What muscles are in your lower arm?
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm are organised into three layers:
- Superficial: flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, pronator teres.
- Intermediate: flexor digitorum superficialis.
- Deep: flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus and pronator quadratus.
What bones are in the upper arm?
The large bones of the arm include:
- Humerus: This bone runs down from the shoulder socket and joins the radius and ulna at the elbow.
- Radius: A forearm bone, it runs from the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist.
- Ulna: This forearm bone runs from the elbow to the “pinkie” side of the wrist.
What are the names of the muscles in your arm?
Which muscles are involved in flexing your arm quizlet?
- Biceps brachii. Flexes and supinates forearm.
- Brachialis. Flexes elbow.
- Deltoid. Flexes, medially rotates, and abducts arm.
- Infraspinatus.
- Supraspinatus.
- Teres minor.
- Teres major.
- Triceps brachii.
What muscles are present in the arm?
Arm muscles. The (upper) arm muscles are a group of five muscles located in the region between the shoulder and elbow joints. They are divided into two distinct compartments of the arm. The anterior (flexor) compartment contains the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles. The posterior (extensor) compartment contains mainly the ...

What is the upper arm?
Each of your arms is composed of your upper arm and forearm. Your upper arm extends from your shoulder to your elbow. Your forearm runs from your elbow to your wrist. Before learning about the different muscles, it’s important to understand the four major types of movement they’re involved in: Flexion.
Which muscle is located in the forearm?
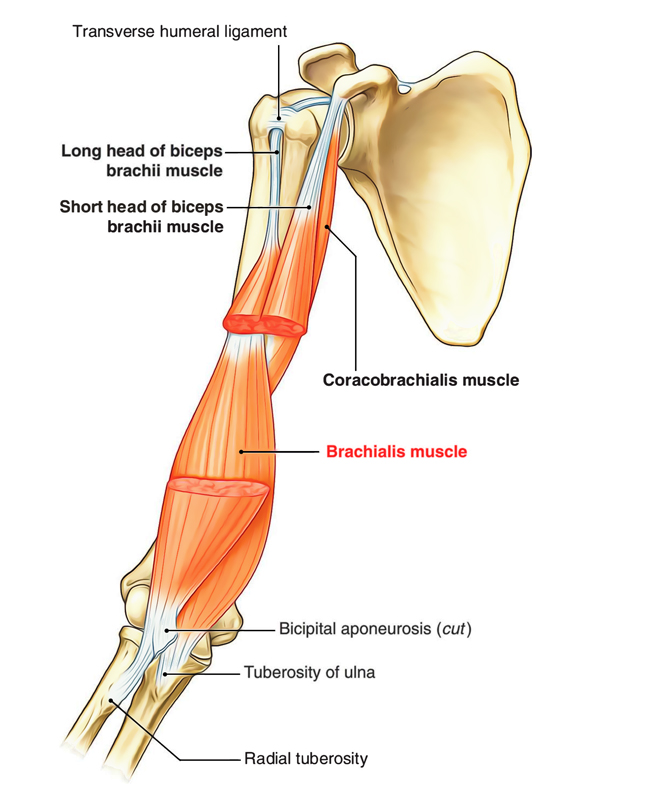
Brachialis. This muscle lies underneath your biceps. It acts as a bridge between your humerus and ulna, one of the main bones of your forearm. It’s involved with the flexing of your forearm. Coracobrachialis. This muscle is located near your shoulder. It allows adduction of your upper arm and flexion of your shoulder.
What muscle is located behind the humerus?
The posterior compartment is located behind your humerus and consists of two muscles: Triceps brachii. This muscle, usually referred to as your triceps, runs along your humerus and allows for the flexion and extension of your forearm. It also helps to stabilize your shoulder joint. Anconeus.
Which muscle flexes and adducts your wrist?
Flexor carpi ulnaris. This muscle flexes and adducts your wrist.
What causes pain in the upper arm?
