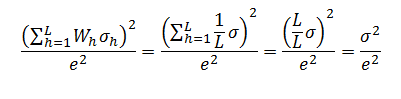
When to use systematic sampling instead of random sampling?
You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population, as in simple random sampling. However, unlike with simple random sampling, you can also use this method when you’re unable to access a list of your population in advance.
Why do you use systematic sampling?
The three main types of quantitative sampling are:
- Random sampling: Random sampling is when all individuals in a population have an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified sampling: Stratified sampling is when the researcher defines the types of individuals in the population based on specific criteria for the study. ...
- Systematic sampling: Systemic sampling is choosing a sample on an orderly basis. ...
What are the 4 types of sampling methods?
The benefit of using probability sampling is that it guarantees the sample that should be the representative of the population. Probability Sampling methods are further classified into different types, such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and clustered sampling.
What sampling method should I use?
Stratified sampling is the best choice among the probability sampling methods when you believe that subgroups will have different mean values for the variable(s) you’re studying. It has several potential advantages:

How do you find K in systematic sampling?
A method of sampling from a list of the population so that the sample is made up of every kth member on the list, after randomly selecting a starting point from 1 to k. Consider choosing a systematic sample of 20 members from a population list numbered from 1 to 836. To find k, divide 836 by 20 to get 41.8.
How is nth number calculated systematic sampling?
To perform systematic sampling, a sample size from a population must be determined. Then the nth value can be calculated. For example, if the population size is 10,000 and the target sample size is 100, then every 10,000/100 = 100 participants should be chosen. 100 is the nth value.
What is an example of systematic random sample?
Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. For example, Lucas can give a survey to every fourth customer that comes in to the movie theater.
How do you do systematic sampling on a calculator?
0:443:39Systematic Sampling TI-84 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhich is the population size or estimate divided by the sample size that you desire. And when youMoreWhich is the population size or estimate divided by the sample size that you desire. And when you calculate this it is not always a whole number right. But you always want to round. Down.
Why is systematic sampling used?
Systematic sampling helps minimize biased samples and poor survey results. If there's a low risk for manipulation of data: If researchers reconfigure a data set, data validity can be jeopardized. When there's little chance of data manipulation, systematic sampling is an ideal method for surveys.
What are the types of systematic sampling?
Types of Systematic SamplingSystematic random sampling: Systematic random sampling is a method used by researchers or statisticians to select samples at an already determined interval. ... Linear systematic sampling: Linear systematic sampling is a method in systematic sampling where you cannot repeat samples at the end.More items...•
Where is systematic sampling used?
Use systematic sampling when there's low risk of data manipulation. Systematic sampling is the preferred method over simple random sampling when a study maintains a low risk of data manipulation.
What is systematic sampling PDF?
Systematic sampling is a sampling technique that is used for its simplicity and convenience. At its simplest, a systematic sample is obtained by selecting a random start near the beginning of the population list and then taking every unit equally spaced thereafter.
Is systematic sampling simple random?
Simple random sampling requires that each element of the population be separately identified and selected, while systematic sampling relies on a sampling interval rule to select all individuals.
How do you select a systematic random sample?
Steps in selecting a systematic random sample: Calculate the sampling interval (the number of households in the population divided by the number of households needed for the sample) Select a random start between 1 and sampling interval. Repeatedly add sampling interval to select subsequent households.
When should I take a systematic sample of size n?
When taking a systematic random sample of size n, every group of size n from the population has the same chance of being selected.
What is systematic sampling excel?
Researchers often take samples from a population and use the data from the sample to draw conclusions about the population as a whole. One commonly used sampling method is systematic sampling, which is implemented with a simple two step process: 1. Place each member of a population in some order.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling met...
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by...
How do I perform systematic sampling?
There are three key steps in systematic sampling : Define and list your population , ensuring that it is not ordered in a cyclical or periodic or...
What is the difference between random sampling and systematic sampling?
