
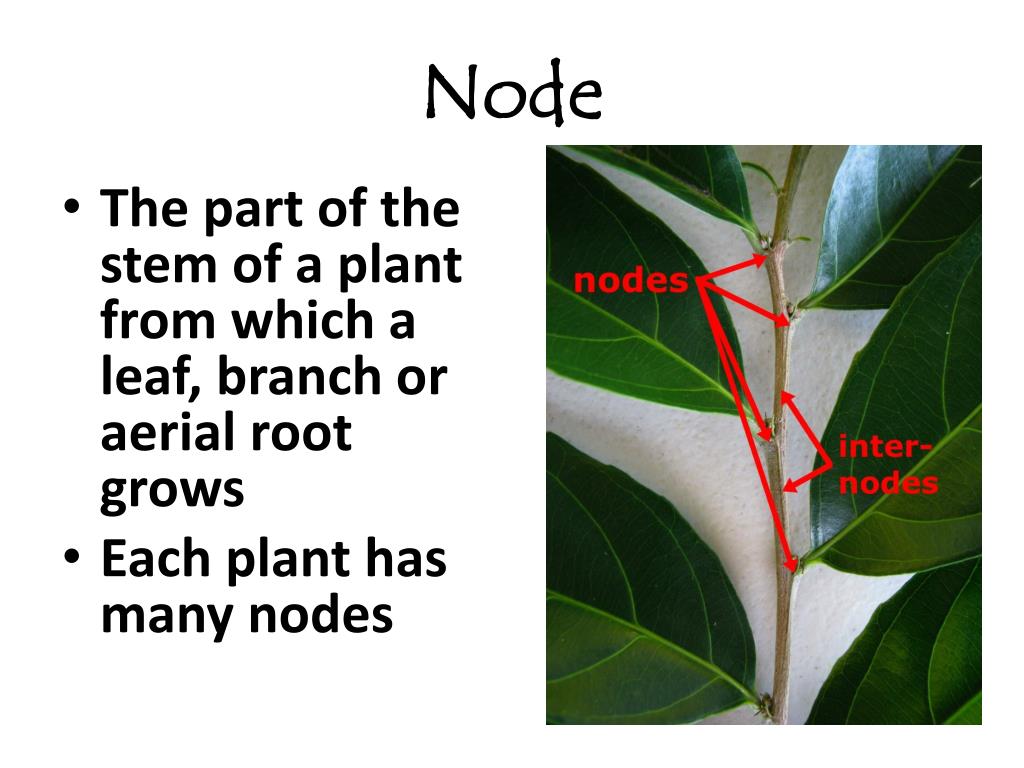
A node is the part of a plant stem where the flowers, branches, and leaves first start to grow. Many growers refer to nodes as the growth tips of the plant’s stem. Nodes can hold several leaves and buds that have the capacity of growing and spreading into branches. In some plants, the nodes can additionally produce adventitious roots.
What is the function of nodes in STEM?
The node is the part of the stem of the plant from which leaves, branches, and aerial roots emerge. There are many nodes on a plant stem. The distance between each node is called the inter node. What is the function of nodes and internodes? The node is the part of the stem of the plant from which leaves, branches, and aerial roots emerge.
What are nodes and internodes in a plant stem?
In the science of plant biology, a plant's stem consists of nodes and internodes. A plant stem's nodes are those critical areas from which leaves, branches, and aerial roots grow out from the stem, while the internodes are those intervals between the nodes.
What is the importance of nodes in plant propagation?
Nodes Play an Important Role in Pruning and Propagation. Locating the nodes of a plant is important when you are doing regular maintenance, such as pruning, and also when you are trying to propagate plants from stem cuttings or grafts.
What is the function of the stem of a plant?
The stem is the portion of the plant located above ground that helps to provide support to the flowers, leaves, and buds. Stems also help to transport nutrients and water throughout the plant. As such, stems help to connect the roots with the leaves and flowers (in an angiosperm, or flowering plant).
What is the function of the node and buds?
A plant's stem is made up of several tiny parts, each with its own function or purpose. A node is responsible for the growth contained in a bud. While the stem structure of trees, shrubs and plants may vary, each requires a bud and a node to produce flowers and leaves.
What does the node of a leaf do?
Plant leaf nodes are small bumps or swelling where new leaves or stems emerge from a plant. These are the sites where new growth occurs. Knowing how to identify them, will easily enable you to Propagate Your Plants , and also help you with other tricks, such as helping your plant branch.
What is the difference between node and stem?
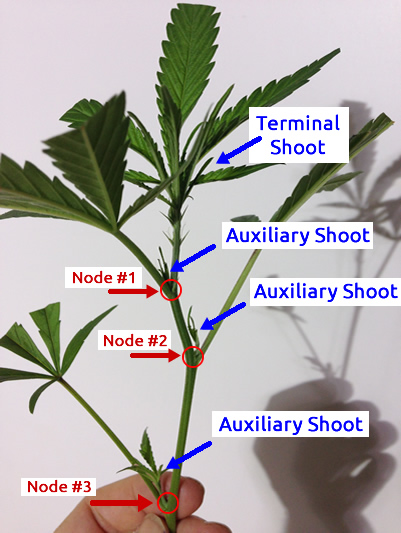
…the stem is called a node, and the region between successive nodes is called an internode. Stems bear leafy shoots (branches) at the nodes, which arise from buds (dormant shoots). Lateral branches develop either from axillary, or lateral, buds found in the angle between the leaf and the stem or…
What is the difference between bud and node?
The interval between two adjacent nodes is called internode.
Axillary bud. The buds which are located in the axil of each leaf are called axillary or lateral buds. These buds grow into branches....QuestionStudents Liked0 +6 more rows
What is a leaf node in a tree?
Leaf. In a tree data structure, the node which does not have a child is called as LEAF Node. In simple words, a leaf is a node with no child. In a tree data structure, the leaf nodes are also called as External Nodes. External node is also a node with no child.
What is a node on a tree?
A tree is a collection of entities called nodes . Nodes are connected by edges . Each node contains a value or data , and it may or may not have a child node . The first node of the tree is called the root .
What is leaf nodes in binary tree?
Nodes with no children are called leaves, or external nodes. Nodes which are not leaves are called internal nodes. Nodes with the same parent are called siblings.
Which nodes are leaf nodes?
A leaf node is a node in a tree that has no children. A leaf node is also sometimes called a terminal node. An internal node (also known as an inner node, inode for short, or branch node) is the area of a tree where the child node resides.
What are the nodes of a plant?
A plant stem's nodes are those critical areas from which leaves, branches, and aerial roots grow out from the stem, while the internodes are those intervals between the nodes.
What is the difference between an internode and a node?
By contrast, internodes are the sections of stem between nodes. If the nodes are the crucial “organs” of the plant, the internodes are the blood vessels carrying water, hormones, and food from node to node. Usually, internodes are lengthy and provide several inches of spacing between adjacent nodes. However, some plants are notable ...
How to prune a plant that is dormant?
Always prune just above a node on a stem. In this way, the dormant buds in the node itself will grow out into new stems. If you cut below a node, you leave a section of stem (the internode) that cannot grow new stems. This section will be prone to rotting and becoming susceptible to diseases that can kill your plant.
How to tell if a twig is attached to a node?
Even without visible buds or leaves, you can tell where the node of a twig is by some signs that are visible only at a node:
How to propagate a plant from a stem?
Many types of plants, both woody and herbaceous, can be propagated by stem cuttings, a process that yields a plant identical to its parent. A 6-inch or longer cu tting is taken from the parent plant for rooting in the soil. For successful rooting, cut immediately below a node, because this is the area that will produce the roots. The cutting also needs a terminal bud or another node above the soil line where the new stem and branch growth can occur.
What happens if you cut through a thick knobby node?
If you were to make these cuts through the thick, knobby nodes, they would not be straight, and the graft union would be likely to fail.
Do conifers have long or short internodes?
Usually, internodes are lengthy and provide several inches of spacing between adjacent nodes. However, some plants are notable for how close together with their leaves, and thus their nodes, always are. Dwarf conifers, for example, have closely spaced nodes. Yews and boxwoods, with their dense leaves, also always have short internodes. This fact is why these plants can be sheared or pruned into any shape, including the special sculpted forms of topiaries.
Which plants have nodes?
However, some plants are notable for how close together their leaves, and thus their nodes, always are. Dwarf conifers have closely-spaced nodes. Yews and boxwoods, with their very dense leaves, also always have short internodes.
What are the sections of stem between nodes?
