What is CSF and its function?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. While the primary function of CSF is to cushion the brain within the skull and serve as a shock absorber for the central nervous system, CSF also circulates nutrients and chemicals filtered from the blood and removes waste products from the brain.
What does CSF stand for in project management?
Critical success factor (CSF) is a management term for an element that is necessary for an organization or project to achieve its mission. To achieve their goals they need to be aware about each key success factor (KSF) and the variations between the keys and the different roles key result area (KRA).
What is a CSF used to test for?
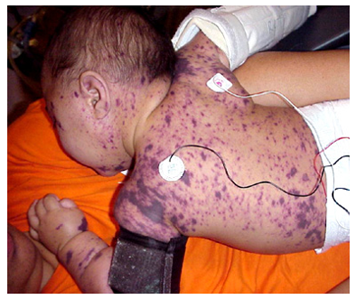
What Can CSF Analysis Identify?
- Infections affecting the brain and spinal cord. Some types of infections will influence the central nervous system. ...
- Autoimmune disorders. To figure out if an autoimmune disorder is present, the CSF analysis will look for high levels of certain proteins in the fluid.
- Bleeding in the brain. ...
- Brain tumors and. ...
What does CSF consist of?
what does CSF consist of? Cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. You may ask, Which diagnostic test evaluates cerebrospinal fluid?

What are the 5 functions of CSF?
CSF performs vital functions including: Support; Shock absorber; Homeostasis; Nutrition; Immune function. Adult CSF volume is estimated to be 150 ml with a distribution of 125 ml within the subarachnoid spaces and 25 ml within the ventricles.
What is the meaning of CSF in medical?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless, watery fluid that flows in and around your brain and spinal cord. Your brain and spinal cord make up your central nervous system. It controls and coordinates everything you do, including your ability to move, breathe, see think, and more.
What causes CSF?
According to the traditional understanding of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) physiology, the majority of CSF is produced by the choroid plexus, circulates through the ventricles, the cisterns, and the subarachnoid space to be absorbed into the blood by the arachnoid villi.
What are the 4 main functions of CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid has three main functions: Protect brain and spinal cord from trauma. Supply nutrients to nervous system tissue. Remove waste products from cerebral metabolism.
What is CSF blood test?
Definition. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a group of laboratory tests that measure chemicals in the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF is a clear fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord. The tests may look for proteins, sugar (glucose), and other substances.
What is normal CSF cell count?
Cell Count Normal CSF may contain up to 5 WBCs per mm3 in adults and 20 WBCs per mm3 in newborns. Eighty-seven percent of patients with bacterial meningitis will have a WBC count higher than 1,000 per mm,3 while 99 percent will have more than 100 per mm3.
Can a CSF leak cause death?
CSF leaks most commonly occur from trauma or surgery; however, they can also occur spontaneously without an identifiable cause. Untreated CSF leaks can represent a potentially life threatening situation leading to meningitis, brain infection, stroke and death.
What is CSF leak symptoms?
The most common symptom of a spinal CSF leak is a headache, while a cranial CSF leak causes symptoms such as clear fluid leaking from the nose or ear. Some CSF leaks may heal with conservative treatments such as bed rest. Many CSF leaks need a blood patch to cover the hole or surgery to repair the leak.
Where is CSF found in the brain?
The CSF flows over the surface of the brain and down the length of the spinal cord while in the subarachnoid space. It leaves the subarachnoid space through arachnoid villi found along the superior sagittal venous sinus, intracranial venous sinuses, and around the roots of spinal nerves.
How do you check for CSF leak?
CT myelography. This test is considered the gold standard for diagnosing and locating CSF leaks. It uses a CT scan and a contrast dye to locate CSF leaks anywhere in the skull base. It provides the most precise location of a CSF leak and helps to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Where does CSF drain?
CSF drains into the lymphatic circulation, through lymph ducts contiguous to the olfactory duct as it passes through the cribriform plate.
How does CSF flow in the brain?
CSF flows from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle via the foramen of Monro. From here, it flows across the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius to the fourth ventricle and onto the subarachnoid space through the apertures of Magendie and Luschka [3].
Is a CSF leak serious?
A CSF leak is a very serious condition, and patients who have tears in their dura with persistent CSF leaks need repair as soon as possible to reduce headache pain and the chance of meningitis.
What is CSF leak symptoms?
The most common symptom of a spinal CSF leak is a headache, while a cranial CSF leak causes symptoms such as clear fluid leaking from the nose or ear. Some CSF leaks may heal with conservative treatments such as bed rest. Many CSF leaks need a blood patch to cover the hole or surgery to repair the leak.
Is CSF test painful?
The provider will numb the skin by injecting a local anesthetic. This injection may sting for a few seconds, but makes the lumbar puncture less painful. The hollow needle will be inserted through the numbed skin and into the space where the CSF is located. You will feel some pressure while the needle is inserted.
How do you check for CSF leak?
