volatilization from soil and water surfaces will not occur since monosodium glutamate is a salt. Several genera of bacteria have been shown to possess enzymatic capability to degrade l-glutamic acid and monosodium glutamate was readily degraded in sediment/ water microcosms using both seawater and estuarine water. If released into water, monosodium glutamate is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. An estimated BCF of 1 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Occupational exposure to monosodium glutamate may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where monosodium glutamate is produced or used. The general population is exposed to monosodium glutamate primarily via ingestion of food products containing this additive. (SRC)
Why is monosodium glutamate not hydrolyzed?
Monosodium glutamate is not expected to undergo hydrolysis in the environment due to the lack of functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions (1). Monosodium glutamate does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight (1).
What is glutamate in the nervous system?
L-Glutamate and GABA supposedly act as excitatory and inhibitory transmitters , respectively, in the central nervous system. Glutamate is also involved in the synthesis of proteins. / Glutamate /. WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts.
How is glutamate absorbed?
Glutamate is absorbed from the gut by an active transport system specific for amino acids. This process is saturable, can be competitively inhibited, and is dependent on sodium ion concentration... . During intestinal absorption, a large proportion of glutamic acid is transaminated and consequently alanine levels in portal blood are elevated. If large amounts of glutamate are ingested, portal glutamate levels increase ... . This elevation results in increased hepatic metabolism of glutamate, leading to release of glucose, lactate, glutamine, and other amino acids, into systemic circulation ... . The pharmacokinetics of glutamate depend on whether it is free or incorporated into protein, and on the presence of other food components. Digestion of protein in the intestinal lumen and at the brush border produces a mixture of small peptides and amino acids; di-and tri-peptides may enter the absorptive cells where intracellular hydrolysis may occur, liberating further amino acids. Defects are known in both amino acid and peptide transport ... .. Glutamic acid in dietary protein, together with endogenous protein secreted into the gut, is digested to free amino acids and small peptides, both of which are absorbed into mucosal cells where peptides are hydrolyzed to free amino acids and some of the glutamate is metabolized. Excess glutamate and other amino acids appear in portal blood. As a consequence of the rapid metabolism of glutamate in intestinal mucosal cells and in the liver, systemic plasma levels are low, even after ingestion of large amounts of dietary protein. / Glutamic acid /
How is glutamic acid metabolized?
Glutamic acid is metabolized in the tissues by oxidative deamination ... or by transamination with pyruvate to yield oxaloacetic acid ... which, via alpha-ketoglutarate, enters the citric acid cycle ... .. Quantitatively minor but physiologically important pathways of glutamate metabolism involve decarboxylation to gamma-aminobutyrate ( GABA) and amidation to glutamine ... . Decarboxylation to GABA is dependent on pyridoxal phosphate, a coenzyme of glutamic acid decarboxylase ..., as is glutamate transaminase. Vitamin B6 -deficient rats have elevated serum glutamate levels and delayed glutamate clearance ... . / Glutamic acid /
What is glutamate used for?
monosodium glutamate (MSG), also called monosodium L-glutamate or sodium glutamate, white crystalline substance, a sodium salt of the amino acid glutamic acid, that is used to intensify the natural flavour of certain foods. Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is an important ingredient in the cuisines of China and Japan and is used commercially in broths, soups, canned and frozen vegetables, flavouring and spice blends, gravies, meats, poultry, and sauces and in other combinations. It is also used to enhance the taste of tobacco and has been used medically to treat hepatic coma. The substance is naturally present at high levels in tomatoes and Parmesan cheese.
How is MSG made?
It is now produced using a bacterial fermentation process with starch or molasses as carbon sources and ammonium salts as nitrogen sources.
When was MSG first discovered?
MSG was first identified as a flavour enhancer in 1908 by Japanese chemist Ikeda Kikunae, who found that soup stocks made from seaweed contained high levels of the substance. MSG elicits a unique taste, known as umami, that is different from the other basic tastes (bitter, salty, sour, sweet) and thus enhances the complex flavours of meat, poultry, seafood, and vegetables. Ikeda’s discovery led to the commercial production of MSG from seaweed. It is now produced using a bacterial fermentation process with starch or molasses as carbon sources and ammonium salts as nitrogen sources.
Does MSG cause tingling?
Learn about the myths and safety of monosodium glutamate (MSG). There have been reports that MSG ingested in large amounts may produce such physical reactions as burning sensations, facial tightness or pressure, and a tingling sensation in some individuals.
What is the formula for monosodium glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate, also known as sodium glutamate is the salt of glutamic acid (one of the more important amino acids). It is a very important flavoring agent in the food-processing industry. Formula and structure: The molecular formula of monosodium glutamate is C 5 H 8 NNaO 4 ...
What is the melting point of monosodium glutamate?
Physical properties: Monosodium glutamate is a white crystalline powder with a slightly peptonelike odor. Its melting point is 232 ºC and it is highly soluble in water. Its insoluble in common organic solvents. Monosodium glutamate is used to impart the umami (meat-like) taste to food.
What is glutamate used for?
Uses: Monosodium glutamate is one of the most important flavoring agents, thus is largely used in the food industry.
Where is monosodium glutamate found?
Occurrence: Monosodium glutamate is largely found in nature, especially in food as tomatoes and cheese.
Is glutamate a carboxylic group?
Monosodium glutamate has the same basic structure of amino acids, with an amine group (-NH 2) and carboxylate ion instead the carboxylic group (-COO - ). Moreover, the monosodium glutamate has other carboxylic group in the side chain.
Does monosodium glutamate cause headaches?
In the past decade, it was thought, monosodium glutamate caused headaches and other side effects, but at the moment, any test has proved it. Related Links: <a href="https://www.softschools.com/formulas/chemistry/monosodium_glutamate_formula/387/">Monosodium glutamate Formula </a>.
What are the symptoms of MSG?
MSG has been used as a food additive for decades. Over the years, the FDA has received many anecdotal reports of adverse reactions to foods containing MSG. These reactions — known as MSG symptom complex — include: 1 Headache 2 Flushing 3 Sweating 4 Facial pressure or tightness 5 Numbness, tingling or burning in the face, neck and other areas 6 Rapid, fluttering heartbeats (heart palpitations) 7 Chest pain 8 Nausea 9 Weakness
Does MSG cause chest pain?
Chest pain. Nausea. Weakness. However, researchers have found no definitive evidence of a link between MSG and these symptoms. Researchers acknowledge, though, that a small percentage of people may have short-term reactions to MSG. Symptoms are usually mild and don't require treatment.
Is MSG safe to eat?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified MSG as a food ingredient that's "generally recognized as safe," but its use remains controversial. For this reason, when MSG is added to food, the FDA requires that it be listed on the label. MSG has been used as a food additive for decades. Over the years, the FDA has received many anecdotal ...
Is MSG a food additive?
MSG has been used as a food additive for decades. Over the years, the FDA has received many anecdotal reports of adverse reactions to foods containing MSG. These reactions — known as MSG symptom complex — include: However, researchers have found no definitive evidence of a link between MSG and these symptoms.
How much glutamate is in a day?
An average adult consumes approximately 13 grams of glutamate each day from the protein in food, while intake of added MSG is estimates at around 0.55 grams per day.
How is MSG made?
Today, instead of extracting and crystallizing MSG from seaweed broth, MSG is produced by the fermentation of starch, sugar beets, sugar cane or molasses. This fermentation process is similar to that used to make yogurt, vinegar and wine.
What is MSG in food?
What is MSG? Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is the sodium salt of the common amino acid glutamic acid. Glutamic acid is naturally present in our bodies, and in many foods and food additives.
Where does MSG come from?
However, MSG occurs naturally in ingredients such as hydrolyzed vegetable protein, autolyzed yeast, hydrolyzed yeast, yeast extract, soy extracts, and protein isolate, as well as in tomatoes and cheeses.
Can MSG cause headaches?
Over the years, FDA has received reports of symptoms such as headache and nausea after eating foods containing MSG. However, we were never able to confirm that the MSG caused the reported effects.
Does MSG have to be on the label?
While FDA requires that these products be listed on the ingredient panel, the agency does not require the label to also specify that they naturally contain MSG. However, foods with any ingredient that naturally contains MSG cannot claim “No MSG” or “No added MSG” on their packaging. MSG also cannot be listed as “spices and flavoring.”.
Is MSG safe to eat?
FASEB’s report concluded that MSG is safe. The FASEB report identified some short-term, transient, and generally mild symptoms, such as headache, numbness, flushing, tingling, palpitations, and drowsiness that may occur in some sensitive individuals who consume 3 grams or more of MSG without food.
Why do you add glutamate to food?
Therefore, both home and restaurant cooks add it to dishes to contribute taste and intensify the flavors of the other ingredients.
What Is MSG?
And although glutamates occur naturally in everything from meat and milk to corn and wheat, MSG is strictly a food additive made by fermenting starch, sugar beets, sugar cane, or molasses.
