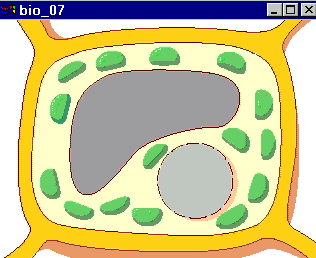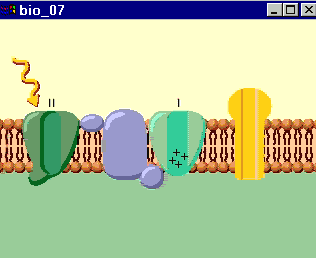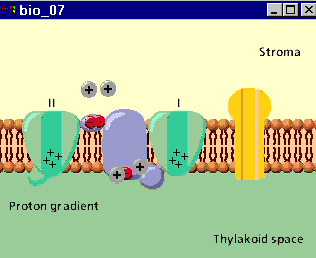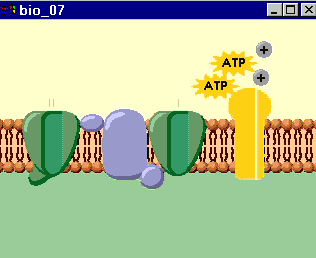
Transport Protein Definition
Transporter proteins are proteins that transport substances across biological membranes. Transport proteins reside within the membrane itself, where they form a transport channel or mechanism to allow their substrate to move from one side to the other.
What is Transport Protein?
A transport protein (also known as a transmembrane pump, transporter, companion protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that has the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transporter proteins are crucial for the growth and life of all living things.
What is the Function of Transport proteins?
Life as we know it depends on the ability of cells to selectively move substances when they need them. Certain important molecules, such as DNA, must be kept in the cell at all times; But other molecules such as ions, sugars, and proteins may need to move in and out for the cell to function properly.
What are the Types of Transport Proteins?
As the name suggests, “channel” or “pore” proteins open holes in the membrane of a cell.
What are the Examples of Transport Proteins?
The best-known example of a primary active transport protein is the sodium-potassium pump. It is this pump that creates the ion gradient that allows neurons to fire.
What are the functions of transport proteins?
Functions of Transport Proteins. Transport proteins function in both active and passive transport to move molecules across the plasma membrane. Two main groups of transport proteins can be found within the plasma membrane, and each helps water-loving molecules pass across the plasma membrane.
How are transport proteins used?
Transport proteins are used in various ways to move substances back and forth across the cell membrane. This lesson will discuss the different types, their functions, and examples of each.
How many sodium ions does the sodium potassium pump transport?
For example, the sodium potassium pump transports three sodium ions into the cell, while pumping two potassium ions out of the cell. Transport proteins act as doors to the cell, helping certain molecules pass back and forth across the plasma membrane, which surrounds every living cell.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
In passive transport molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Active transport, on the other hand , moves molecules from a low concentration to a higher concentration. There are two main classes of transport proteins that are found within the plasma membrane.
What is channel protein?
A channel protein serves as a tunnel across the membrane into the cell. More specifically, channel proteins help molecules across the membrane via passive transport, a process called facilitated diffusion. These channel proteins are responsible for bringing in ions and other small molecules into the cell.
What type of protein is used to transport water across the plasma membrane?
In fact, there's even a channel specifically for transporting water across the plasma membrane. The other type of transport protein is called a carrier protein . Carrier proteins have to change shape in order to pass the molecule across the plasma membrane. Think of it as a revolving door to the post office.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Each cell has a plasma membrane, or a filter, that helps regulate materials moving in and out of the cell. Each plasma membrane has different transport proteins embedded within it, which are used to help with this process. Each transport protein only allows a certain molecule to enter or exit the cell. Think of these transport proteins as ...
What are two types of transport proteins?
Carrier proteins and channel proteins are the two major classes of membrane transport proteins.
Which transport proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion?
Two classes of proteins that mediate facilitated diffusion are generally distinguished: carrier proteins and channel proteins. Carrier proteins bind specific molecules to be transported on one side of the membrane.
What are two active transport examples?
Active transport is usually associated with accumulating high concentrations of molecules that the cell needs, such as ions, glucose and amino acids. Examples of active transport include the uptake of glucose in the intestines in humans and the uptake of mineral ions into root hair cells of plants.
What protein is referred to in protein mediated transport?
Mediated transport refers to transport mediated by a membrane transport protein. … One example of a uniport mediated transport protein is GLUT1. GLUT1 is a transmembrane protein, which means it spans the entire width of the cell membrane, connecting the extracellular and intracellular region.
What is the role of carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion?
Carrier proteins can change their shape to move a target molecule from one side of the membrane to the other. … The carrier proteins involved in facilitated diffusion simply provide hydrophilic molecules with a way to move down an existing concentration gradient (rather than acting as pumps).
What is the role of proteins classified as an aquaporin?
What is the role of proteins classified as an Aquaporin? To allow water to go through the membrane. They also control the amount of water that goes through it.
What are three examples of active transport?
1. Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls)
Transport Protein Definition
Function of Transport Protein
- Life as we know it depends on the ability of cells to selectively move substances when they need to. Certain important molecules, such as DNA, must be kept inside the cell at all times; but other molecules such as ions, sugars, and proteins, may need to pass in and out in order for the cell to function properly. Each transport protein is designed to transport a specific substance as neede…
Types of Transport Proteins
- Channels/Pores
As suggested by their name, “channel” or “pore” proteins open holes in the membrane of a cell. These proteins are characterized by being open to both the intracellular and extracellular space at the same time. By contrast, carrier proteins are only open to the inside or outside of a cell at any … - Carrier Proteins
Carrier proteins are transport proteins that are only open to one side of the membrane at once. They are often designed this way because they transport substances against their concentration gradient. Being open to both sides of the membrane simultaneously might allow these substanc…
Examples of Transport Proteins
- The Sodium-Potassium Pump
The most famous example of a primary active transport protein is the sodium-potassium pump. It is this pump that creates the ion gradient that allows neurons to fire. The sodium-potassium pump begins with its sodium binding sites facing the inside of the cell. These sites attract sodiu… - Sodium-Glucose Transport Proteins
The sodium-glucose transport protein uses secondary active transport to move glucose into cells. They are active in intestinal cells and kidneycells, both of which need to move glucose into the body’s systems against its concentration gradient. This operation requires energy, because the c…
Related Biology Terms
- Active Transport– Transport of substances across biological membranes, which requires the cell to expend energy.
- Gated Ion Channel– A protein that allows ions to pass through when open, which opens in response to a specific stimulus.
- Passive Transport– Transport of substances across biological membranes which happens n…
- Active Transport– Transport of substances across biological membranes, which requires the cell to expend energy.
- Gated Ion Channel– A protein that allows ions to pass through when open, which opens in response to a specific stimulus.
- Passive Transport– Transport of substances across biological membranes which happens naturally, without the requirement to expend energy.
Quiz
- 1. Why is it called “facilitated diffusion?” A. Because the substance diffuses naturally down its concentration gradient, with no help from a transport protein. B. Because the substance requires a transport protein to expend energy in order to facilitate its movement. C. Because the substance diffuses naturally down its concentration gradient, but is helped by a protein that opens a chann…
References
- Hall, John E.; Guyton, Arthur C. (2006). Textbook of medical physiology. St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-0240-1
- Lever, J. E. (1992). Cell and Molecular Biology of Na /Glucose Symport. Membrane Transport in Biology, 56-72. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-76983-2_2