CT myelography. This test is considered the gold standard for diagnosing and locating CSF leaks. It uses a CT scan and a contrast dye to locate CSF leaks anywhere in the skull base. It provides the most precise location of a CSF leak and helps to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
What happens if a CSF leak is not treated?
If a cerebrospinal fluid leak is not treated, a person can have chronic headaches, cognitive changes, hearing changes and vision changes. In a wors...
What does cerebrospinal fluid consist of?
The electrolytes found in cerebrospinal fluid are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca++), magnesium (Mg+), and chloride (Cl-). These are need...
What is CSF and its function?
The cerebrospinal fluid filters waste, carries nutrients, and provides cushioning to the brain and spine. These functions are critical for the norm...
What does CSF mean?
CSF means cerebrospinal fluid. It is a clear, colorless fluid that is found only in the subarachnoid spaces that surrounds the brain and spine, and...
Where is CSF absorbed?
Reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the bloodstream happens in structures located in the outer layer of the meninges. These structures are cal...
What is the CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid, the full name for CSF, is a sterile, clear, colorless fluid from filtrate of the blood containing ions: sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chlorine (Cl-), and calcium (Ca++); protein; glucose; and other nutrients. It cushions, protects, nourishes, and detoxifies the brain.
What is CSF in the brain?
That's what the inside of your skull is like. But what's this fluid inside your skull? Cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, is clear, colorless, and filtered from the blood by cells in the ventricles (fluid spaces).
What happens when CSF pressure rises?
When CSF pressure rises, the brain is compressed and the fluid must be removed. Often a device called a shunt is placed for this purpose. A number of diseases can be diagnosed by analysis of CSF, obtained by a lumbar puncture or spinal tap.
What is hydrocephalus in CSF?
Hydrocephalus is an abnormality of CSF volume. When absorption sites are blocked, absorption is slowed but production remains constant. This is communicating hydrocephalus and can occur when proteins or cells have caused a blockage (head trauma, bleeding in the brain, infection, or inflammation).
How is CSF pressure measured?
CSF pressure is measured by lumbar puncture (LP) or spinal tap. The skin is anesthetized and a thin needle is introduced below the end of the spinal cord, allowing removal of CSF without damaging the spinal cord. Elevated pressure usually indicates swelling, infection, or mass (tumor or clot).
What is the normal CSF protein?
Normal CSF glucose is usually 2/3 of blood glucose. Normal CSF protein is 15-60 mg/100 ml and contains no red blood cells (RBC) or clotting factors and only 0-3 white blood cells (or WBC). CSF is in a closed system, so pressure is an important component of analysis.
Where does CSF come from?
Cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, is clear, colorless, and filtered from the blood by cells in the ventricles (fluid spaces). The body produces 500 ml/day, but reabsorption is slower, so only 100-150 ml is found circulating around the brain and spine. CSF flows from the ventricles to the subarachnoid space, which is a space between ...
Definition of CSF
CSF is a clear body fluid found within the tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord of vertebrates.
Important Points to Remember About CSF Full Form
CSF is a clear body fluid found within the tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord of vertebrates. It protects the brain and spinal cord from injuries.
What is the CSF test for?
CSF tests for infections look at white blood cells, bacteria, and other substances in the cerebrospinal fluid. Autoimmune disorders, such as Guillain-Barré Syndrome and multiple sclerosis (MS). CSF tests for these disorders look for high levels of certain proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. These tests are called albumin protein and igG/albumin.
What happens during a CSF analysis?
Your cerebrospinal fluid will be collected through a procedure called a spinal tap, also known as a lumbar puncture. A spinal tap is usually done in a hospital. During the procedure:
What is a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid found in your brain and spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord make up your central nervous system. Your central nervous system controls and coordinates everything you do including, muscle movement, organ function, and even complex thinking and planning. CSF helps protect this system by acting like a cushion against sudden impact or injury to the brain or spinal cord. CSF also removes waste products from the brain and helps your central nervous system work properly.
Why do I need a CSF analysis?
You may need a CSF analysis if you have symptoms of an infection of the brain or spinal cord, or of an autoimmune disorder, such as multiple sclerosis (MS).
How long does it take for a cerebrospinal fluid to be withdrawn?
Your provider will withdraw a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid for testing. This will take about five minutes. You'll need to stay very still while the fluid is being withdrawn. Your provider may ask you to lie on your back for an hour or two after the procedure.
Acronyms & Abbreviations
Get instant explanation for any acronym or abbreviation that hits you anywhere on the web!
A Member Of The STANDS4 Network
Get instant explanation for any acronym or abbreviation that hits you anywhere on the web!
How is CSF propelled?
CSF is propelled along the neuroaxis from the site of secretion to the site of absorption, mainly by the rhythmic systolic pulse wave within the choroidal arteries.
How does CSF help the brain?
CSF assists the brain by providing protection, nourishment, and waste removal. CSF provides hydromechanical protection of the neuroaxis through two mechanisms. First, CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushioning the brain against the skull. Second, CSF allows the brain and spinal cord to become buoyant, reducing the effective weight of the brain from its normal 1,500 grams to a much lesser 50 grams. The reduction in weight lessens the force applied to the brain parenchyma and cerebral vessels during mechanical injury. Another function of CSF is to maintain homeostasis of the interstitial fluid of the brain. A stable environment for brain parenchyma is imperative for maintaining normal neuronal function.
What is CSF 2021?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is an ultrafiltrate of plasma contained within the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid spaces of the cranium and spine .[1] . It performs vital functions, including providing nourishment, waste removal, and protection to the brain.[2] .
What is the CSF turnover?
The reduction of CSF turnover may contribute to the accumulation of metabolites seen in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. The composition of CSF is strictly regulated, and any variation can be useful for diagnostic purposes.[1] Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is an ultrafiltrate of plasma contained within the ventricles of the brain and ...
What causes CSF to accumulate in the brain?
Hydrocephalus is a pathological condition in which CSF abnormally accumulates due to increased CSF production, blockage of flow, or decreased absorption. The ventricles distend to accommodate elevated CSF volumes, potentially causing damage to the brain by pressing its tissue against the boney skull. Hydrocephalus may be congenital or acquired. Blocked CSF flow throughout the ventricles is classified as non-communicating, or obstructive, hydrocephalus. The blockage is often a mass such as a tumor or an abscess located within a foramen. Because CSF secretion is constant, obstruction of flow will lead to CSF build up in front of the blockage. For example, stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct, one of the most common causes of obstructive hydrocephalus , leads to enlargement of both lateral ventricles as well as the third ventricle. If the flow of CSF becomes obstructed outside the ventricles, in either the subarachnoid space or site of absorption, it classifies as communicating, or non-obstructive, hydrocephalus.
What percent of CSF is produced by a network of modified ependymal cells?
The composition of CSF is strictly regulated, and any variation can be useful for diagnostic purposes. [1] Cellular. Seventy to eighty percent of CSF production is via a network of modified ependymal cells known as the choroid plexus (CP).[1] .
What is the effect of CSF turnover on aging?
The reduction of CSF turnover may contribute to the accumulation of metabolites seen in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. The composition of CSF is strictly regulated, and any variation can be useful for diagnostic purposes.[1] NCBI.
Why is CSF analysis important?
Hence analysis of CSF by various methods will help in diagnosis as well as prognostication and response to therapy . CSF analysis is particularly useful in various acute neurological conditions and helps in rapid diagnosis of the conditions and initiate therapeutic measures .
How much CSF is produced in a day?
CSF is produced at a rate of 0.2–0.7 mL per minute or 500–700 mL per day.1The main function of the CSF is to reduce buoyancy of the brain. It also supplies nutrients as well as helps in removal of various substances like amino acids, neurotransmitters, metabolic byproducts and cells.
What is cerebral fluid?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear fluid circulating in the intracranial and spinal compartments. Under normal conditions, the composition of CSF remains constant. However, in various neurological disease especially in acute conditions, the composition, quantity and its pressure can be altered. By measuring the levels ...
What are the indications for LP and CSF?
Patients with suspected meningitis is one of the major indication for LP and CSF study. Meningitis can be community acquired or hospital acquired and caused by various micro organisms ranging from bacteria, virus, fungus, protozoa, etc.9,10Aseptic meningitis is a condition that needs to be distinguished from other forms of meningitis that need a CSF analysis.11Presentation of meningitis varies from acute debilitating illness or chronic symptoms as in tuberculosis. Patients suspected to have acute meningitis usually present with altered consciousness, fever and neck stiffness. The classic triad is seen only in 46% of patients. In others one or two of the signs of triad may be present. In addition patients can present with nausea, vomiting, headache and photophobia. In patients with meningoencephalitis additional clinical signs at presentation include altered sensorium, confusion, behavioural changes, seizures, focal neurological deficits.
Where is cerebral fluid secreted?
CSF is present in both the intracranial and spinal compartments. It is continuously being secreted by the choroid plexus at a constant rate inside the ventricles of the brain and circulates in the subarachnoid space of the brain ...
Can a manometer be used to measure CSF?
A manometer can be connected if CSF opening pressure measurement is planned. Color of CSF is noted and if blood stained due to traumatic puncture, it may be needed to wait for the blood to be cleared before samples are collected. Samples are usually collected in three to four test tubes each of 3–5 mL CSF for analysis.
What are CSFs?
CSFs are the ways a company can accomplish its goals. They are the tasks, methods, tools, skills, mindsets and other components necessary for a business's operation and prosperity. In order to know their CSFs, a company's leaders first have to create a mission, goals and definitions of success.
What are KPIs?
KPIs are signs of how well a company is doing, or its capabilities and effectiveness. They are data points that measure and show whether a company is meeting its goals, and whether its CSFs are working properly. KPIs are usually numbers, percentages or ratios that quantify a company's success.
CSFs vs. KPIs
While CSFs qualify success, representing what a business needs to meet its goals, KPIs quantify success and represent numerical evidence of a business's performance. Here are some differences between the two: