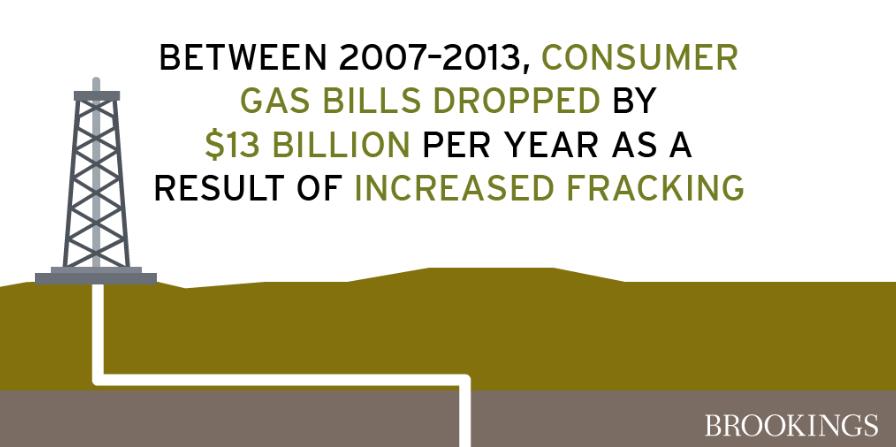
What are the positives and negatives of fracking?
- The Fracking Drill Holes in the procedure takes a huge consumption of energy to produce
- The Fracking Holes are exhausted quickly and more holes need to be frequently done than the standard method of producing Natural Gas.
- In Fracking about 3% of the Natural Gas is lost to the atmosphere
- Fracking has been blamed for inducing earthquakes
What are the pros and cons of 'fracking'?
What Are the Pros of Fracking?
- Fracking has greatly reduced the need for coal in the United States. ...
- Technologies exist to capture potential emissions. Clean coal technologies have helped to pioneer products that can help to capture emissions and particles as they are produced.
- The real fracking process occurs under most groundwater tables. ...
What is fracking and why is it so controversial?
This technique used to recover gas and oil from shale rock has a lot of controversy surrounding it. But it could also give the construction industry a welcome boost. What exactly is Fracking? Fracking is the process of drilling down and creating tiny explosions to shatter and crack hard shale to release gas.
What's so bad about fracking?
Fracking increases the presence of methane gas underground , contaminating drinking water and homes (the photo above, from the excellent film Gasland, shows how water coming out of the faucet in a fracked community contained so much methane, it caught on fire). In some cases, families have experienced explosions in their homes as a result.

What is fracking?
Fracking is the injection of a fluid at high pressure into an underground rock formation to open fissures and allow trapped gas or crude oil to flo...
What are the environmental concerns with fracking?
The environmental concerns with fracking are freshwater contamination through the liberation of contaminated liquids and shale gas into the water t...
How long has fracking technology been used?
The technology of fracking has been in use since the 1940s, when liquids such as gasoline and crude oil were injected into poorly performing gas an...
What is the Process of Fracking?
Once natural gas (also known as ‘shale gas’) has been found, measures can start being taken to set up the fracking process to access the essential fossil fuel, most commonly used for cooking and heating. If the natural gas is not too far below the surface, other extraction methods can be used and may even be preferred.
How Does Fracking Work?
Why is fracking so effective at getting natural gas out of the ground ready for us to use to heat our homes and cook our food? Unlike previous methods of natural gas extraction, fracking allows us to dig down many hundreds of feet into the ground, which means that we can get access to many more natural deposits of shale gas that have previously been beyond our reach. Fracking is very effective, and there are a number of details that explain why it is fast becoming a favored way of extracting natural gas from the ground.
How many fracking wells are there in the US?
According to this, there are more than 500,000 active natural gas wells in the US. Hydraulic fracking produces several barrels of gas a day but at the cost of numerous environmental, health and safety hazards.
How is fracking water stored?
The water that has been used in the process of fracking is then stored in steel tanks to be injected into oil and gas waste wells for a long period of time without harming the environment. Because of the chemicals used added to this water, it cannot simply be returned to the sea or into other waterways.
What is fracking used for?
Fracking is one method that we are currently using in order to gain access to natural gas and oil (petroleum ) buried miles and miles beneath the Earth’s surface. During this process, a huge drill is used to pass through many layers of earth and rock that lie between us as the natural gas. A special water mixture is then pumped directly at ...
What is hydrofracturing in science?
According to Wikipedia, “Hydraulic fracturing, also called fracking, fracing, hydrofracking, fraccing, frac’ing, and hydrofracturing, is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid.
Why is sand pumped through a well?
It is pumped at high pressures so that it can break through the rocks containing the gas, allowing it to escape.
Has test drilling been completed?
In 2011, Cuadrilla suspended test fracking operations near Blackpool after earthquakes of 1.5 and 2.2 magnitude hit the area.