What does MSG taste like?
Glutamates such as MSG taste like umami, or more accurately, are umami (just as sugar is sweet and lemons are sour). Umami is described as "savory," "meaty," or "earthy.". It has come to be recognized as the fifth taste, in addition to sweet, salty, sour, and bitter.
What is MSG used for in food?
The additive can be used in a variety of dishes, from meat to fish to egg, as well as in gravies and soups. MSG helps to balance out the sweet and sour while mellowing the natural bitterness found in certain vegetables. It is also a good way to cut down on the sodium in foods because less salt will need to be added.
What is MSG powder?
Storage. Back to Top. MSG, or monosodium glutamate, is a flavor-enhancing food additive used in Asian cooking, fast foods, and commercially packaged food products. It is a white powder derived from a natural glutamic acid found in seaweed, sugar beets, and certain vegetables.
Can you use MSG and salt together?
Too much MSG will create an undesirable flavor and will not improve the taste of food that is poor in quality. When using both MSG and salt, begin with a smaller amount of salt than called for to see how both seasonings work together in the recipe.
Is MSG in hot dogs?
MSG is included in many commercially packaged food products, such as flavored chips and crackers (especially cheese flavored), canned soups, instant noodles, soup and dip mix, seasoning salt, bouillon cubes, salad dressings, gravy mixes or premade gravies, and cold cuts and hot dogs, including soy-based (i.e., vegetarian) varieties. MSG is also present in many of the menu items at fast-food restaurants, particularly in chicken dishes.
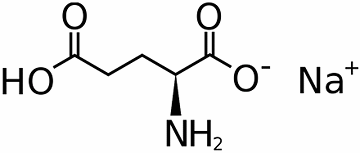
Overview
Monosodium glutamate (MSG), also known as sodium glutamate, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese in this glutamic acid form. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.
Use
Pure MSG is reported to not have a highly pleasant taste until it is combined with a savory aroma. The basic sensory function of MSG is attributed to its ability to enhance savory taste-active compounds when added in the proper concentration. The optimal concentration varies by food; in clear soup, the "pleasure score" rapidly falls with the addition of more than one gram of MSG per 100 mL.
Safety
MSG is generally recognized as safe to eat. A popular belief is that MSG can cause headaches and other feelings of discomfort, but blinded tests have not provided strong evidence of this. International bodies governing food additives currently consider MSG safe for human consumption as a flavor enhancer. Under normal conditions, humans can metabolize relatively large quantities of glutamate, which is naturally produced in the gut in the course of protein hydr…
Production
MSG has been produced by three methods: hydrolysis of vegetable proteins with hydrochloric acid to disrupt peptide bonds (1909–1962); direct chemical synthesis with acrylonitrile (1962–1973), and bacterial fermentation (the current method). Wheat gluten was originally used for hydrolysis because it contains more than 30 g of glutamate and glutamine in 100 g of protein. As demand for MSG increased, chemical synthesis and fermentation were studied. The polyacrylic fiber indu…
Chemical properties
The compound is usually available as the monohydrate, a white, odorless, crystalline powder. The solid contains separate sodium cations Na and glutamate anions in zwitterionic form, OOC-CH(NH 3)-(CH 2)2-COO . In solution it dissociates into glutamate and sodium ions.
MSG is freely soluble in water, but it is not hygroscopic and is insoluble in common organic solvents (such as ether). It is generally stable under food-processing conditions. MSG does not b…
History
Glutamic acid was discovered and identified in 1866 by the German chemist Karl Heinrich Ritthausen, who treated wheat gluten (for which it was named) with sulfuric acid. Kikunae Ikeda of Tokyo Imperial University isolated glutamic acid as a taste substance in 1908 from the seaweed Laminaria japonica (kombu) by aqueous extraction and crystallization, calling its taste umami ("pleasant savory taste"). Ikeda noticed that dashi, the Japanese broth of katsuobushi and kombu, …
Society and culture
MSG is one of several forms of glutamic acid found in foods, in large part because glutamic acid (an amino acid) is pervasive in nature. Glutamic acid and its salts may be present in a variety of other additives, including hydrolyzed vegetable protein, autolyzed yeast, hydrolyzed yeast, yeast extract, soy extracts, and protein isolate, which must be specifically labeled. Since 1998, MSG cannot be included in the term "spices and flavorings". However, the term "natural flavor" is used …
See also
• Acceptable daily intake
• Adenosine monophosphate
• Garum
• Guanosine monophosphate
• Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase