Full Answer
What is the melting point of lauric acid?
The choice of lauric acid is convenient because the melting point of the pure compound is relatively high (43.8°C). Its cryoscopic constant is 3.9°C·kg/mol.
Is lauric acid saturated or unsaturated?
?) Lauric acid or systematically, dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids, is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates .
What is the standard state of lauric acid in KPA?
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). ?) Lauric acid or systematically, dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids, is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap.
What is lauric acid in infobox?
Infobox references. Lauric acid or systematically, dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium chain fatty acids, is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates.
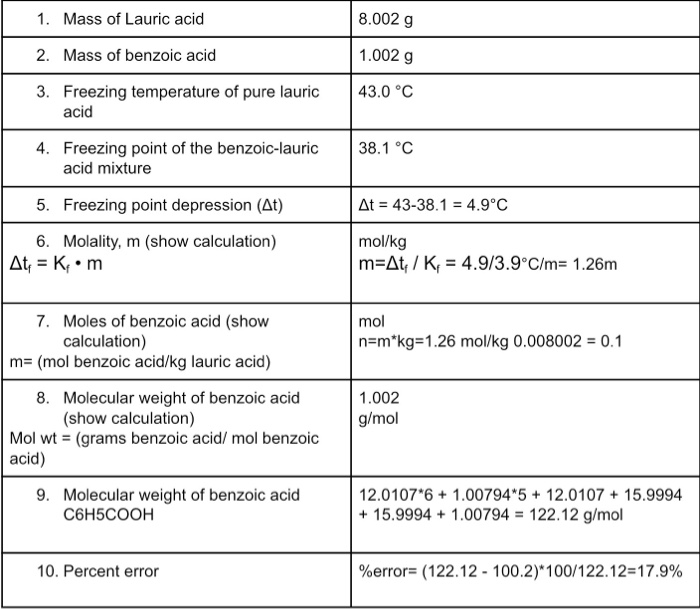
What is the freezing point of lauric acid and benzoic acid?
A mixture containing 3.0 g of Lauric Acid and 0.5 g of Benzoic Acid has a freezing point of 36.6 C. I calculated the freezing point depression as 7.5 C. I calculated the molality of the Benzoic and Lauric Acid as 1.92 mol/kg.
What is the freezing point of benzoic acid?
252.1°F (122.3°C)Benzoic acid / Melting point
How do you calculate the freezing point?
The freezing point depression ∆T = KF·m where KF is the molal freezing point depression constant and m is the molality of the solute. Rearrangement gives: mol solute = (m) x (kg solvent) where kg of solvent is the mass of the solvent (lauric acid) in the mixture. This gives the moles of the solute.
Is lauric acid solid at room temperature?
Lauric acid is a solid at room temperature but melts easily in boiling water, so liquid lauric acid can be treated with various solutes and used to determine their molecular masses.
What is the freezing point of stearic acid?
156.7°F (69.3°C)Stearic acid / Melting point
How do you heat up lauric acid?
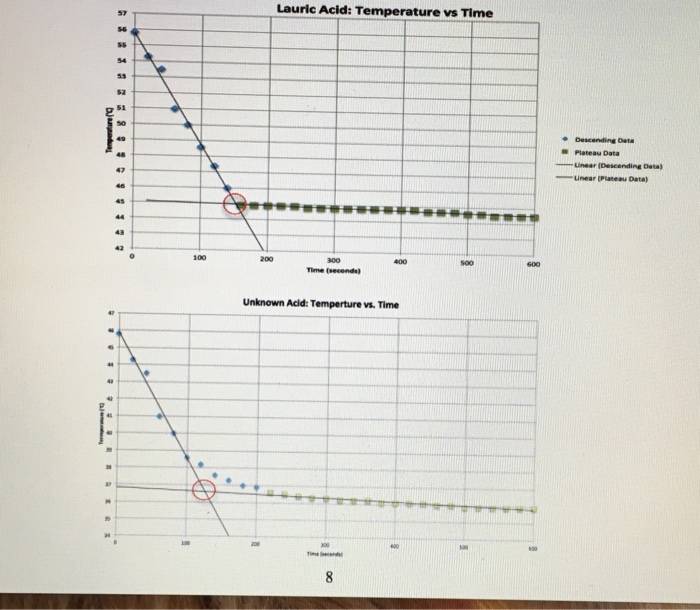
Using a test tube holder, transfer the liquid lauric acid tube to the 30oC water bath and record the temperature at 30-second intervals until the temperature reaches at least 40oC. Gently stir with the thermometer as you take data until the lauric acid starts to solidify.
What is the lowest freezing point?
Helium happens to be the only element that can't be solidified or frozen at normal atmospheric pressure. Only once you apply a pressure of 25 atmospheres at Helium's freezing point of −458 °F can you solidify it.
What is the highest freezing point?
1M glucose solution has the highest freezing point because it has lower ΔTf(ΔTf=Tf∘+ΔTf) since it does not undergo dissociation to increase the number of particles.
How do you find the freezing point and melting point?
0:114:35Boiling Point and Freezing Point Calculations - Mr Pauller - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTemperature. We'll calculate by multiplying kf by the molality multiplied by something called the i.MoreTemperature. We'll calculate by multiplying kf by the molality multiplied by something called the i.
Why is lauric acid polar?
Because lauric acid has a non-polar hydrocarbon tail and a polar carboxylic acid head, it can interact with polar solvents (the most important being water) as well as fats, allowing water to dissolve fats. This accounts for the abilities of shampoos to remove grease from hair.
Is lauric polar or nonpolar?
Lauric acid is a nonpolar molecule. Lauric acid has a carboxylic acid group (COOH) that is polar.
What type of solid is lauric acid?
Lauric acid, systematically dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids, is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates.
What is the melting point range of benzoic acid?
252.1°F (122.3°C)Benzoic acid / Melting point
Is benzoic acid soluble in cold water?
Benzoic acid is nearly insoluble in cold water. It has some solubility in hot water and in boiling water, the solubility of benzoic acid is 56.31 g/L.
Is benzoic acid non polar?
The following details may give you a clear idea about Benzoic acid. The experts say that most of the benzoic acid molecules are nonpolar.
What is the boiling point of benzoic acid?
480.6°F (249.2°C)Benzoic acid / Boiling point
What is the cryoscopic constant of lauric acid?
Its cryoscopic constant is 3.9°C·kg/mol. By melting lauric acid with the unknown substance, allowing it to cool, and recording the temperature at which the mixture freezes, the molar mass of the unknown compound may be determined.
Why is lauric acid used in the laboratory?
Laboratory use. In the laboratory, lauric acid may be used to investigate the molar mass of an unknown substance via the freezing-point depression. The choice of lauric acid is convenient because the melting point of the pure compound is relatively high (43.8°C). Its cryoscopic constant is 3.9°C·kg/mol.
What is the chemical name for dodecanoic acid?
The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates .
How much lauric acid is absorbed through the portal vein?
Although 95% of medium-chain triglycerides are absorbed through the portal vein, only 25–30% of lauric acid is absorbed through it.
Is laurel oil a triglyceride?
Lauric acid, as a component of triglycerides, comprises about half of the fatty-acid content in coconut milk, coconut oil, laurel oil, and palm kernel oil (not to be confused with palm oil ), Otherwise, it is relatively uncommon. It is also found in human breast milk (6.2% of total fat), cow's milk (2.9%), and goat's milk (3.1%).
Does lauric acid affect cholesterol?
Lauric acid increase s total serum cholesterol more than many other fatty acids, but mostly high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (the "good" blood cholesterol). As a result, lauric acid has been characterized as having "a more favorable effect on total HDL cholesterol than any other fatty acid [examined], either saturated or unsaturated". In general, a lower total/HDL serum cholesterol ratio correlates with a decrease in atherosclerotic risk. Nonetheless, an extensive meta-analysis on foods affecting the total LDL /serum cholesterol ratio found in 2003 that the net effects of lauric acid on coronary artery disease outcomes remained uncertain. A 2016 review of coconut oil (which is nearly half lauric acid) was similarly inconclusive about the effects on cardiovascular disease risk.
What is lauric acid?
Lauric acid is a major component of coconut oil and palm kernel oil. It is used as an intermediate and surface active agent in industry and in the manufacture of personal care products in the consumer market.
How long does it take to ship lupic acid?
Lauric Acid is available for shipping throughout the continental United States with one (1) week lead time. Please call (401) 360-2800 for details.
What is the name of the fatty acid that is found in coconut oil?
Lauric Acid. Lauric acid, C 12 H 24 O 2, also known as dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain. The powdery, white crystalline acid has a slight odor of oil of bay and occurs naturally in various plant and animal fats and oils. Lauric acid is a major component of coconut oil and palm kernel oil.
Is lauric acid a sulfate?
It is non-toxic, safe to handle, inexpensive, and has a long shelf life. It is mainly used in the manufacture and production of soaps and other cosmetics as well as scientific laboratory uses.
Does lauric acid increase cholesterol?
The consumer market uses lauric acid in the cleaning, furnishing, and production of personal care products. In medicine, lauric acid is known to increase total serum cholesterol more than many of the other fatty acids.