Shoulder injuries. Several of the muscles in your upper arm are connected to your shoulder. That means pain from a shoulder injury, such as a torn rotator cuff, often radiates down your arm.
How to keep your arm muscles healthy?
Follow the tips below to help keep your arm muscles healthy and avoid injury: Exercise. Try to get at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week. To avoid injuries, make sure you begin by gently stretching. To build more muscle, gradually increase the frequency and intensity of your exercise.
What are the compartments of the upper arm?
Your upper arm contains two compartments, known as the anterior compartment and the posterior compartment.
Overview
You have more than twenty muscles in your upper arm and your forearm (the area between your elbow and your wrist). Your arm muscles help you with small, precise (fine motor) movements, such as wiggling your fingers or fastening a button.
Function
The muscles in your upper arm and forearm allow you to move your arms, hands, fingers and thumbs. Different muscles help with precise movements, such as threading a needle, as well as big movements like throwing a ball.
Anatomy
You have many muscles in your forearm (between your elbow and your wrist). Some of these muscles are in the top and some are on the underside of your forearm. Your forearm muscle anatomy includes:
Care
To avoid problems with your arm muscles, you should take time to stretch and warm up before using them. Warm muscles are less likely to stretch too far or tear. When exercising, increase the intensity gradually. Avoid lifting anything too heavy, and stop if you feel pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
See your healthcare provider if you have any sudden changes in how your arm looks, or have muscle pain or weakness that doesn’t get better in a few days. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have muscle pain and:
Where do the muscles of the upper arm originate?
The five muscles of the upper arm originate from the front portion of the shoulder blade, called the scapula, or from the upper position of the humerus, the long bone that makes up the upper arm. Muscles of the upper arm that have more than one head, or muscle segment, have a portion that originates from each location.
What muscles are in the anterior lower arm?
The pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and palmaris longus all originate from a specific portion of the lower end of the humerus called the medial epicondyle.
What muscles are in the back of the arm?
Like the muscles of the front of the arm, the superficial muscles of the back of the arm are long and span the length of the forearm. The extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, and extensor digiti minimi all start from a specific portion of the lower end of the humerus called the lateral epicondyle. The extensor carpi radialis longus and brachioradialis originate from the area directly above the lateral epicondyle called the supracondylar ridge. 1
How many heads does the triceps brachii have?
The biceps brachii in the front of the arm has two heads, while the triceps brachii in the back of the arm has three heads. While each head originates at different locations, all heads of the same muscle group conjoin and attach to the same spot. 1. The biceps brachii attaches to the top of the radius, the forearm bone on the thumb side of the arm, ...
What are the four tendons that attach to the phalange bones of the index, middle, ring, and?
While the flexor digitorum superficialis starts as one muscle, it separates into four separate tendons that attach to the phalange bones of the index, middle, ring, and pinky fingers . 1. The deep muscles of the front of the arm underlie the superficial muscles.
Which muscles control the movement of the elbow?
The muscles of the upper arm, the area between the shoulder and elbow, primarily control movement of the elbow. The biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, and brachialis all control flexion at the elbow joint, or bending of the elbow. The brachioradialis of the lower arm also contributes to elbow flexibility. The triceps brachii, along with a small contribution from the anconeus, controls the opposite motion of extension of the elbow. The biceps brachii and triceps brachialis contribute to flexion and extension of the shoulder. 1
Where does the supinator attach to?
The supinator attaches to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus like most of the superficial muscles of the back of the forearm, while the abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and extensor indicis originate at varying points along the ulna, radius, and the connective tissue that joins the radius and ulna together in the forearm. 1
Which muscle is used to anchor and flex the forearm?
It helps anchor and flex the forearm. Coracobrachialis: This muscle is on the upper anterior part of the arm near the shoulder. It starts in the scapula and extends to the shaft of the humerus. The coracobrachialis allows flexion at the shoulder joint and adduction in the upper arm. It also helps stabilize the humerus.
Where are the anterior muscles located?
There are also terms for the location of a muscle within the body. Anterior muscles are toward the front of the body. Posterior muscles are toward the back of the body. Lateral muscles are toward the side of the body or away from the midline of a given area.
Where does the Flexor Pollicis longus start?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist. Flexor pollicis longus: This muscle helps flex the thumb. It starts on the front of the radius and attaches to the base of the thumb.
What is the anatomy of the arm?
Anatomy of the arm. Upper arm muscles. Forearm muscles. Arm conditions. Symptoms. Arm muscle health. Summary. The arm extends from the shoulder to the wrist, including the upper arm and forearm. Different muscles may work together in intricate ways to help the arm, wrists, fingers, and hands function.
Why do the muscles in my arm stop working?
This complex system works together to help the arm carry out the most basic actions. Several issues, such as injury or overuse, may cause the muscles to stop working properly.
How to keep your arm strong?
General tips for muscle health can include: warming up slowly with gentle stretches. regularly exercising the muscles to keep them strong. eating a balanced diet, which provides the muscles with the nutrients they need to rebuild and stay strong.
What is the term for when two muscles move closer together?
Flexion: This occurs when two muscles move closer together, such as when moving the hand up toward the shoulder. Extension: This occurs when increasing the space between two body parts, such as when moving the hand down to straighten the elbow.
What are the muscles in the upper arm?
They are divided into two distinct compartments of the arm. The anterior (flexor) compartment contains the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles . The posterior (extensor) compartment contains mainly the triceps brachii muscle. Even though the anconeus muscle is not anatomically located in the arm region, it is often considered to be a part of this muscle group. This is mainly due to the fact that its function is closely related to the triceps bra chii muscle.
Which muscle group extends the forearm?
Muscles. Biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis, triceps brachii and anconeus. Innervation. Flexors: nervus musculocutaneus, nervus radialis (musculus brachialis only) Extensors: nervus radialis.
What nerve is the triceps brachii innervated by?
Triceps brachii is innervated by the radial nerve (C6-C8) and receives its blood supply from the deep brachial and superior ulnar collateral arteries. Triceps brachii is the prime extensor of the forearm at the elbow joint. Additionally, due to its attachment on the scapula, it can also act as a weak extensor and adductor of the arm at the shoulder joint.
What muscle is located at the posterior side of the elbow?
Anconeus. Anconeus is a small muscle located at the posterior aspect of the elbow. It stretches between the lateral epicondyle of humerus and the lateral surface of the olecranon of ulna. It assists the triceps brachii in elbow extension and stabilizes the elbow joint.
Where is the biceps brachii located?
Biceps brachii is one of the three muscles found in the anterior compartment of the arm. It gets its name from its two heads, each of which has a separate origin. The long head originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of scapula, while the short head shares its origin with the coracobrachialis muscle at the coracoid process of scapula.
What nerve innervates the flexors?
The muscles in the flexor compartment are mainly innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, while the extensors are innervated by the radial nerve. This article will introduce you to the anatomy and function of the arm muscles. Key facts about the arm muscles. Definition and function.
Which muscle group is located in the posterior compartment?
The posterior (extensor) compartment contains mainly the triceps brachii muscle. Even though the anconeus muscle is not anatomically located in the arm region, it is often considered to be a part of this muscle group. This is mainly due to the fact that its function is closely related to the triceps brachii muscle.
What is the muscle that moves the arm?
Biceps: The biceps or biceps brachii is the main muscle of the arm. It originates from the shoulder blade and is attached to the forearm bone (called the radius). Thus, it can cause movements at the shoulder and elbow joints. The term bicep comes from the fact that this muscle has two heads at the origin, the short and the long heads. The two heads fuse to form a single muscle. The long head of the biceps is prone to rupture because of injuries. The rupture produces a characteristic bulge in the arm called the “Popeye sign.” The functions of this muscle include flexion of the arm and supination of the lower arm or forearm. Supination is the movement of the forearm that makes the palm and forearm face upward.
What is the anterior compartment of the arm?
The muscles in front of the arm (the anterior compartment): These muscles are mainly involved in the flexion of the arm at the elbow and shoulder joints, which helps in raising the arm. These muscles are supplied by a nerve called the musculocutaneous nerve. Their blood supply is through the muscular branches of the artery called the brachial artery. The muscles in the anterior compartment of the arm are:
What is the arm?
The arm is the part of the upper extremity between the shoulder joint and the elbow joint.
Why does the biceps rupture?
The long head of the biceps is prone to rupture because of injuries. The rupture produces a characteristic bulge in the arm called the “Popeye sign.”. The functions of this muscle include flexion of the arm and supination of the lower arm or forearm.
What muscle is used to lift the forearm?
As the biceps muscle contracts, it can do one of two things (or both together): Aid the brachialis in the flexions (lifting) of the forearm. Aid the supinator muscle (which starts at the outer elbow and ends at the inner wrist) in rotating the forearm upward.
Which muscles are involved in the supination of the forearm?
Although the supination of the forearm involves the biceps, pronation (in which the palm is turned downward) is facilitated by the brachialis and corresponding pronator muscles.
What is bicep tenodesis?
Biceps tenodesis is used to treat chronic or severe shoulder pain caused by a biceps tendon injury. 7 The procedure, performed under general anesthesia, will either directly repair the tendon or use hardware to secure the compromised tissue.
Why are my biceps so vulnerable?
Because the biceps are involved in such vital tasks as lifting and gesturing, the tendons and tissues that make up the muscle are vulnerable to harm. Most occur as a result of physical trauma or repetitive activity .
What causes biceps to tear?
Among some of the more common conditions affecting the biceps: Biceps strains occur when the muscle is overstretched or "pulled," causing some of the muscle fibers or tendons to tear. Sudden pain and swelling are common. 1 .
Which nerve is responsible for the biceps?
Nerve Supply. The movements of the biceps are facilitated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which runs from the cervical (neck) spine and ends just above the elbow. The brachialis and coracobrachialis muscles are also serviced by the nerve.
What is the function of the biceps?
Also known by the Latin name biceps brachii (meaning "two-headed muscle of the arm"), the muscle's primary function is to flex the elbow and rotate the forearm. The heads of the muscle arise from the scapula (shoulder blade) and combine in the middle arm to form a muscle mass. The other end attaches to the radius, ...
Which muscle is located at the upper and medial part of the arm?
(The other two muscles that attach here are the pectoralis minor and the short head of the biceps brachii.) It is situated at the upper and medial part of the arm. It is supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve. The coracobrachialis draws the humerus forward ( shoulder flexion) and towards the torso (shoulder adduction) at the shoulder ( glenohumeral) joint.
Which muscle pulls the arm in towards the body?
Pectoralis major. A chest muscle that pulls the arm in towards the body. This is one of the internal rotator muscles that attach the humerus and internally rotate the arm. The pectoralis major originates along the clavicle, down the sternum, and across the ribs and inserts into the humerus.
What muscle is the teres major?
Teres major muscle. is a muscle of the arm and one of six scapulohumeral muscles. It is not part of the rotator cuff. The teres major is a medial rotator and adductor of the humerus and assists the latissimus dorsi in drawing the previously raised humerus down and backward (extension, but not hyper extension).
What is the muscle that flexes and rotates the thigh?
A muscle of the medial thigh that originates on the pubis. It inserts onto the linea aspera of the femur. It adducts, flexes, and rotates the thigh medially. It is controlled by the obturator nerve. It pulls the leg toward the body’s midline (i.e. adduction)
Which muscle connects the humerus to the radius at the styloid process?
A muscle lying on the lateral side of the forearm. This muscle connects the humerus to the radius at the styloid process. It flexes the forearm. Also depending on the position of your hand, it can rotate the forearm in either direction.