What are the advantages of fracking?
Fracking allows drilling firms to access difficult-to-reach resources of oil and gas.
Why is it controversial?
The extensive use of fracking in the US, where it has revolutionised the energy industry, has prompted environmental concerns.
What about National Parks?
In January 2015, MPs overwhelmingly rejected an outright ban on fracking but did pledge an "outright ban" on fracking in national parks.
How is gas injected into rock?
Water, sand and chemicals are injected into the rock at high pressure which allows the gas to flow out to the head of the well. The process can be carried out vertically or, more commonly, by drilling horizontally to the rock layer, which can create new pathways to release gas or used to extend existing channels.
What is hydraulic fracturing?
Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, is a technique designed to recover gas and oil from shale rock.
Why is shale gas important?
Prime Minister Theresa May told the Yorkshire Post shale gas extraction was important "because of the impact it can have on our future energy security". Her predecessor David Cameron was also a supporter of fracking, saying it could support tens of thousands of UK jobs and reduce bills.
How is shale gas extracted?
Three steps in the extraction of shale gas: drilling a borehole into the shale formation and lining it with pipe casing; fracking, or fracturing, the shale by injecting fluid under pressure; and producing gas that flows up the borehole, frequently accompanied by liquids. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Why are gas producers developing different methods for treating and reusing flowback from fracking operations?
Partly in response to environmental regulations, gas producers are developing various methods for treating and reusing flowback from fracking operations. In the United States the refusal of drilling companies to disclose the formulas of their fracking fluids is a major point of contention.
What is fracturing in petroleum?
Alternative Titles: fraccing, fracing, hydraulic fracturing, hydrofracking. Fracking, also spelled fracing or fraccing, also called hydrofracking, in full hydraulic fracturing, in natural gas and petroleum production, injection of a fluid at high pressure into an underground rock formation in order to open fissures and allow trapped gas ...
What is the surface casing of a borehole?
This portion of the borehole is lined with a cemented steel pipe called the surface casing.
How to find gas shales?
Most gas shales are found in extensive seams hundreds or thousands of metres beneath the surface. These seams can be accessed through conventional vertical drilling, but the most productive method is usually horizontal drilling. In this technique a well is begun in the traditional way, with the auguring of a pilot hole usually some 6 to 15 metres (20 to 50 feet) deep. This is lined with a steel pipe some 40 to 50 cm (16 to 20 inches) in diameter, called the conductor casing, that is cemented into place. From there the borehole is drilled straight down, passing through numerous rock layers that may include contaminable freshwater aquifers used for private wells or municipal water supply. This portion of the borehole is lined with a cemented steel pipe called the surface casing. Depending on production needs or environmental regulations, another pipe, called the intermediate casing, may be cemented inside the surface casing.
What is gas from unconventional deposits?
Gas from unconventional deposits includes coal bed methane (gas located in the joints and fractures of coal seams), “tight gas” (gas locked into relatively impermeable sandstone or limestone formations), and shale gas (gas incorporated into dense microporous shales ).
Is fracking fluid required to be disclosed?
In the United States the refusal of drilling companies to disclose the formulas of their fracking fluids is a major point of contention. Local and state laws could require drillers to disclose their formulas, but at the federal level fracturing fluid is explicitly exempted from regulation under such laws as the Safe Drinking Water Act of 1974. The gas industry maintains that regulation is unnecessary, since the chemical additives in fracturing fluid are safe and are not injected anywhere near aquifers. Environmentalists, on the other hand, question the gas industry’s motives in refusing to divulge their formulas and insist that the industry will never be trusted so long as it refuses to do so.
What Is Fracking?
The technique of fracking involves injecting liquid and other substances at high pressure into tight shale formations to cause small fractures in the rock. The gas that escapes from these cracks is then captured and stored.
Why is fracking so controversial?
Fracking is controversial because of its detrimental environmental and health impacts. The drilling process has been linked to water contamination and air pollution, and the wastewater disposal process has been associated with an increase in earthquakes in regions where it’s done.
What are the effects of fracking on the environment?
The controversial process has been linked to water contamination and the disposal of wastewater from fracking has triggered earthquakes. Air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions and threats to worker health are also causing alarm.
What is the fluid that is used in fracking?
The sand and other solid components in the fracking fluid — also known as proppants — essentially prop up, or keep open, the fractures.
How long has fracking been around?
Forms of fracking have been around since the 1940s, but improvements in technology have made it more feasible for energy companies to retrieve oil and gas that were once inaccessible. Fracking has significantly increased domestic oil and natural gas production.
What happens after fracking?
After the drilling is complete, a fracking fluid that contains a mixture of water, sand and chemicals is blasted into the well under extremely high pressure. This forces the fluid into the cracks and crevices of the shale where natural gas is trapped. Because of the immense internal pressure, the petroleum-rich (or gas rich) fluid flows back up to the surface of the well and collects in a tank.
How deep does a well drill go?
It begins with drilling a well vertically into the earth until it reaches the gas-rich shale layers of rock. At that point — usually at a depth of around 10,000 feet underground — the drill is turned sideways and continues to bore through the shale.
How Does Fracking Work?
It involves blasting fluid deep below the earth’s surface to crack sedimentary rock formations— this includes shale, sandstone, limestone, and carbonite—to unlock natural gas and crude oil reserves.
Why Is Fracking Bad?
While fracking has charged ahead, the research into how safe it is for human health and the environment hasn’t kept pace. Many questions remain about the dangers of the process, with mounting evidence raising serious red flags about the impact on drinking water, air pollution, and our climate.
What is the oil state of North Dakota?
Home to 20 of the country’s 100 largest oil fields, North Dakota sits atop the Bakken Shale and underlying Three Forks formations, themselves located in the larger Williston Basin (which spans portions of South Dakota, Montana, and the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan). The nation’s number two crude oil state (behind Texas) since 2012, North Dakota shattered its own production records in 2018, in large part due to the improved efficiency of its fracking operations. This boom in production has come at a cost, however, particularly to land, air, and water resources. According to a 2016 Duke University study, wastewater spills from fracked oil wells in the Bakken region have caused “widespread and persistent” water and soil contamination with “clear evidence of direct water contamination.” And while North Dakota produces just 2 percent of the nation’s natural gas, its operations still flare a “ substantial ” amount, producing significant air pollution. According to a 2014 study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, drilling and fracking operations in the Bakken oil and gas fields alone contributed as much as 3 percent of global emissions of ethane (a greenhouse gas and precursor for ozone formation).
How does fracking affect oil wells?
Acidizing dissolves portions of the oil‐bearing rock formations through the injection of acid mixed with water and other chemicals, allowing oil to more easily flow to the well bore. In Florida, acidizing is more likely to be used than fracking due to the state’s geology. Aquifers—crucial sources of drinking water—are vulnerable to contamination because large areas are characterized by sandy soils and porous limestone. Since Florida oil fields generally lie deeper than the shallow aquifers that provide the state with fresh drinking water, acidizing techniques threaten groundwater resources. Additionally, wastewater from acidizing techniques can contain hazardous pollutants and pose threats to underground aquifers. Proposals for a statewide legislative ban on fracking and acidizing techniques have been introduced, with bipartisan support, in both houses of the state legislature.
How does fracking affect the environment?
Fracking, like other oil and gas operations, involves intense industrial development. Well pads, access roads, pipelines, and utility corridors are typically accompanied by intense, round-the-clock noise, lights, and truck traffic. In addition to potentially polluting local water and air resources, this vast web of infrastructure can fragment forests and rural landscapes and degrade important wildlife habitat. One study of mule deer in northwestern Colorado, for example, found that natural gas drilling operations had compromised as much as half of the animals’ critical winter habitat. Another study, analyzing the impact of fracking wastewater sprayed on forested land in West Virginia, found that more than half of the trees in the area had died within two years.
What is hydraulic fracturing?
Modern high-volume hydraulic fracturing is a technique used to enable the extraction of natural gas or oil from shale and other forms of “tight” rock (in other words, impermeable rock formations that lock in oil and gas and make fossil fuel production difficult).
What are the effects of natural gas?
When gas is flared, vented, or accidentally leaked, it accelerates the costly health impacts of climate change. Oil and gas operations, such as hydraulic fracturing, also release numerous toxic air contaminants: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene; fine particulate matter (PM2.5); hydrogen sulfide; silica dust; and nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, which produce smog when combined. In rural northeastern Utah, researchers estimated that the amount of smog-forming compounds coming from oil and gas operations each year was equivalent to the emissions of 100 million cars. A broad range of health effects are associated with exposure to these air pollutants, including mild to severe respiratory and neurological problems, cardiovascular damage, endocrine disruption, birth defects, cancer, and premature mortality. Meanwhile, industry workers face even greater risks from on-site exposure to toxic chemicals and other airborne materials, including silica (the main component of frac sand ), which can lead to lung disease and cancer when inhaled.
How does fracking work?
Fracking works by first drilling deep down into the Earth to create an avenue to inject high pressure fluids into shale or other types of rock formations that contain hydrocarbons, which are the key components of fossil fuels . Once the desired hole is drilled, a highly pressurized mixture of water, sand, and chemicals is delivered directly to the rock area to release the oil and gas trapped within. The newly released hydrocarbons then flow towards the surface for collection.
How big of an earthquake does fracking cause?
That said, fracking typically causes only very small earthquakes with less than 1 magnitude, and usually less than 0.5 magnitude.