A random sampling procedure requires that each sample is selected one at a time, each having an equal probability of being selected. In a systemati...
How do you do a systematic random sample?
Step 1: Decide on a sample size. Step 2: Divide the total target population by the desired sample size. This is the interval that will be used for...
Why is systematic sampling used?
Systematic sampling is used because it is a very simple and convenient way of forming a sample population that is free from favoritism or bias. The...
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is defined as a probability sampling method where the researcher chooses elements from a target population by selecting a random starting point and selects sample members after a fixed ‘sampling interval. ’
Why is systematic sampling important?
Here are the advantages of systematic sampling. It’s extremely simple and convenient for the researchers to create, conduct, analyze samples. As there’s no need to number each member of a sample, it is better for representing a population in a faster and simpler manner.
How to calculate sampling interval?
Researchers calculate the sampling interval by dividing the entire population size by the desired sample size. Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of probability sampling in which each member of the group is selected at regular periods to form a sample.
What is the sample interval for 5000?
For example, the sample interval should be 10, which is the result of the division of 5000 (N= size of the population) and 500 (n=size of the sample).
What are the samples of K=3?
If we consider k=3, the samples will be – ad, be, ca, db and ec.
Is convenience sampling biased?
In the other methods of probability samplingmethods such as cluster samplingand stratified sampling or non-probability methods such as convenience sampling, there are chances of the clusters created to be highly biased which is avoided in systematic sampling as the members are at a fixed distance from one another.
What Is Systematic Random Sampling?
Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. For example, Lucas can give a survey to every fourth customer that comes in to the movie theater. The fact that Lucas is giving the survey to every fourth customer is what makes the sampling systematic because there is an interval system. Likewise, this is a random sample because Lucas cannot control what type of customer comes through the movie theater.
Why is Lucas a random sample?
Likewise, this is a random sample because Lucas cannot control what type of customer comes through the movie theater. Additionally, remember that systematic random sampling must still ensure that all outcomes are given equal chance of getting selected in the sample.
Which is better, systematic sampling or random sampling?
However, when the population is ordered, the systematic sampling is usually better than simple random sampling and the above formula will overestimate the variance.
What are the 10 numbers that were randomly sampled?
The 10 numbers sampled randomly without replacement from 1 to 50 are: 2, 5, 7, 13, 26, 31, 35, 40, 45, 46 . In the following table, the car that will be sampled is listed with the number of people per car (the response) in parentheses.
How many samples can we do in 9000/1200?
Since, 9000/1200 = 7.5, we can perform a 1-in-7 systematic sample. Or, we should sample every 7th student. We can pick a starting point randomly from 1 to 600 and sample every 7th student from that on until we have reached 1200 samples.
How many primary units are there in a sample?
Here we might take a sample every 4 elements, or 1 in 4 elements from the population. (1, 5, 9) or (2, 6, 10), etc. There are four primary units: (1, 5, 9), (2, 6, 10), (3, 7, 11), (4, 8, 12).
Can you use the naive method to calculate variance?
Unless the population is randomly ordered we can't use the naive method to compute variance. [Look in the textbook page 162 for more advanced ways.] Thus, we need more than one primary unit.
What is systematic sampling?
In statistics, a sampling method is systematic if it involves selecting individuals or items for a sample in such a way that every nth item is selected.
Systematic sampling types (with examples)
Each type of systematic sampling can be used for single or multi-phase surveys.
How to use systematic samples in 7 steps
Select a population and determine its size. For example: If you’re doing a retail store study, the customers make up your target population. To determine the population size, you will need a list of every customer who has ever shopped at the store during the time period relevant to your study.**
Wrapping up
That’s all folks! Hopefully, after reading this article, you’ll be able to determine the most appropriate method for your project, whether it’s about analyzing survey data or collecting customer experience feedback.
How is systematic sampling calculated?
This interval, called the sampling interval, is calculated by dividing the population size by the desired sample size. Despite the sample population being selected in advance, systematic sampling is still thought of as being random if the periodic interval is determined beforehand and the starting point is random.
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which a random sample, with a fixed periodic interval, is selected from a larger population.
What Are the Disadvantages of Systematic Sampling?
The main disadvantage of systematic sampling is that the size of the population is needed. Without knowing the specific number of participants in a population, systematic sampling does not work well. For example, if a statistician would like to examine the age of homeless people in a specific region but cannot accurately obtain how many homeless people there are, then they won't have a population size or a starting point. Another disadvantage is that the population needs to exhibit a natural amount of randomness to it else the risk of choosing similar instances is increased, defeating the purpose of the sample.
What is cluster sampling?
Cluster sampling divides the population into clusters and then takes a simple random sample from each cluster. Cluster sampling is considered less precise than other methods of sampling. However, it may save costs on obtaining a sample. Cluster sampling is a two-step sampling procedure.
Why do statisticians use systematic sampling?
Since simple random sampling of a population can be inefficient and time-consuming, statisticians turn to other methods, such as systematic sampling. Choosing a sample size through a systematic approach can be done quickly. Once a fixed starting point has been identified, a constant interval is selected to facilitate participant selection.
How many people are sampled in a systematic sampling?
As a hypothetical example of systematic sampling, assume that in a population of 10,000 people, a statistician selects every 100th person for sampling. The sampling intervals can also be systematic, such as choosing a new sample to draw from every 12 hours.
Why is cluster sampling important?
Cluster sampling is considered less precise than other methods of sampling. However, it may save costs on obtaining a sample. Cluster sampling is a two-step sampling procedure. It may be used when completing a list of the entire population is difficult. For example, it could be difficult to construct the entire population of the customers of a grocery store to interview.
When should you use systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is an effective sampling method to use under any or all of the following circumstances:
How can systematic sampling be used to manipulate data?
Researchers could potentially manipulate data in a number of ways, such as by setting their own starting points or selecting an inaccurate sample size. If any such manipulations occur, the results would invite scrutiny and not be representative of the population.
How to achieve a random sample population?
As mentioned, to achieve a random sample population, a patternless organization is ideal. If patterns exist, however, this can introduce biases to the results. For instance, you might want to interview all the residents of an apartment building about their living conditions, and you calculate a sampling interval of 21. However, if there are 20 units per floor, with the first two and last two units corresponding to larger corner apartments, the results leave out insights from those who live in smaller, possibly less desirable units.
Why is it important to have a sample population?
When you're studying a large population or group, it's important to have a sample population that's representative of the whole. An accurate sample population can result in findings that are both more insightful and better applicable to business efforts, such as marketing and sales. Systematic sampling is one way of establishing a random sample population that can produce representative findings. In this article, we explain what systematic sampling is, show you how to create a sample with this method, discuss optimal circumstances for its use, look at some of its advantages and disadvantages and provide examples.
Why is simplicity important in sampling?
Simplicity is a desirable characteristic because it reduces the chances of skewing the data set through complex modification. As a result, systematic sampling can produce accurate and significant results.
When using systematic sampling, do researchers operate under the assumption that the population size is quantifiable?
When using systematic sampling, researchers operate under the assumption that the population size is quantifiable. When definite data about population numbers exist, the size is measurable, but some populations may not meet that criterion. If the total number of the population is indeterminable, researchers must first approximate the population before applying the formula to determine the sampling interval. In that case, the integrity of the results hinges on the accuracy of the approximation.
How many people are in a sneaker survey?
It decides to define its population based on the number of people who subscribe to the company newsletter, which amounts to 23,421 people. The researchers decide on a sample size of 2,300, which is approximately 10% of the population, rounded down to the nearest hundred. That figure divided by 2,300 equals 10.18, which rounds down to 10. The researchers organize the list of subscribers in alphabetical order and randomly generate a starting point of 10. From there, they count off every tenth subscriber.