Internodes are the sections of stem between nodes. If the nodes are the crucial “organs” of the plant, the internodes are the blood vessels carrying water, hormones, and food from node to node.Usually, internodes seem long and provide spacing between nodes of many inches. However, some plants are notable for how close together their leaves, and thus their nodes, always are. Dwarf conifers have closely-spaced nodes. Yews and boxwoods, with their very dense leaves, also always have short internodes. This fact is why they can be sheared or pruned into any shape, including the special form of topiaries.
How many internodes are joined by a node?
Two internodes are joined by a node.
What gives rise to the lateral branches?
The axillary buds give rise to the lateral branches. A lateral branch ,therefore, typically arises at a node. The internode adds towards the height of plant. A ‘tall’ and ‘dwarf’ plant shall have the same number of leaves but only different inter-nodal lengths ( see fig below: 1. dwarf 2. medium 3. tall).
How many leaves are there at a node?
The number of leaves that appear at a node depends on the species of plant; one leaf per node is common, but two or or more leaves may grow at the nodes of some species. Distance between two nodes is internode . 9 lessons from millionaires who are good with money.
Why do dicots need vascular systems?
As the dicots are longer lived plants as they grow they need efficient vascular system in order to fulfill the increased demand of water and food materials. Cork cambium forms a protective layer in the outer regions of stem which is formed to cope up with the pressure due to secondary growth in inner vascular regions.
How do plants help the environment?
The functions of plants can be seen in environment as well in the following ways: (1) Through photosynthesis, green algae and land plants absorb CO2 reducing the effects of global warming. (2) Land plants can hold water, preventing flood and erosion of rocks.
What is the function of a plant node?
A plant node represents a structure responsible for attaching the petiole to the stem. Nodes are often associated with stem locations where leaves and buds grow. Because they are capable of generating a great deal of metabolic activity, nodes help to promote the growth of leaves, secondary stems, and flowers. Only stems are associated with nodes, as these structures are not found elsewhere on the plant. The place where the node attaches the petiole and associated leaf to the stem is known as a leaf axil. Nodes are important landmarks on the plant stem, as they help gardeners to locate the best spot for pruning plants. An experienced gardener or botanist will typically prune the plant a short distance away from a node.
Where is the plant node located?
A plant node is located on the exterior surface of the stem. Plant nodes help to connect the petiole to the plant stem.
What is the role of the vascular cambium in stem cell development?
The vascular cambium represents a layer of tissue that separates the phloem from the xylem. Moreover, cambium is responsible for producing new phloem and xylem cells, which help to increase the diameter of the stem.
What are the structures that connect a leaf to its associated node?
Petioles are the structures linking a leaf with its associated node. The internal structures of the stem, including the xylem and phloem extend through the petiole. Some petioles are edible, such as celery and rhubarb. Petioles can be short or long, or not even present at all. Leaves attached to a stem without the petiole are known as sessile.
What is a monocot plant?
A monocot plant is based on the presence of a single cotyledon, or embryo leaf, within the seed. When a monocot produces flowers, they are characterized by multiples of three petals, leaves with parallel venation, and a network of roots that all emerge from the main stem (also known as adventitious roots). The overall size and shape of the monocot leaf is also more grass-like in structure. In monocots, the vascular system occurs in pairs of phloem and xylem. These vascular pairs are randomly distributed throughout the stem.
What is a cross section of the xylem and phloem bundles in?
A cross-section of the xylem and phloem bundles in a monocot.
What is the function of phloem in plants?
The phloem represents the series of tubes carrying nutrients throughout the plant. The distribution of phloem within the stem depends on whether the plant is a monocot or a dicot.
What is a node in a plant?
A node is the part of a plant where all new growth (leaves, stems, and aerial roots) originates. When cutting a Monstera deliciosa to propagate, slicing a few inches under the node ensures a cutting with all the elements needed to grow into a new plant. Understanding and being able to identify nodes is essential when you are pruning ...
Why does it take so long for a leafless node to grow?
It takes a lot longer for growth to come from a leafless node cutting than a regular cutting because it doesn’t have leaves to capture energy from the sun. Eventually, you should see roots emerging from the node. This is exciting, but don’t do anything yet. Keep on caring for the stem cuttings in the same way.
How Can You Identify a Node on a Monstera Deliciosa?
The first way to identify a node is by location: if there is (or was) a leaf or stem splitting off from the main stem, there will always be a node just below that growth. This is because Monsteras need that node to generate growth.
How to inspect Monstera node cutting?
Inspect the Monstera node cutting and see if it has a start of a root coming out. Often a little nub will be emerging from one side of the node. If there is one, you’ll want to place that side down (so the nub is in contact with the growing medium). If you can’t find one, you can place any side down.
Why does Monstera deliciosa have a large number of nodes?
Monstera deliciosa usually has a large number of nodes because it is a vining plant that produces growth from many different locations on a single stem. If you are not sure that you have found a node at first, try looking elsewhere on the plant to see if you can locate one that’s more obvious.
How long is a Monstera node?
They are sold under the names “stem cutting,” “node cutting,” and “wet sticks.”. Monstera node cuttings tend to be three to four inches long, with a single node in the middle of the piece. They usually only have one node since the seller can maximize their selling price by selling each node cutting individually.
Why does a monstera need a node?
This is because the required cells for new growth are concentrated in these areas of the plant.
Why are roots important to plant?
However, it's important to understand plant root systems because they have a pronounced effect on a plant's size and vigor, method of propagation, adaptation to soil types, and response to cultural practices and irrigation.
What are the parts of a plant called?
Vegetative Plant Parts. External plant structures such as leaves, stems, roots, flowers, fruits, and seeds are known as plant organs. Each organ is an organized group of tissues that works together to perform a specific function. These structures can be divided into two groups: sexual reproductive and vegetative.
Why is the vascular cambium important?
The vascular cambium is important to gardeners. For example, the tissues on a grafted scion and rootstock need to line up. In addition, careless weed trimming can strip the bark off a tree, thus injuring the cambium and causing the tree to die. The vascular systems of monocots and dicots differ (Figure 5).
What is the role of fertilizer in early seedlings?
During early development, a seed ling absorbs nutrients and moisture from the soil around the sprouting seed. A band of fertilizer several inches to each side and slightly below newly planted seeds helps early growth of most row crops.
What are the two parts of a plant that are not directly involved in sexual reproduction?
These structures can be divided into two groups: sexual reproductive and vegetative. Vegetative parts (Figure 1) include roots, stems, shoot buds, and leaves; they are not directly involved in sexual reproduction. Vegetative parts often are used in asexual forms of reproduction such as cuttings, budding, or grafting.
How many parts are there in a root?
Internally, there are three major parts of a root (Figure 2):
Where does the primary root originate?
A primary root originates at the lower end of a seedling's embryo. If the primary root continues to elongate downward, becomes the central feature of the root system, and has limited secondary branching, it is called a taproot (Figure 4). Hickory and pecan trees, as well as carrots, have taproots.
Nodes
Identifying Nodes
- The base of a bud, leaf, twig, or branch is always attached to a node, so this is one easy way to find them. Even without visible buds or leaves, you can tell where the node of a twig is by some signs that are visible only at a node: 1. A scar in the wood where a leaf has fallen away 2. A knob-like, slight fattening of the wood (such as the rings on a bamboo cane) 3. Solid sections of the st…
Plant Internodes
- By contrast, internodes are the sections of stem between nodes. If the nodes are the crucial “organs” of the plant, the internodes are the blood vessels carrying water, hormones, and food from node to node. Usually, internodes are lengthy and provide several inches of spacing between adjacent nodes. However, some plants are notable for how close together with their lea…
Pruning
- Whether you are new to pruning, or just intimidated by it, locating the node is an important step in the pruning process. 1. Always prune just above a node on a stem. In this way, the dormant buds in the node itself will grow out into new stems. If you cut below a node, you leave a section of stem (the internode) that cannot grow new stems. This section will be prone to rotting and beco…
Propagation
- Many types of plants, both woody and herbaceous, can be propagated by stem cuttings, a process that yields a plant identical to its parent. A cutting about 6 inches or longer cutting is taken from the parent plant for rooting in the soil. For successful rooting, cut immediately below a node, because this is the area that will produce the roots. The cutting also needs a terminal bud or ano…
Grafting
- In contrast to pruning, when you want to make cuts for grafting—joining a branch tissue segment of one plant to the stem tissue of another host plant—you make these cuts in the host plant not near the nodes, but right through the center of an internode. In the whip and tongue graft, for example, careful cuts need to be made along the grain of the wood in the internode space. If yo…