Why is fracking controversial?
There are numerous reasons why fracking is considered controversial. The process involves using enormous quantities of freshwater, which not only becomes degraded after it’s injected into fractures (due to contamination with sand and chemicals), but it must also be transported to fracking sites with extra environmental costs.
Why is fracking bad?
Natural gas fracking is considered “bad” for the same reasons that it is considered controversial: fears of environmental contamination, increased seismic activity, and unsustainable water use.
What is hydraulic fracturing?
Hydraulic fracturing is a controversial method for extracting fossil fuels — in the form of oil or natural gas — that are embedded within rock formations deep below the Earth’s surface. It involves fracturing bedrock formations to release trapped fossil liquids and gases by using pressurized fluids.
How has fracking impacted the US?
While this has lowered oil prices and given the U.S. more energy independence, there are serious environmental concerns associated with fracking and how it alters the areas in which it operates.
What are the negative effects of fracking?
The most negative effects of fracking are potential contamination of the surrounding environment, excess water usage, and drinking water degradation (especially in water-scarce regions), and increased seismic activity associated with fluid injection.
What is frac sand?
Frac sand is a specialized type of sand that is added to fracking fluids that are injected into unconventional oil and gas wells during hydraulic fracturing. Frac sand keep induced fractures open and extend the time and flow rate of oil and gas from a well. (Credit: John Jackson, USGS)
What is the process of injecting wells with water, sand, and chemicals at very high pressure?
Science or Soundbite? Shale Gas, Hydraulic Fracturing, and Induced Earthquakes. Hydraulic fracturing is the process of injecting wells with water, sand, and chemicals at very high pressure.
How does fracking affect the environment?
The actual practice of fracking is only a small part of the overall process of drilling, completing, and producing an oil and gas well. However, since fracking involves injecting a chemical solution into the ground to free up oil and gas resources, there are some potential environmental impacts related to this process. These include: 1 spills of chemicals at the surface 2 surface-water-quality degradation from waste fluid disposal 3 groundwater quality contamination 4 induced seismicity from the injection of waste fluids into deep disposal wells
What is hydraulic fracturing?
Hydraulic fracturing is the process of injecting wells with water, sand, and chemicals at very high pressure to enable oil and natural gas production. These "unconventional" resources pose both opportunities and challenges.
Why is water important for the United States?
Water quality studied in areas of unconventional oil and gas development, including areas where hydraulic fracturing techniques are used, in the United States. Domestic oil and gas production and clean water are critical for economic growth, public health, and national security of the United States.
What is the USGS newsroom?
The USGS newsroom distributes media alerts, press releases, and technical memos that highlight new and relevant research.
What is the role of the USGS?
Through an agreement among the Department of the Interior, the Department of Energy, and the Environmental Protection Agency, the USGS plays a large role in improving our scientific understanding of the environmental issues related to unconventional oil and gas.
Why Is Hydraulic Fracturing Done?
Fracking is the most effective technique for hydrocarbon recovery in challenging oil and gas fields where unconventional drilling techniques are needed to achieve target production volumes. Formations having crude or gas-saturated rocks with low permeability and poor water-oil connectivity are prime examples.
How to extract natural gas from shale?
To extract natural gas from shale using the hydraulic fracturing process, high-pressure frac fluid is injected into the reservoir which creates fissures in the shale formations. As individual fissures connect, the gas pools together from several sections within the rock. It is then tapped off via the production casing.
What is fracking fluid injection?
Injection: Fracking fluid is injected into the reservoir at very high pressures, which creates fissures in hydrocarbon-bearing rocks and releases the products.
What is fracking fluid?
Fracking fluid may be a mixture of water, fine-grained silica sand, and special chemicals capable of creating fissures in underlying rocks. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 95% of new oil and gas wells in the country are exploited using fracking techniques which accounts for over 60% of the total volume of U.S. marketed natural gas and 50% of total U.S. crude production.
How does fracking improve hydrocarbon mobility?
The chemicals improve hydrocarbon mobility by reducing the interfacial tension between the oil molecules and water present in the reservoir. Fracking is safer and more efficient than chemical injection.
What is the most effective technique for hydrocarbon recovery in challenging oil and gas fields?
Fracking is the most effective technique for hydrocarbon recovery in challenging oil and gas fields where unconventional drilling techniques are needed to achieve target production volumes. Formations having crude or gas-saturated rocks with low permeability and poor water-oil connectivity are prime examples.
What is integrated flow solutions?
Integrated Flow Solutions is leading process skid manufacturer for the oil & gas industry. We offer a wide range of skid-mounted and modular process equipment to support your fracking operations such as LACT skids, truck or railcar loading/unloading equipment, metering systems, oil & gas pipeline pumps, salt water disposal packages, horizontal pump packages, and oil and gas sand separators.