What is the antagonist of a muscle?
Usually as one muscle contracts (or shortens), the opposing muscle (known as the antagonist) elongates and vice versa. For example, think about when you bend your arm to bring food to your mouth. Multiple muscles on the front of your arm shorten ( biceps, brachialis, etc.) to allow for this to happen. Conversely, as you do this, the antagonist ...
What is the axis of motion?
Motion about these planes can be described by an axis of movement. For instance, movement about the sagittal axis occurs in the sagittal plane e.g. bending forwards at the waist (known as flexion) and backwards (known as extension ). Accordingly, movement about the transverse axis occurs in the transverse plane e.g. twisting at the waist (known as rotation ). Finally, movement about the coronal axis occurs in the coronal plane e.g. bending your body to the left or right.
What muscle is on the back of the arm?
And finally, we get to the triceps brachii. This is the large muscle on the back side of your upper arm. You can feel it when flexing your arm, or when gripping the muscle like pliers. There is only one point in your triceps that can cause muscle pain in the upper arm.
What muscles are used to massage the upper arm?
Muscles: Subclavius, Sternalis. Begin by massaging the area just below your collarbone. Your subclavius muscle, which is very often the cause of muscle pain in the upper arm, is located here. This area is best massaged using the Finger technique or the Trigger Fairy.
How to feel your arm when it's too tight?
From this point, move upwards about 4-5 cm. 5. Loosen your muscles again, move your thumb 1-2 centimetres upwards and inwards and press on the muscle there. Now you are in the area that can cause upper arm pain when too tight.
How to help upper arm pain when too tight?
Examine the area where your thumb is positioned and massage each painful point with a maximum of 15 slow massage strokes. Do this by briefly adding pressure on the area immediately next to the point in the muscle, ...
How to stop upper arm muscle pain?
Most of the time, daily massages (multiple times per day) help alleviate muscle pain in the upper arm within a few days or weeks, and can even eliminate it. Afterwards, they help maintaining tension at a normal level, and prevent pain from flaring up again. These are of course primarily my experiences.
What muscle is felt when lifting your arm?
By lifting your arm, you will be able to feel the anterior part of the deltoid muscle.
Where to massage biceps brachii?
Begin by massaging the biceps brachii, the large muscle on the front of your upper arm.

Anatomical Structure and Location
Function
- The muscles of the upper arm, the area between the shoulder and elbow, primarily control movement of the elbow. The biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, and brachialis all control flexion at the elbow joint, or bending of the elbow. The brachioradialis of the lower arm also contributes to elbow flexion. The triceps brachii, along with a small contribu...
Associated Conditions
- Neuromuscular Disorders
Neuromuscular disorders are conditions that affect the nerves that send electrical signals to muscles to control movement. Symptoms of these disorders include muscle weakness, muscle wasting, called atrophy, muscle twitching, cramps, or spasms, muscle pain, numbness and tingli… - Injury
Trauma or injury to the arms can cause various issues, including pain, weakness, and difficulty with everyday and work-related tasks. Common injuries that affect the muscles of the arms include:1 1. Carpal tunnel syndrome 2. Tennis elbow 3. Golfer’s elbow 4. Muscle tears or strains …
Tests
- Different tests are used to confirm a diagnosis of an injury or disorder of the muscles of the arm, including:2 1. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):An MRI is a scan that provides a clear image of soft tissue structures, including muscles and tendons, to check for a muscle tear or tendinitis, which is inflammation of a muscle’s tendon. 2. Electromyography (EMG):EMG testing can be use…
A Word from Verywell
- There are 24 different muscles that make up the upper and lower arms. Problems can result from injury, repetitive use, or neuromuscular disorders that cause weakness of the elbow, forearm, wrist, or finger muscles. This weakness can interfere with your ability to perform daily tasks. Allowing injured or overused muscles to rest can help ease the pain and discomfort. Seeing a ph…